Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 66-75.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20241111.001
Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect and mechanism of Sanqi (Radix Notoginseng) in treating periodontitis
AN Yuanyuan, LIU Wang, LI Yanjie, WANG Yanchun, REN Xiaobin( ), HE Hongbing(
), HE Hongbing( )
)
- Department of Periodontology, Kunming Medical University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Yunnan Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Kunming 650106, China
-
Received:2023-11-21Accepted:2024-03-13Online:2025-02-15Published:2024-11-11 -
Contact:HE Hongbing, Department of Periodontology, Kunming Medical University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Kunming 650106, China.kmykdxyz6688@163.com ; REN Xiaobin, Department of Periodontology, Kunming Medical University School and Hospital of Stomatology, Kunming 650106, China.renxiaobin6688@163.com Telephone: +86-871-65330099 -
Supported by:Scientific Research Fund of Education Department of Yunnan Province Project: Potential Targets and Molecular Mechanisms of Sanqi (Radix Notoginseng), an Active Component of Yunnan Baiyao, in the Treatment of Periodontitis(2022Y204);Special Project for The Selection of High-level Scientific and Technological Talents and Innovation Teams-technical Innovation Talents Training Object Project: Technical Innovation Personnel Training Object Project(202405AD350005)
Cite this article
AN Yuanyuan, LIU Wang, LI Yanjie, WANG Yanchun, REN Xiaobin, HE Hongbing. Effect and mechanism of Sanqi (Radix Notoginseng) in treating periodontitis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 66-75.
share this article
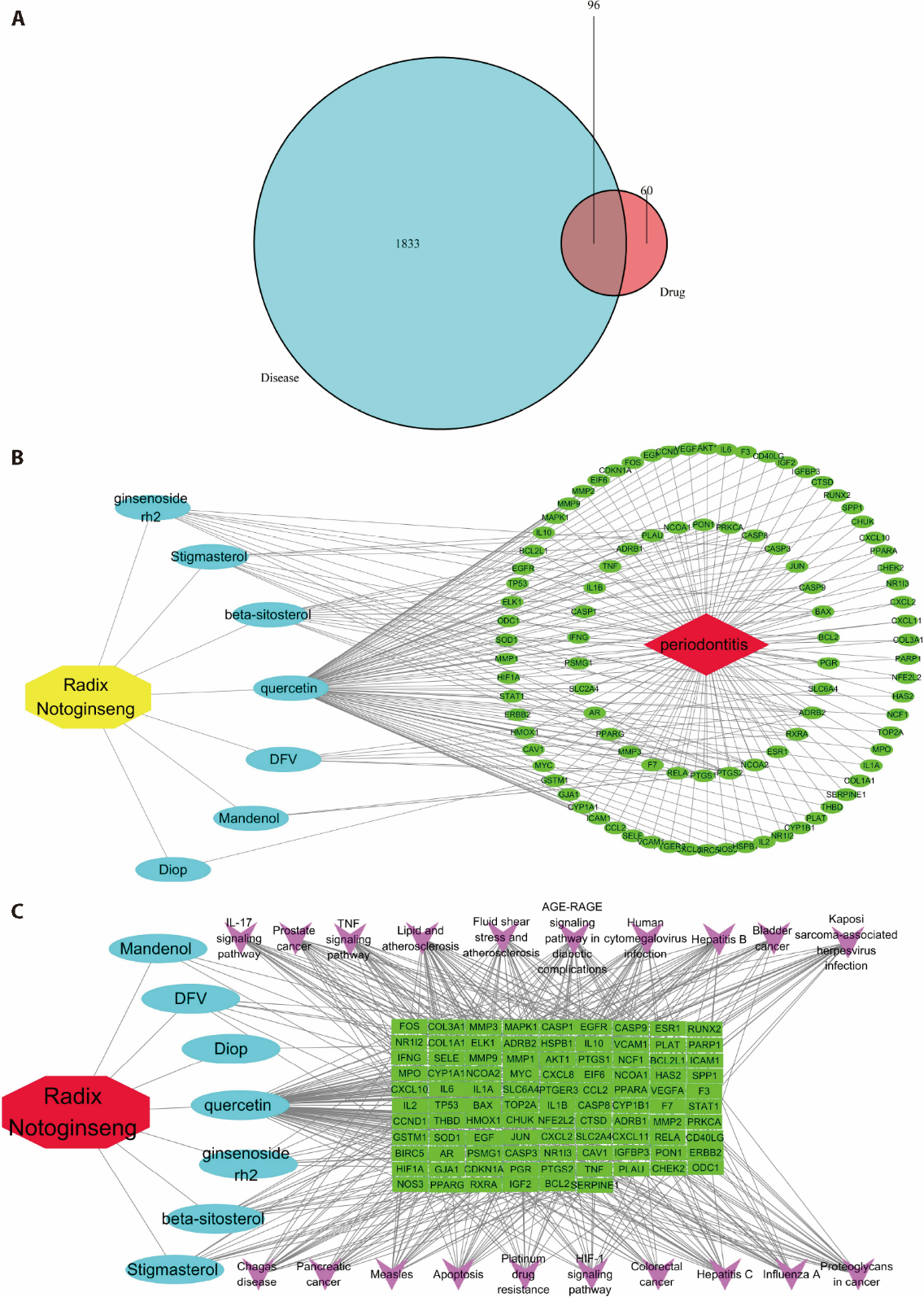
Figure 1 Regulatory network of common targets in Sanqi (Radix Notoginseng) and periodontitis A: Venn diagram showing overlapping targets of periodontitis and Sanqi (Radix Notoginseng); B: TCM-compound-target-disease network of core targets; C: disease-target-pathway network of core targets. The active ingredient of Sanqi (Radix Notoginseng), quercetin, exhibits the greatest correlation and the most binding nodes with the common targets. DFV: liquiritigenin; Diop: diiso-propyl adipate; FOS: Fos proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor sub-unit; COL3A1: collagen type III alpha 1 chain; MMP3: matrix metallo-pep-tidase 3; MAPK1: mitogen-activated protein kinase 1; CASP1: caspase 1; EGFR: epidermal growth factor receptor; CASP9: caspase 9; ESR1: estrogen receptor 1; RUNX2: runt-related transcription factor 2; NR1I2: nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group I member 2; COL1A1: col-lagen type I alpha 1 chain; ELK1: ETS trans-cription factor ELK1; ADRB2: adr-enoceptor beta 2; HSPB1: heat shock protein family B (small) member 1; IL10: interleukin 10; VCAM1: vascular cell adhesion molecule 1; PLAT: plas-minogen acti-vator, tissue type; PARP1: poly (ADP-ribose) poly-merase 1; IFNG: interferon gamma; SELE: selectin E; MMP9: matrix metallopeptidase 9; MMP1: matrix metallopeptidase 1; AKT1: AKT serine/threonine kinase 1; PTGS1: prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1; NCF1: neutrophil cytosolic factor 1; BCL2L1: BCL2 like 1; ICAM1: intercellular adhesion molecule 1; MPO: myeloperoxidase; CYP1A1: cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily A member 1; NCOA2: nuclear receptor coactivator 2; MYC: MYC proto-oncogene, BHLH transcription factor; CXCL8: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8; EIF6: eukaryotic translation initiation factor 6; NCOA1: nuclear receptor coactivator 1; HAS2: hyaluronan synthase 2; SPP1: secreted phosphoprotein 1; CXCL10: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 10; IL6: interleukin 6; IL1A: interleukin 1 alpha; SLC6A4: solute carrier family 6 member 4; PTGER3: prostaglandin E receptor 3; CCL2: C-C motif chemokine ligand 2; PPARA: peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha; VEGFA: vascular endothelial growth factor A; F3:coagulation factor Ⅲ, tissue factor; IL2: interleukin 2; TP53: tumor protein P53; BAX: BCL2 associated X, apoptosis regulator; TOP2A: DNA topoisomerase Ⅱ alpha; IL1B: interleukin 1 beta; CASP8: caspase 8; CYP1B1: cytochrome P450 family 1 subfamily B member 1; F7: coagulation factor Ⅶ; STAT1: signal transducer and activator of transcription 1; CCND1: cyclin D1; THBD: thrombomodulin; HMOX1: heme oxygenase 1; CHUK: component of inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B kinase complex; NFE2L2: NFE2 like BZIP transcription factor 2; CTSD: cathepsin D; ADRB1: adrenoceptor beta 1; MMP2: matrix metallopeptidase 2; PRKCA: protein kinase C alpha; GSTM1: glutathione S-transferase Mu 1; SOD1: superoxide dismutase 1; EGF: epidermal growth factor; JUN: Jun proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit; CXCL2: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 2; SLC2A4: solute carrier family 2 member 4; CXCL11: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 11; RELA: RELA proto-oncogene, NF-KB subunit; CD40LG: CD40 ligand; BIRC5: baculoviral IAP repeat containing 5; AR: androgen receptor; PSMG1: proteasome assembly chaperone 1; CASP3: caspase 3; NR1I3: nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group I member 3; CAV1: caveolin 1; IGFBP3: insulin like growth factor binding protein 3; PON1: paraoxonase 1; ERBB2: Erb-B2 receptor tyrosine kinase 2; HIF1A: hypoxia inducible factor 1 subunit alpha; GJA1: gap junction protein alpha 1; CDKN1A: cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1A; PGR: progesterone receptor; PTGS2: prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; PLAU: plasminogen activator, urokinase; CHEK2: checkpoint kinase 2; ODC1: ornithine decarboxylase 1; NOS3: nitric oxide synthase 3; PPARG: peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma; RXRA: retinoid X receptor alpha; IGF2: insulin like growth factor 2; BCL2: BCL2 apoptosis regulator; SERPINE1: serpin family E member 1.
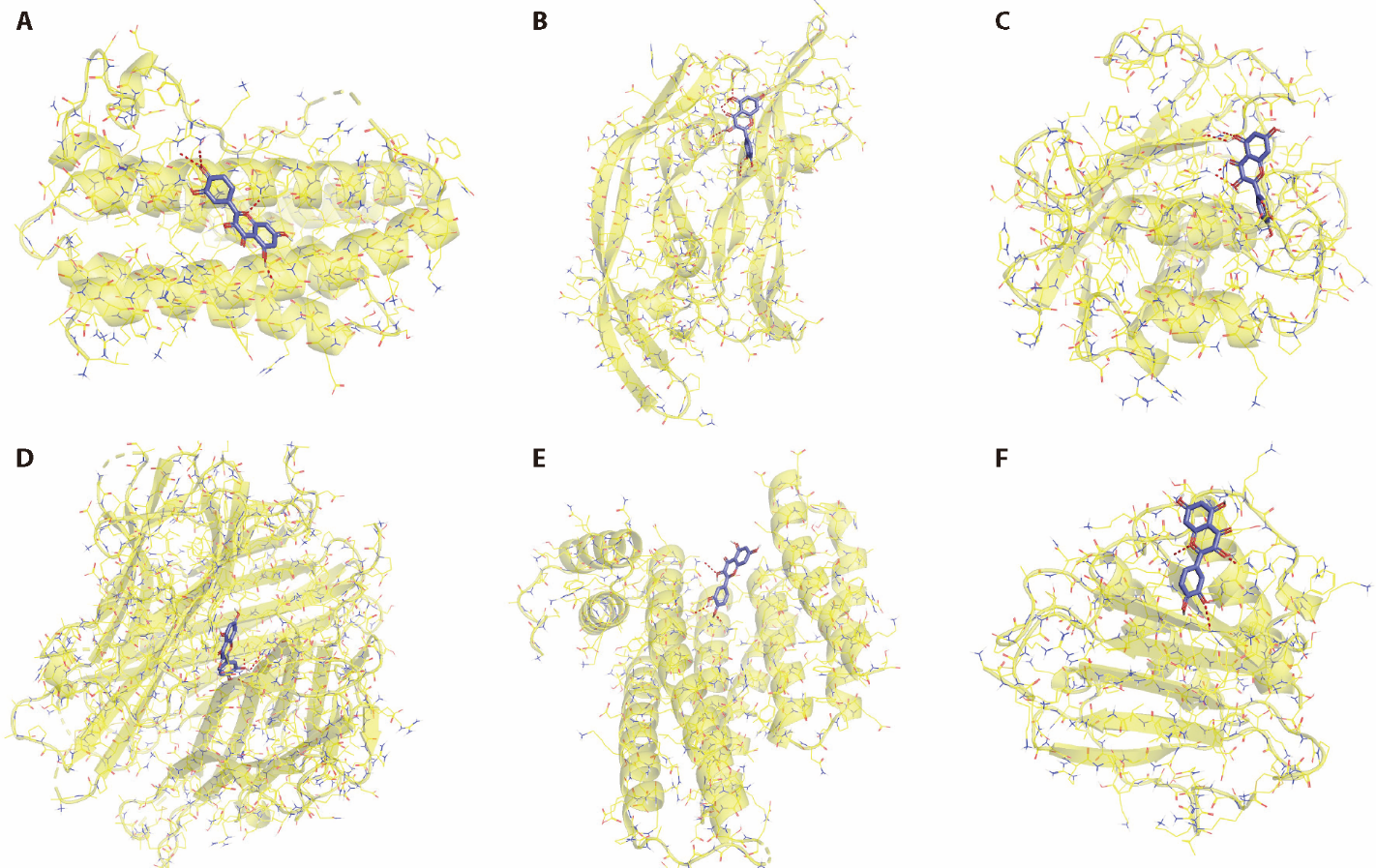
Figure 2 Molecular docking results of the Sanqi (Radix Notoginseng) composition and periodontitis targets A: quercetin + IL6; B: quercetin + VEGFA; C: quercetin + MMP9; D: quercetin + TNF; E: quercetin + JUN; F: quercetin + CXCL8. Yellow objects represent molecular targets, and the surrounding chain represents the compound. IL6: interleukin 6; VEGFA: vascular endothelial growth factor A; MMP9: matrix metallopeptidase 9; TNF: tumor necrosis factor; JUN: Jun proto-oncogene; AP-1 transcription factor subunit; CXCL8: C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8.

Figure 3 Sanqi (Radix Notoginseng) improved periodontal tissue structure in rats with periodontitis A: micro-CT was used to observe effects of Sanqi (Radix Notoginseng) on the morphology and structure of alveolar bone; B: statistical analysis of the distance from the cementoenamel junction (CEJ) to the alveolar bone (AB) (n = 3); C: Hematoxylin eosin staining was performed to observe the changes of periodontal tissue structure after Sanqi (Radix Notoginseng) treatment (Scale bar = 500 μm, × 2) (n = 3). A1, C1: Normal group; A2, C2: Periodontitis group; A3, C3: Low-dose group; A4, C4: Middle-dose group; A5, C5: High-dose group. Normal group: normal rats were intragastric with solvent; Periodontitis group: periodontitis rats were intragastric with solvent; Low-dose group: periodontitis rats were intragastric with Sanqi (Radix Notoginseng) (0.625 g/kg); Middle-dose group: periodontitis rats were intragastric with Sanqi (Radix Notoginseng) (1.25 g/kg); High-dose group: periodontitis rats were intragastric with Sanqi (Radix Notoginseng) (2.5 g/kg). Student t-test and one-way analysis of variance were performed for the normal, periodontitis, and Sanqi (Radix Notoginseng) treatment group comparisons analysis, and data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Compared with the normal group, aP < 0.05; compared with the periodontitis group, bP < 0.05.

Figure 4 Sanqi (Radix Notoginseng) regulated the expression of inflammation-related factors A: immunohistochemical staining was used to detect the expression of IL-6, TNF-α, IL-17, RORγt, FOXP3, and IL-10 in local periodontal tissues (scale bar = 10 μm, × 150). A1-A5: IL-6; A6-A10: TNF-α; A11-A15: IL-17; A16-A20: RORγt; A21-A25: FOXP3; A26-A30: IL-10. A1, A6, A11, A16, A21, A26: Normal group; A2, A7, A12, A17, A22, A27: Periodontitis group; A3, A8, A13, A18, A23, A28: Low-dose group; A4, A9, A14, A19, A24, A29: Middle-dose group; A5, A10, A15, A20, A25, A30: High-dose group; B: statistical analysis of IL-6 expression changes in each group; C: statistical analysis of TNF-α expression changes in each group; D: statistical analysis of IL-17 expression changes in each group; E: statistical analysis of RORγt expression changes in each group; F: statistical analysis of FOXP3 expression changes in each group; G: statistical analysis of IL-10 expression changes in each group. Normal group: normal rats were intragastric with solvent; Periodontitis group: periodontitis rats were intragastric with solvent; Low-dose group: periodontitis rats were intragastric with Sanqi (0.625 g/kg); Middle-dose group: periodontitis rats were intragastric with Sanqi (1.25 g/kg); High-dose group: periodontitis rats were intragastric with Sanqi (2.5 g/kg). IL-6: interleukin 6; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor α; IL-17: interleukin 17; RORγt: retinoid-ralated orphan receptor γt; FOXP3: Forkhead Box P3; IL-10: interleukin 10. Student t-test and one-way analysis of variance were performed for the normal, periodontitis, and Sanqi (Radix Notoginseng) treatment group comparisons analysis and data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 3). Compared with the normal group, aP < 0.05; compared with the periodontitis group, bP < 0.05.
| 1 |
Tsukasaki M. RANKL and osteoimmunology in speriodontitis. J Bone Miner Metab 2021; 39: 82-90.
DOI PMID |
| 2 |
Bao J, Yang Y, Xia M, Sun W, Chen L. Wnt signaling: an attractive target for periodontitis treatment. Biomed Pharmacother 2021; 133: 110935.
DOI PMID |
| 3 |
Miller CS, Ding X, Dawson DR, Ebersole JL. Salivary biomarkers for discriminating periodontitis in the presence of diabetes. J Clin Periodontol 2021; 48: 216-25.
DOI PMID |
| 4 | Gasparoni LM, Alves FA, Holzhausen M, Pannuti CM, Serpa MS. Periodontitis as a risk factor for head and neck cancer. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal 2021; 26: e430-6. |
| 5 | Al-Maweri SA, Ibraheem WI, Al-Ak'Hali MS, Shamala A, Halboub E, Alhajj MN. Association of periodontitis and tooth loss with liver cancer: a systematic review. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 2021; 159: 103221. |
| 6 |
Tiensripojamarn N, Lertpimonchai A, Tavedhikul K, et al. Periodontitis is associated with cardiovascular diseases: a 13-year study. J Clin Periodontol 2021; 48: 348-56.
DOI PMID |
| 7 |
Rekabi A, Ram A, Nazari A, Arefnezhad R, Rezaei-Tazangi F. Does crocin create new hope for the treatment of oral problems? A focus on periodontitis. Mol Biol Rep 2024; 51: 224.
DOI PMID |
| 8 | Guo H, Chang S, Pi X, et al. The effect of periodontitis on dementia and cognitive impairment: a Meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021; 18: 6823. |
| 9 | Gonzalez-Febles J, Sanz M. Periodontitis and rheumatoid arthritis: what have we learned about their connection and their treatment? Periodontol 2000 2021; 87: 181-203. |
| 10 |
Sculean A, Deppe H, Miron R, Schwarz F, Romanos G, Cosgarea R. Effectiveness of photodynamic therapy in the treatment of periodontal and peri-implant diseases. Monogr Oral Sci 2021; 29: 133-43.
DOI PMID |
| 11 |
Kwon T, Lamster IB, Levin L. Current concepts in the management of periodontitis. Int Dent J 2021; 71: 462-76.
DOI PMID |
| 12 | Wang R, Bao B, Bao C, et al. Resveratrol and celastrol loaded collagen dental implants regulate periodontal ligament fibroblast growth and osteoclastogenesis of bone marrow macrophages. Chem Biodivers 2020; 17: e2000295. |
| 13 |
Medara N, Lenzo JC, Walsh KA, et al. Peripheral memory T-cell profile is modified in patients undergoing periodontal management. J Clin Periodontol 2021; 48: 249-62.
DOI PMID |
| 14 |
Wu X, Wu S, Liu Y, et al. Health risk assessment of arsenic in realgar and Niuhuangjiedu tablets based on pharmacokinetic study. J Trace Elem Med Biol 2018; 48: 81-6.
DOI PMID |
| 15 | Xu Y, Tan HY, Li S, Wang N, Feng Y. Panax notoginseng for inflammation-related chronic diseases: a review on the modulations of multiple pathways. Am J Chin Med 2018; 46: 971-96. |
| 16 | Li S, Zhang R, Wang A, et al. Panax notoginseng: derived exosome-like nanoparticles attenuate ischemia reperfusion injury via altering microglia polarization. J Nanobiotechnology 2023; 21: 416. |
| 17 | Wang S, Tao P, Zhao L, Zhang W, Hu H, Lin J. Panax notoginseng promotes repair of colonic microvascular injury in Sprague-Dawley rats with experimental colitis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2018; 2018: 4386571. |
| 18 | Shou DW, Yu ZL, Meng JB, et al. Panax notoginseng alleviates sepsis-induced acute kidney injury by reducing inflammation in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2022; 2022: 9742169. |
| 19 |
Piao C, Sun Z, Jin D, et al. Network pharmacology-based investigation of the underlying mechanism of Panax Notoginseng treatment of diabetic retinopathy. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 2020; 23: 334-44.
DOI PMID |
| 20 | Fang T, Liu L, Liu W. Network pharmacology-based strategy for predicting therapy targets of Tripterygium wilfordii on acute myeloid leukemia. Medicine (Baltimore) 2020; 99: e23546. |
| 21 | Xie W, Meng X, Zhai Y, et al. Panax notoginseng saponins: a review of its mechanisms of antidepressant or anxiolytic effects and network analysis on phytochemistry and pharmacology. Molecules 2018; 23: 940. |
| 22 |
Tao Q, Du J, Li X, et al. Network pharmacology and molecular docking analysis on molecular targets and mechanisms of Huashi Baidu formula in the treatment of COVID-19. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 2020; 46: 1345-53.
DOI PMID |
| 23 | Zhang X, Zhang X, Qiu C, et al. The imbalance of Th17/Treg via STAT3 activation modulates cognitive impairment in P. gingivalis LPS-induced periodontitis mice. J Leukoc Biol 2021; 110: 511-24. |
| 24 |
Cafferata EA, Terraza-Aguirre C, Barrera R, et al. Interleukin-35 inhibits alveolar bone resorption by modulating the Th17/Treg imbalance during periodontitis. J Clin Periodontol 2020; 47: 676-88.
DOI PMID |
| 25 |
Shindo S, Hosokawa Y, Hosokawa I, Shiba H. Interleukin (IL)-35 suppresses IL-6 and IL-8 production in IL-17A-stimulated human periodontal ligament cells. Inflammation 2019; 42: 835-40.
DOI PMID |
| 26 | He W, Zhu H, Liu C. Profiles of inflammation factors and inflammatory pathways around the peri-miniscrew implant. Histol Histopathol 2021; 36: 899-906. |
| 27 |
Cardoso EM, Reis C, Manzanares-Cespedes MC. Chronic periodontitis, inflammatory cytokines, and interrelationship with other chronic diseases. Postgrad Med 2018; 130: 98-104.
DOI PMID |
| 28 | Bunte K, Beikler T. Th 17 Cells and the IL-23/IL-17 axis in the pathogenesis of periodontitis and immune-mediated inflammatory diseases. Int J Mol Sci 2019; 20: 3394. |
| 29 |
Schenkein HA, Papapanou PN, Genco R, Sanz M. Mechanisms underlying the association between periodontitis and atherosclerotic disease. Periodontol 2000 2020; 83: 90-106.
DOI PMID |
| 30 | Lu SL, Huang CF, Li CL, Lu HK, Chen LS. Role of IL-6 and STAT3 signaling in dihydropyridine-induced gingival overgrowth fibroblasts. Oral Dis 2021; 27: 1796-805. |
| 31 | Rath-Deschner B, Nogueira A, Beisel-Memmert S, et al. Interaction of periodontitis and orthodontic tooth movement-an in vitro and in vivo study. Clin Oral Investig 2021; 26: 171-81. |
| 32 | Basic A, Serino G, Leonhardt A, Dahlen G, Bylund J. The secretion of cytokines by peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with periodontitis and healthy controls when exposed to H2S. J Oral Microbiol 2021; 13: 1957368. |
| 33 | Kirschneck C, Thuy M, Leikam A, et al. Role and regulation of mechanotransductive HIF-1alpha stabilisation in periodontal ligament fibroblasts. Int J Mol Sci 2020; 21: 9530. |
| 34 | Isola G, Polizzi A, Ronsivalle V, Alibrandi A, Palazzo G, Lo GA. Impact of matrix metalloproteinase-9 during periodontitis and cardiovascular diseases. Molecules 2021; 26: 1777. |
| 35 | Figueiredo LC, Bueno-Silva B, Nogueira C, et al. Levels of gene expression of immunological biomarkers in peri-implant and periodontal tissues. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020; 17: 9100. |
| 36 |
Nakao Y, Fukuda T, Zhang Q, et al. Exosomes from TNF-alpha-treated human gingiva-derived MSCs enhance M2 macrophage polarization and inhibit periodontal bone loss. Acta Biomater 2021; 122: 306-24.
DOI PMID |
| 37 | Plemmenos G, Evangeliou E, Polizogopoulos N, Chalazias A, Deligianni M, Piperi C. Central regulatory role of cytokines in periodontitis and targeting options. Curr Med Chem 2021; 28: 3032-58. |
| 38 | Rath-Deschner B, Memmert S, Damanaki A, et al. CXCL5, CXCL8, and CXCL 10 regulation by bacteria and mechanical forces in periodontium. Ann Anat 2021; 234: 151648. |
| 39 | Patil S, Sayed ME, Mugri MH, et al. Allicin may promote reversal of T-cell dysfunction in periodontitis via the PD-1 pathway. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22: 9162. |
| 40 | Kim WJ, Park SY, Kim OS, Park HS, Jung JY. Autophagy upregulates inflammatory cytokines in gingival tissue of patients with periodontitis and lipopolysaccharide-stimulated human gingival fibroblasts. J Periodontol 2021; 93: 380-91. |
| 41 |
Yang Y, Wang L, Zhang H, Luo L. Mixed lineage kinase domain-like pseudokinase-mediated necroptosis aggravates periodontitis progression. J Mol Med (Berl) 2021; 100: 77-86.
DOI PMID |
| 42 |
Chang Z, Jiang D, Zhang S, et al. Genetic association of the epidermal growth factor gene polymorphisms with peri-implantitis risk in Chinese population. Bioengineered 2021; 12: 8468-75.
DOI PMID |
| 43 | Basile JR, Castle JT, Redman RS. Immunohistochemical profile of the anti-apoptosis, apoptosis and proliferation markers Bcl-2, caspase-3, p53, and Ki-67 in botryoid odontogenic cysts compared to lateral periodontal cysts and gingival cysts of the adult. Biotech Histochem 2021; 96: 263-8. |
| 44 | Han J, Hou J, Liu Y, Liu P, Zhao T, Wang X. Using network pharmacology to explore the mechanism of panax notoginseng in the treatment of myocardial fibrosis. J Diabetes Res 2022; 2022: 8895950. |
| 45 | Shen MY, Di YX, Wang X, et al. Panax notoginseng saponins (PNS) attenuate Th17 cell differentiation in CIA mice via inhibition of nuclear PKM2-mediated STAT3 phosphorylation. Pharm Biol 2023; 61: 459-72. |
| 46 | Yang F, Ma Q, Matsabisa MG, Chabalala H, Braga FC, Tang M. Panax notoginseng for cerebral ischemia: a systematic review. Am J Chin Med 2020; 48: 1331-51. |
| 47 |
Qu J, Xu N, Zhang J, Geng X, Zhang R. Panax notoginseng saponins and their applications in nervous system disorders: a narrative review. Ann Transl Med 2020; 8: 1525.
DOI PMID |
| 48 | Deng J, Lu C, Zhao Q, Chen K, Ma S, Li Z. The Th17/Treg cell balance: crosstalk among the immune system, bone and microbes in periodontitis. J Periodontal Res 2022; 57: 246-55. |
| 49 | Wang W, Wang X, Lu S, et al. Metabolic disturbance and Th17/Treg imbalance are associated with progression of gingivitis. Front Immunol 2021; 12: 670178. |
| [1] | Emre Bulut, Didem Özkal Eminoğlu, Yasemin Çayır. Effect of electroacupuncture on pain after periodontal flap surgery: a randomized controlled trial [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(1): 184-191. |
| [2] | JIA Lihua, KUANG Haodan, XU Yuan. Efficacy of Buzhong Yiqi decoction (补中益气汤) on benign prostatic hyperplasia and its possible mechanism [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(3): 533-541. |
| [3] | Rabbi Fazle, Zada Amir, Nisar Amna, Adhikari Achyut, Ullah Irfan, Ur Rahman Shafiq. Detailed approach toward the anti-hyperglycemic potential of Sterculia diversifolia G. Don against alloxan-induced in vivo hyperglycemia model [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(1): 17-22. |
| [4] | Fazle Rabbi, Amir Zada, Amna Nisar, Muhammad Sohail, Saifullah Khan Khalil, Abid Ali Ahmad. In vivo laxative, anti-diarrheal, hepatoprotective and diuretic investigations of Sterculia diversifolia and its isolated compounds [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(5): 717-724. |
| [5] | YAN Bin, WANG Jingbo, TIAN Guoqing. Efficacy of quercetin, oleanolic acid, icariin on apoptosis and mitogen-activated protein kinases signaling pathways in hippocampal neurons of Sprague-Dawley rats cultured with high glucose medium [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(5): 732-738. |
| [6] | DONG Lei, XU Pei. Danzhi Jiangtang capsule (丹蛭降糖胶囊) alleviate hyperglycemiaand periodontitis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling in diabetic rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(4): 608-616. |
| [7] | Zhan Kai, Xu Yan, Han Mengling, Cheng Liangbin. Daifan San intervenes in forkhead box P3 and the interleukin(IL)-23/IL-17A signaling pathway to help prevent and treat primary biliary cirrhosis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(4): 571-583. |
| [8] | Zeng Chuang, Bai Xuejing, Qin Heping, Wang Hong, Rong Xiaofeng, Yan Jin. Effect of adjuvant therapy with electroacupuncture on bone turnover markers and interleukin 17 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(04): 582-586. |
| [9] | Zhang Xiaowei, Guo Huijun, Li Zhen, Xu Liran, Zhang Aiping, Ji Aiying. Effectiveness of Xielikang capsules in treating HIV-related diarrhea by increasing the plasma concentration of interleukin-17 [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 37(05): 616-620. |
| [10] | Rahimifard Maryam, Sadeghi Faegheh, Asadi-Samani Majid, Nejati-Koshki Kazem. Effect of quercetin on secretion and gene expression of leptin in breast cancer [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 37(03): 321-325. |
| [11] | Wang Xiaodan, Yan Yongping, Yang Liu, Li Mu, Zhong Xiuhui. Effect of quercetin on the expression of Bcl-2/Bax apoptotic proteins in endometrial cells of lipopolysaccharide-induced-abortion mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 36(06): 737-742. |
| [12] | Shuna Cui, Jing Qian, Ping Bo. Inhibitive effect on phagocytosis of Candida albicans induced by pretreatment with quercetin via actin cytoskeleton interference [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(06): 804-809. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

