Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1204-1216.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240706.001
• Research Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Evaluation indicators of Traditional Chinese Medicine syndromes for gouty arthritis with damp heat accumulation and the effect of administering Tongfeng Qingxiao formula (痛风清消方)
ZHANG Xiaoyun1,2, LI Yongjin4, LI Huanan3( ), CHAI Yuan2, CHENG Feng4, LI Binglin4, ZHOU Yi4, LAI Yu4
), CHAI Yuan2, CHENG Feng4, LI Binglin4, ZHOU Yi4, LAI Yu4
- 1 College for Clinical Medicine, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330006, China
2 Department of Orthopedics, Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, China
3 Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330006, China
4 Graduate school, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530000, China
-
Received:2023-09-21Accepted:2023-12-22Online:2024-12-15Published:2024-06-06 -
Contact:LI Huanan, Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330006, China. Lihuanan1974@126.com Telephone: +86-13367005220; +86-15277047342 -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China: a Study on the Use of Tongfengqingxiao for Treating Gouty Arthritis and Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Formation based on the Transforming Growth Factor-β1 Signaling Pathway(81860857);a Study on the Mechanism by which Tongfeng Qingxiao Regulates the Toll-like receptors-myeloid Differentiation Factor 88-nuclear Factor Kappa-B Signaling Pathway in Gouty Arthritis Rats with Gut Dysbiosis and Dampness-Heat Syndrome based on the Gut-enteric-microbiota Axis(82060871);National Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province: a Study on the Regulatory Mechanism of the Toll-like receptors-Myeloid differentiation factor 88-nuclear factor kappa-B Signaling Pathway Related to Dysbacteriosis of the Intestinal Flora with Gouty Arthritis in Rats Mediated by Tongfengqingxiao, based on the “Gut-Microbiota” Axis(20202BAB206071)
Cite this article
ZHANG Xiaoyun, LI Yongjin, LI Huanan, CHAI Yuan, CHENG Feng, LI Binglin, ZHOU Yi, LAI Yu. Evaluation indicators of Traditional Chinese Medicine syndromes for gouty arthritis with damp heat accumulation and the effect of administering Tongfeng Qingxiao formula (痛风清消方)[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(6): 1204-1216.
share this article
| Group | n | 4 h | 12 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 12 | 0.27±0.10 | 0.11±0.05 | 0.11±0.07 | 0.13±0.08 | 0.17±0.10 |
| Model | 10 | 2.13±0.30a | 4.98±0.32a | 3.74±0.28a | 2.87±0.29a | 1.92±0.42a |
| TFQXF-H | 11 | 1.20±0.46ab | 3.65±0.38abc | 2.59±0.40abc | 1.35±0.36ab | 0.56±0.17ab |
| TFQXF-M | 11 | 1.35±0.29abc | 3.81±0.37abc | 2.66±0.43abc | 1.56±0.33abc | 0.61±0.16ab |
| TFQXF-L | 10 | 1.73±0.31abc | 4.17±0.17abc | 3.11±0.29abc | 2.00±0.45abc | 1.06±0.24abc |
| Diclofenac | 11 | 1.15±0.32ab | 3.39±0.36ab | 2.32±0.24ab | 1.22±0.21ab | 0.52±0.19ab |
Table 1 Ankle swelling index of rats at different time (mm, $\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | 4 h | 12 h | 24 h | 48 h | 72 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 12 | 0.27±0.10 | 0.11±0.05 | 0.11±0.07 | 0.13±0.08 | 0.17±0.10 |
| Model | 10 | 2.13±0.30a | 4.98±0.32a | 3.74±0.28a | 2.87±0.29a | 1.92±0.42a |
| TFQXF-H | 11 | 1.20±0.46ab | 3.65±0.38abc | 2.59±0.40abc | 1.35±0.36ab | 0.56±0.17ab |
| TFQXF-M | 11 | 1.35±0.29abc | 3.81±0.37abc | 2.66±0.43abc | 1.56±0.33abc | 0.61±0.16ab |
| TFQXF-L | 10 | 1.73±0.31abc | 4.17±0.17abc | 3.11±0.29abc | 2.00±0.45abc | 1.06±0.24abc |
| Diclofenac | 11 | 1.15±0.32ab | 3.39±0.36ab | 2.32±0.24ab | 1.22±0.21ab | 0.52±0.19ab |
| Group | n | ALT (U/L) | AST (U/L) | UREA (mmol/L) | CREA (μmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 12 | 34.25±4.56 | 54.17±2.66 | 3.70±0.35 | 52.25±4.73 |
| Model | 10 | 72.10±4.48a | 97.70±6.82a | 10.68±1.02a | 80.40±3.86a |
| TFQXF-H | 11 | 46.91±3.30ab | 76.36±3.72ab | 6.07±0.10abc | 63.18±3.54abc |
| TFQXF-M | 11 | 47.73±1.62ab | 77.91±3.02ab | 6.16±0.18abc | 63.64±2.25abc |
| TFQXF-L | 10 | 56.55±3.88abc | 81.91±3.18abc | 6.65±0.26abc | 67.64±2.38abc |
| Diclofenac | 11 | 49.18±2.89ab | 75.64±6.58ab | 5.37±0.24ab | 58.82±2.27ab |
Table 2 Liver and kidney function of rats in each group ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | ALT (U/L) | AST (U/L) | UREA (mmol/L) | CREA (μmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 12 | 34.25±4.56 | 54.17±2.66 | 3.70±0.35 | 52.25±4.73 |
| Model | 10 | 72.10±4.48a | 97.70±6.82a | 10.68±1.02a | 80.40±3.86a |
| TFQXF-H | 11 | 46.91±3.30ab | 76.36±3.72ab | 6.07±0.10abc | 63.18±3.54abc |
| TFQXF-M | 11 | 47.73±1.62ab | 77.91±3.02ab | 6.16±0.18abc | 63.64±2.25abc |
| TFQXF-L | 10 | 56.55±3.88abc | 81.91±3.18abc | 6.65±0.26abc | 67.64±2.38abc |
| Diclofenac | 11 | 49.18±2.89ab | 75.64±6.58ab | 5.37±0.24ab | 58.82±2.27ab |
| Group | n | TG | TC | HDL-C | LDL-C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 12 | 0.64±0.09 | 1.39±0.13 | 0.90±0.07 | 0.36±0.06 |
| Model | 10 | 0.95±0.13a | 1.92±0.19a | 0.51±0.06a | 0.71±0.03a |
| TFQXF-H | 11 | 0.72±0.06ab | 1.54±0.11ab | 0.78±0.06ab | 0.50±0.07ab |
| TFQXF-M | 11 | 0.74±0.08ab | 1.57±0.12ab | 0.76±0.06ab | 0.52±0.05ab |
| TFQXF-L | 10 | 0.81±0.05abc | 1.73±0.11abc | 0.61±0.07abc | 0.62±0.04abc |
| Diclofenac | 11 | 0.72±0.05ab | 1.52±0.12ab | 0.81±0.05ab | 0.46±0.10ab |
Table 3 Blood lipid metabolism of rats in each group (mmol/L, $\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | TG | TC | HDL-C | LDL-C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 12 | 0.64±0.09 | 1.39±0.13 | 0.90±0.07 | 0.36±0.06 |
| Model | 10 | 0.95±0.13a | 1.92±0.19a | 0.51±0.06a | 0.71±0.03a |
| TFQXF-H | 11 | 0.72±0.06ab | 1.54±0.11ab | 0.78±0.06ab | 0.50±0.07ab |
| TFQXF-M | 11 | 0.74±0.08ab | 1.57±0.12ab | 0.76±0.06ab | 0.52±0.05ab |
| TFQXF-L | 10 | 0.81±0.05abc | 1.73±0.11abc | 0.61±0.07abc | 0.62±0.04abc |
| Diclofenac | 11 | 0.72±0.05ab | 1.52±0.12ab | 0.81±0.05ab | 0.46±0.10ab |
| Group | n | MTL | GAS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 8 | 23.3±3.2 | 18.8±2.0 |
| Model | 8 | 43.9±7.7a | 32.1±5.2a |
| TFQXF-H | 8 | 28.1±3.2b | 22.7±3.2ab |
| TFQXF-M | 8 | 29.8±5.3ab | 23.5±3.6ab |
| TFQXF-L | 8 | 35.9±6.8abc | 27.9±3.8abc |
| Diclofenac | 8 | 27.7±6.1b | 22.0±2.9b |
Table 4 Gastrointestinal function of rats in each group (pg/mL, $\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | MTL | GAS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 8 | 23.3±3.2 | 18.8±2.0 |
| Model | 8 | 43.9±7.7a | 32.1±5.2a |
| TFQXF-H | 8 | 28.1±3.2b | 22.7±3.2ab |
| TFQXF-M | 8 | 29.8±5.3ab | 23.5±3.6ab |
| TFQXF-L | 8 | 35.9±6.8abc | 27.9±3.8abc |
| Diclofenac | 8 | 27.7±6.1b | 22.0±2.9b |
| Group | n | ET | CGRP | HSP70 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 8 | 7.24±1.14 | 20.03±3.19 | 29.84±4.60 |
| Model | 8 | 16.75±2.71a | 10.22±1.55a | 89.41±10.87a |
| TFQXF-H | 8 | 9.32±1.50ab | 16.89±2.63ab | 51.63±10.78abc |
| TFQXF-M | 8 | 9.56±1.55ab | 16.55±2.15ab | 52.10±7.81abc |
| TFQXF-L | 8 | 12.82±2.15abc | 14.01±1.94abc | 74.25±9.90abc |
| Diclofenac | 8 | 8.25±1.41b | 17.45±2.28ab | 39.94±5.10ab |
Table 5 Objective indexes of heat syndrome in each group (pg/mL, $\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | ET | CGRP | HSP70 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 8 | 7.24±1.14 | 20.03±3.19 | 29.84±4.60 |
| Model | 8 | 16.75±2.71a | 10.22±1.55a | 89.41±10.87a |
| TFQXF-H | 8 | 9.32±1.50ab | 16.89±2.63ab | 51.63±10.78abc |
| TFQXF-M | 8 | 9.56±1.55ab | 16.55±2.15ab | 52.10±7.81abc |
| TFQXF-L | 8 | 12.82±2.15abc | 14.01±1.94abc | 74.25±9.90abc |
| Diclofenac | 8 | 8.25±1.41b | 17.45±2.28ab | 39.94±5.10ab |
| Group | n | IL-1β (ng/L) | NF-κB (μmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 8 | 25.03±4.06 | 31.01±5.09 |
| Model | 8 | 108.74±8.70a | 124.79±18.94a |
| TFQXF-H | 8 | 65.50±11.46abc | 54.53±7.92abc |
| TFQXF-M | 8 | 59.41±10.50abc | 39.30±8.05bc |
| TFQXF-L | 8 | 72.57±7.94abc | 92.32±9.55abc |
| Diclofenac | 8 | 26.94±4.10b | 79.26±12.67ab |
Table 6 Serum inflammatory indexes of rats in each group ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | IL-1β (ng/L) | NF-κB (μmol/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 8 | 25.03±4.06 | 31.01±5.09 |
| Model | 8 | 108.74±8.70a | 124.79±18.94a |
| TFQXF-H | 8 | 65.50±11.46abc | 54.53±7.92abc |
| TFQXF-M | 8 | 59.41±10.50abc | 39.30±8.05bc |
| TFQXF-L | 8 | 72.57±7.94abc | 92.32±9.55abc |
| Diclofenac | 8 | 26.94±4.10b | 79.26±12.67ab |

Figure 1 Expression levels of AQPs in kidney and colon tissues A: Western blot analyses of AQP1-4 in kidney and colon tissues; B: statistical graphs of AQP1 Protein expression levels; C: statistical graphs of AQP2 Protein expression levels; D: statistical graphs of AQP3 Protein expression levels; E: statistical graphs of AQP4 protein expression levels; F: statistical graphs of AQP1 mRNA expression levels; G: statistical graphs of AQP2 mRNA expression levels; H: statistical graphs of AQP3 mRNA expression levels; I: statistical graphs of AQP4 mRNA expression levels. Normal group: healthy cases; Model group: gouty arthritis animal model of Damp-Heat Accumulation type without treatment; TFQXF-H group: gouty arthritis animal model of Damp-Heat Accumulation type rats treated with Tongfeng Qingxiao formula at a daily dose of 4.5 g/mL (1 mL/100 g) for 1 week; TFQXF-M group: gouty arthritis animal model of Damp-Heat Accumulation type rats treated with TFQXF at a daily dose of 2.25 g/mL (1 mL/100 g) for 1 week; TFQXF-L group: gouty arthritis animal model of Damp-Heat Accumulation type rats treated with TFQXF at a daily dose of 1.125 g/mL (1 mL/100 g) for 1 week; Diclofenac group: gouty arthritis animal model of Damp-Heat Accumulation type rats treated with diclofenac sodium at a daily dose of 1 mL/100 g for 1 week. AQP: aquaporin; TFQXF-H: high-dose group of Tongfeng Qingxiao formula; TFQXF-M: medium-dose group of Tongfeng Qingxiao formula; TFQXF-L: low-dose group of Tongfeng Qingxiao formula. One-way analysis of variance was performed to determine differences between groups, and a least significant difference test was conducted to perform multiple comparisons between groups. The data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (n = 8). Compared with the normal group, aP < 0.05; compared with the model group, bP < 0.05; compared with diclofenac group, cP < 0.05.
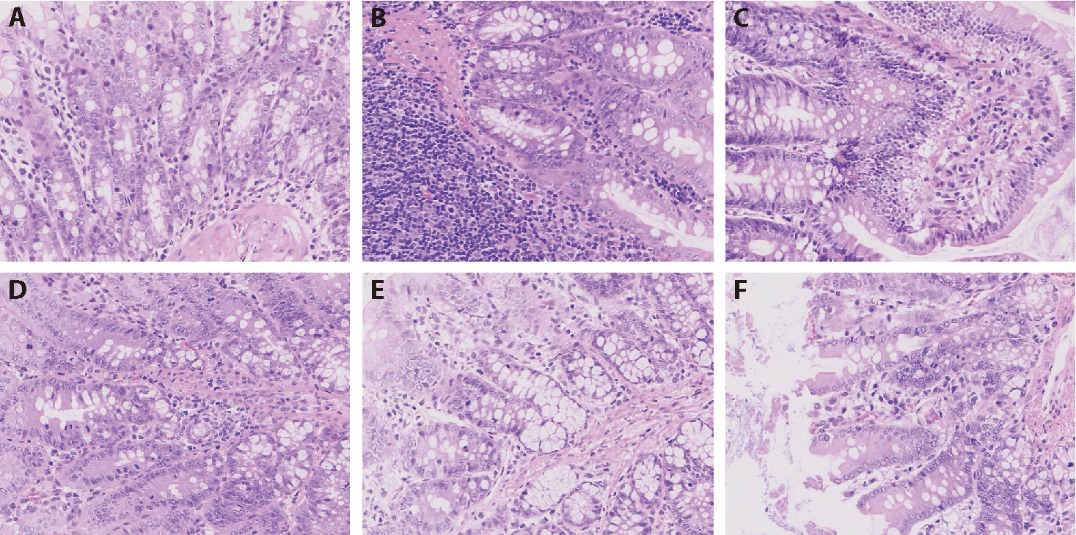
Figure 2 Results of intestinal pathological examination A: Normal group; B: Model group; C: TFQXF-H group; D: TFQXF-M group; E: TFQXF-L group; F: Diclofenac group. Normal group: healthy cases; Model group: gouty arthritis animal model of Damp-Heat Accumulation type without treatment; TFQXF-H group: gouty arthritis animal model of Damp-Heat Accumulation type rats treated with Tongfeng Qingxiao formula at a daily dose of 4.5 g/mL (1 mL/100 g) for 1 week; TFQXF-M group: gouty arthritis animal model of Damp-Heat Accumulation type rats treated with TFQXF at a daily dose of 2.25 g/mL (1 mL/100 g) for 1 week; TFQXF-L group: gouty arthritis animal model of Damp-Heat Accumulation type rats treated with TFQXF at a daily dose of 1.125 g/mL (1 mL/100 g) for 1 week; Diclofenac group: gouty arthritis animal model of Damp-Heat Accumulation type rats treated with diclofenac sodium at a daily dose of 1 mL/100 g for 1 week. Colon sections from all groups were stained with HE to assess changes in morphology. Method multiplier, × 400. TFQXF-H: high-dose group of Tongfeng Qingxiao formula; TFQXF-M: medium-dose group of Tongfeng Qingxiao formula; TFQXF-L: low-dose group of Tongfeng Qingxiao formula; HE: hematoxylin and eosin.
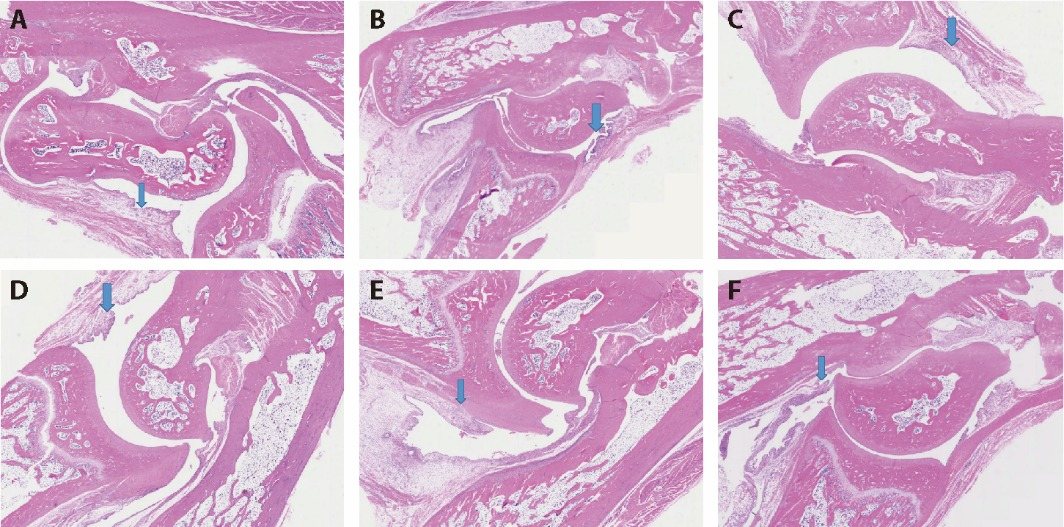
Figure 3 Results of synovial tissues examination A: Normal group; B: Model group; C: TFQXF-H group; D: TFQXF-M group; E: TFQXF-L group; F: Diclofenac group. Normal group: healthy cases; Model group: gouty arthritis animal model of Damp-Heat Accumulation type without treatment; TFQXF-H group: gouty arthritis animal model of Damp-Heat Accumulation type rats treated with Tongfeng Qingxiao formula at a daily dose of 4.5 g/mL (1 mL/100 g) for 1 week; TFQXF-M group: gouty arthritis animal model of Damp-Heat Accumulation type rats treated with TFQXF at a daily dose of 2.25 g/mL (1 mL/100 g) for 1 week; TFQXF-L group: gouty arthritis animal model of Damp-Heat Accumulation type rats treated with TFQXF at a daily dose of 1.125 g/mL (1 mL/100 g) for 1 week; Diclofenac group: gouty arthritis animal model of Damp-Heat Accumulation type rats treated with diclofenac sodium at a daily dose of 1 mL/100 g for 1 week. Synovium sections from all groups were stained with HE to assess changes in morphology. Method multiplier, × 40. Blue arrow: synovial tissues. TFQXF-H: high-dose group of Tongfeng Qingxiao formula; TFQXF-M: medium-dose group of Tongfeng Qingxiao formula; TFQXF-L: low-dose group of Tongfeng Qingxiao formula; HE: hematoxylin and eosin.
| 1. | Zhou Y, Chen YJ, Zhong XW, et al. Lipoxin A4 attenuates MSU-crystal-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation through suppressing Nrf2 thereby increasing TXNRD2. Front Immunol 2022; 13: 1060441. |
| 2. | Zheng WL, Lu PM, Jiang DH, Chen LX, Li Y, Deng HW. An ultrasonographic study of gouty arthritis: synovitis and its relationship to clinical symptoms: a retrospective analysis. Health Sci Rep 2023; 6: e1312. |
| 3. | Sami F, Sami SA, Arora S. Rare presentation of disseminated gout nodulosis and chronic inflammatory arthritis. Case Rep Rheumatol 2023: 8083212. |
| 4. | Xu LJ, Liu X, Zhang YR, et al. Tanshinone ⅡA improves acute gouty arthritis in rats through regulating neutrophil activation and the NLRP3 inflammasome. Dis Markers 2022: 5851412. |
| 5. | Zhou R, Jia YY, Wang Y, Wang XK, Leng XY. Application of state-target application of painful arthritis liver and kidney deficiency: A review. Medicine (Baltimore) 2022; 101: e31463. |
| 6. | Chang JG, Tu SJ, Huang CM, et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing of immune cells in patients with acute gout. Sci Rep 2022; 12: 22130. |
| 7. |
Dalbeth N, Gosling AL, Gaffo A. Gout. Lancet 2021; 397: 1843-55.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Shu C, Yang F, Zhu FB, Hua DP. Effect of external use of Qingluo San on clinical efficacy in patients with acute gouty arthritis. Eur J Med Res 2022; 27: 245.
DOI PMID |
| 9. | Lang JR, Li L, Chen SL, et al. Mechanism investigation of Wuwei Shexiang pills on gouty arthritis via network pharmacology, molecule docking, and pharmacological verification. Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 2022; 2022: 2377692. |
| 10. |
Pascart T, Lioté F. Gout: state of the art after a decade of developments. Rheumatology 2019; 58: 27-44.
DOI PMID |
| 11. | Li YB, Deng W, Wu L, Chen SH, Zheng ZP, Song HB. Anti-inflammatory effects of polyphenols from plum (prunus salicina lindl) on RAW264.7 macrophages induced by monosodium urate and potential mechanisms. Foods 2023; 12: 254. |
| 12. | Liu PY, Xu Y, Ye JX, et al. Qingre Huazhuo Jiangsuan decoction promotes autophagy by inhibiting PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway to relieve acute gouty arthritis. J Ethnopharmacol 2023; 302: 115875. |
| 13. | Zhang F, Zhou YX, Zhou SL. Data mining and mechanism research of Traditional Chinese Medicine treatment for gouty arthritis of damp-heat obstruction. Zhejiang Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2022; 46: 1015-22. |
| 14. | Lai GW. Effects of Tongfeng Qingxiao recipe on serum IL-1β, IL-8 and TNF-α levels in patients with damp-heat syndrome acute gouty arthritis. Nanchang: Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020: 1-45. |
| 15. | Jiang Q, Han M, Tang XP, Luo CG, Gong X. Guideline for diagnosis and treatment of gout and hyperuricemia with integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2021; 62: 1276-88. |
| 16. | Gan B, Li HN, Li S, et al. Establishment of two rat models of gouty arthritis with damp-heat syndrome based on lipid metabolism and proinflammatory factors. Zhong Guo Bi Jiao Yi Xue Za Zhi 2023; 33: 26-33. |
| 17. | Gan B, Li HN, Zhang XY. Establishment and evaluation of an animal model of acute gouty arthritis with damp heat syndrome. Jiangxi Zhong Yi Yao 2021; 52: 77-80. |
| 18. | Guo YX, Zhu SY, Kang PZ, et al. Significance of AQP2 and HSP70 expression in gout model with damp-heat syndrome. Shi Jie Ke Xue Ji Shu Zhong Yi Yao Xian Dai Hua 2020; 22: 3894-9. |
| 19. | Xiong H, Qu LY, Xiang LL. A rat model of gouty arthritis combined with dampness-heat syndrome. Zhong Yi Zheng Gu 2014; 26: 14-20. |
| 20. | Yin M, Xiang LL, Xiong H. Study of the establishment of the gouty arthritis rat models with damp-heat syndrome. Hunan Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2015; 35: 6-10. |
| 21. | Yi H. Exploring the effect of TR on MSU-induced NETs based on network pharmacology and in vitro experiments. Jiangxi: Jiangxi Science and Technology Normal University, 2022: 1-48. |
| 22. | Zhang XY, Gu B, Chen YN. Reflections on animal model integrated with disease and syndrome for gouty arthritis. Zhong Guo Yao Li Xue Tong Bao 2020; 36: 1490-6. |
| 23. | Liang D, Li XH, Tang YP. Preliminary study on establishment and evaluation of spleen-stomach damp-heat syndrome model ofcynomolgus monkey with acute alcoholic fatty liver. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2021; 36: 1374-8. |
| 24. | Yang ZT. Study on mechanism of Sishen decoction in treating gouty arthritis based on xuanfu theory. Beijing: China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, 2019: 1-84. |
| 25. | Hu XQ, Zeng XX, Fu R, et al. Property-efficacy relationship of scutellariae radix and atractylodis rhizoma in drying dampness in rats with spleen-stomach dampness-heat syndrome. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi 2021; 27: 35-42. |
| 26. |
Ma WZ, Liang X, Su ZW. Effects of a Chinese herbal extract on the intestinal tract and aquaporin in adriamycin-induced nephropathy. Bioengineered 2022; 13: 2732-45.
DOI PMID |
| 27. | Zuo ZY, Zhang BL, Cui YK, Huang YM, Yao FY. Effect of modified Wendan decoction on AQPs expression of rats with dampness heat syndrome. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2022; 40: 6-9. |
| 28. | Gong X, Hu C. The effect and mechanism of new processing method of codonopsis pilosula on endocrine physique index in rats. Comput Math Methods Med 2022; 2022: 7703612. |
| 29. | Luo SJ, Li YL, Li SW, et al. Expression regulation of water reabsorption genes and transcription factors in the kidneys of lepus yarkandensis. front physiol 2022; 13: 856427. |
| 30. | Liu SL, Qiu YQ, Gu F, et al. Niacin improves intestinal health through up-regulation of AQPs expression induced by GPR109A. Int J Mol Sci 2022; 23: 8332. |
| 31. |
Meng YX, Li XJ, Wang XT, Zhang L, Guan JQ. Network pharmacological prediction and molecular docking analysis of the combination of atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. and Paeonia lactiflora Pall. in the treatment of functional constipation and its verification. Animal Model Exp Med 2022; 5: 120-32.
DOI PMID |
| 32. | Xie Y, Zhan X, Tu JY, et al. Atractylodes oil alleviates diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome by regulating intestinal inflammation and intestinal barrier via SCF/c-kit and MLCK/ MLC2 pathways. J Ethnopharmacol 2021; 272: 113925. |
| 33. |
Li J, Cao YX, Chen KL, Cao L, Ma Z, Xu CB. Regional variations of vasomotion to G-protein coupled receptor agonists following heat stress in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 2010; 62: 315-22.
DOI PMID |
| 34. | Hanafi SA, Zulkifli I, Ramiah SK, Chung ELT, Awad EA, Sazili AQ. Prenatal thermal stress affects acute-phase proteins, heat shock protein 70, and circulating corticosterone in developing broiler embryos and neonates. J Therm Biol 2022; 109: 103328. |
| 35. | Li H, Li SY, Chen J, et al. A heat shock 70kDa protein MaltHSP70- 2 contributes to thermal resistance in monochamus alternatus (coleoptera: cerambycidae): quantification, localization, and functional analysis. BMC Genom 2022; 23: 646. |
| 36. | Quan YD, Wang ZY, Wei HY, He KL. Transcription dynamics of heat shock proteins in response to thermal acclimation in ostrinia furnacalis. Front Physiol 2022; 13: 992293. |
| 37. | Gan B. AnimaI modeI validation of gouty arthritis with damp-heat syndrome based on literature review. Nanchang: Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022: 1-60. |
| 38. | Feng W, Zhong XQ, Zheng XX, et al. Study on the effect and mechanism of quercetin in treating gout arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol 2022; 111: 09112. |
| 39. | Hu JG, Jin C, Fang L, et al. MicroRNA-486-5p suppresses inflammatory response by targeting FOXO1 in MSU-treated macrophages. Autoimmunity 2022; 55: 661-9. |
| 40. | Huang Y, Zhou MJ, Yuan F. Clinical features and risk factors of fever in acute gouty arthritis. Biomed Res Int 2022: 8798838. |
| 41. | Jia M. Clinical study of Guzhongqingxiao prescription in treating acute gouty on CD4+, CD8+ and CD4/CD8. Nanchang: Jiangxi University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019: 1-53. |
| 42. | Zhang XY, Gu B, Li HN. Screening of target genes of Simiao powder in treatment of gouty arthritis and analysis of their biological functions. Shandong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2021; 61: 54-8. |
| 43. | Cao L, Zhao TY, Xue Y, et al. The anti-inflammatory and uric acid lowering effects of Si-Miao-San on gout. Front Immunol 2022; 12: 777522. |
| 44. | Wei X, Ni JD, Song DY, Guo SF, Zhu W. Study on the therapeutic mechanism of Jiawei Simiao powder on rats with acute gouty arthritis induced by sodium urate. Xian Dai Sheng Wu Yi Xue Jin Zhan 2019; 19: 1257-60. |
| 45. | Zhao H, Chen J, Shen DY. Effects of modified Simiaosan on uric acid metabolism and gut microbiota in rats with hyperuricemia. Hubei Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2022; 24: 26-30. |
| 46. | Bai ZX, Cao XH, Sun CY, Yang YJ, Sun WD. A network pharmacology approach to explore the functional mechanisms of Bixie and Tufuling for treating gouty arthritis. Hannan Yi Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2020; 26: 611-7. |
| 47. | Li QQ. Based on data excavated the medicine application of Traditional Chinese Medicine in the treatment of gout. Nanning: Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, 2022: 1-68. |
| 48. | Wu XT. Exploring the medication patterns of clearing heat and removing dampness in the treatment of acute gouty arthritis with dampness heat accumulation syndrome. Shenyang: Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021: 1-43. |
| 49. | Lim DW, Kim H, Park SY, Park SD, Park WH, Kim JE. Study of the suppressive effect and its mechanism of amomum cardamomum L. on free fatty acid-induced liver steatosis. J Physiol Pathol Korean Med 2017; 31: 159-66. |
| 50. | Chen JX, Cheng CS, Chen J, et al. Cynanchum paniculatum and its major active constituents for inflammatory-related diseases: a review of traditional use, multiple pathway modulations, and clinical applications. Evid Based Complementary Altern Med 2020; 2020: 7259686. |
| 51. | Yan XX, Pan QD, Sun HY, Gao L, Yang R, Yang LX. Traditional use of paris polyphylla and its active components. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2021; 46: 6343-52. |
| 52. | Liu ST, Yu H, Hou AJ, et al. A review of the pharmacology, application, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, quality control, processing, toxicology, and pharmacokineticsof Paridis Rhizoma. World J Tradit Chin Med 2022; 8: 21-49. |
| [1] | FANG Congcong, ZHU Xiaoliang, ZHANG Yongjian, QI Huan, ZHANG Yingjie. Combination of allopurinol with Dahuang Mudan Tang (大黄牡丹汤) significantly improve kidney function and alleviate oxidative stress and inflammation of chronic kidney disease stage Ⅰ-Ⅲ patients with hyperuricemia [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 182-187. |
| [2] | Li Aiwu, Huang Yinger, Zheng Songyuan, Tang Cuiping, Zhu Junqing, Li Juan. Clinical observation of Qushi Xiezhuo formula in reducing monosodium urate crystal deposition in patients with axial spondyloarthritis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 39(05): 722-729. |
| [3] | Wang Xinyi, Liu Bingyun, Wang Shan, Sui Minghe. Effects of acupuncture at Shu, Yuan, and Mu acupoints on blood serum uric acid and xanthine oxidase levels in a rat model of gout and hyperuricemia [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 37(06): 841-845. |
| [4] | Kou Yiying, Li Yongfang, Ma Husai, Li Wangyu, Li Ruilian, Dang Zhancui. Uric acid lowering effect of Tibetan Medicine RuPeng15 powder in animal models of hyperuricemia [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016, 36(02): 205-210. |
| [5] | Yingyi Pan, Zhifeng Chu, Wenjuan Wang, Baican Yang. Pretreatment with Jieduxiezhuo decoction impedes elevations in serum uric acid levels in mice [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(06): 794-797. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

