Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 715-724.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20221214.002
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Chinese Tuina remodels the synaptic structure in neuropathic pain rats by downregulating the expression of N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B and postsynaptic density protein-95 in the spinal cord dorsal horn
HUANG Hongye1, WANG Bingqian4, CHEN Shuijin2,3, FANG Jiayu1, WANG Xiaohua1, CHEN Lechun2,3, JIANG Yu2,3, ZHANG Huanzhen2,3, CHEN Jincheng2,3, LIN Zhigang2,3( )
)
- 1 College of Rehabilitation Medicine, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, China
2 Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Subsidiary Rehabilitation Hospital, Fuzhou 350003, China
3 Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Rehabilitation Technology, Fuzhou 350003, China
4 Peking University International Hospital, Beijing 102206, China
-
Received:2022-02-23Accepted:2022-07-08Online:2022-12-14Published:2022-12-14 -
Contact:LIN Zhigang -
About author:Dr. LIN Zhigang, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Subsidiary Rehabilitation Hospital, Fuzhou 350003, China. linzhigang@fjtcm.edu.cn. Telephone: +86-18159191681
-
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation-funded Project: Study on the Mechanism of Tuina and Tuina in Regulating the Synaptic Plasticity of Spinal Dorsal Horn in Lumbar Disc Herniation Based on LncRNA-HOTAIR/miR-219 Mediated NMDAR Pathway(82174523);Natural Science Foundation of Fujian Province: Study on the Mechanism of Tuina Regulating the Synaptic Plasticity of Spinal Dorsal Horn in Lumbar Disc Herniation based on NMDAR-CAMK2-CREB Pathway(2020J01757);Study on Analgesic Mechanism of Tuina on Neuropathic Pain in Spinal Dorsal Horn/ACC Brain Region based on PKA-NMDA-NR2B Pathway(2020J01758);Fujian Health Science and Technology Program: Study on the Analgesic Mechanism of Tuina Manipulation On Lumbar Disc Herniation from the Efficacy of miR-219/NR2B Mediated Synaptic Transmission(2020GGA070);Effects of Tuina Point Press on AMPA/NMDA Receptor Scaffold Protein and Synaptic Plasticity in Spinal Dorsal Horn of Rats with Neuropathic Pain(2020CXA052)
Cite this article
HUANG Hongye, WANG Bingqian, CHEN Shuijin, FANG Jiayu, WANG Xiaohua, CHEN Lechun, JIANG Yu, ZHANG Huanzhen, CHEN Jincheng, LIN Zhigang. Chinese Tuina remodels the synaptic structure in neuropathic pain rats by downregulating the expression of N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B and postsynaptic density protein-95 in the spinal cord dorsal horn[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 715-724.
share this article
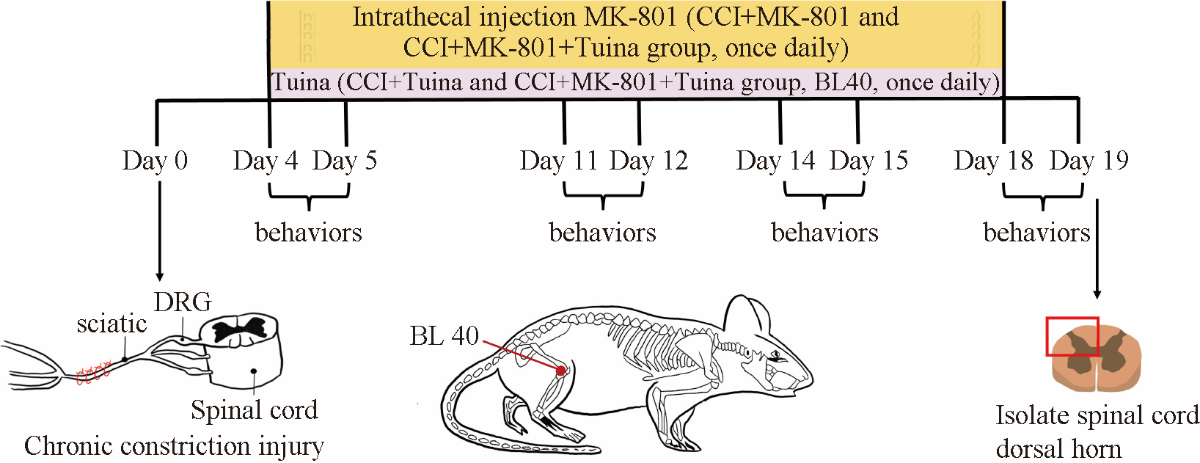
Figure 1 Experimental process Inclined-plate test and Von Frey test were performed on days 4, 11, 14, 18 after CCI surgery; acetone spray test was performed on days 5, 12, 15, 19 after CCI surgery; spinal cord dorsal horn was isolated on day 19; CCI + MK-801 and CCI + MK-801 + Tuina group received intrathecal injection of MK-801 once daily from days 4-19 after CCI surgery, CCI + Tuina and CCI + MK-801 + Tuina group received Tuina treatment once daily from day 4-19 after CCI surgery. Tuina started half an hour after receiving intrathecal injection. DRG: dorsal root ganglia; CCI: chronic constriction injury; BL40: bladder meridian 40.

Figure 2 Tuina manipulation emulator with micro pressure sensor simulates the effect of Tuina manipulation on the body surface of rats A: photograph of Tuina manipulation emulator equipped with a pressure sensor and demonstration of rat fixation; B: control board can display and collect real-time mechanical information through corresponding software which can be immediately transmitted to a computer; C: real-time force display in a 15 s interval included pressing and circular rubbing manipulation (5 ± 1N).
| Group | n | Baseline | Day 4 | Day 11 | Day 14 | Day 18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 5 | 53.7±2.2 | 52.7±1.9 | 53.3±1.7 | 54.0±2.8 | 53.3±1.7 |
| Sham | 5 | 51.7±1.2 | 45.3±1.8a | 45.7±1.9a | 50.7±2.8 | 50.7±3.0 |
| CCI | 5 | 51.7±2.0 | 32.7±0.9ab | 32.3±1.5ab | 34.0±1.9ab | 38.0±4.0ab |
| CCI+Tuina | 5 | 52.0±0.7 | 33.7±1.8 | 37.3±1.9c | 40.3±1.8c | 43.4±1.7 |
| CCI+MK-801 | 4 | 51.2±0.8 | 34.6±1.6 | 36.2±1.6 | 41.7±1.4c | 41.2±3.5 |
| CCI+MK-801+Tuina | 5 | 53.0±1.4 | 33.0±1.4 | 36.0±2.2 | 44.0±1.5c | 45.7±3.8d |
Table 1 Inclined plate test results at different intervention times ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | Baseline | Day 4 | Day 11 | Day 14 | Day 18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 5 | 53.7±2.2 | 52.7±1.9 | 53.3±1.7 | 54.0±2.8 | 53.3±1.7 |
| Sham | 5 | 51.7±1.2 | 45.3±1.8a | 45.7±1.9a | 50.7±2.8 | 50.7±3.0 |
| CCI | 5 | 51.7±2.0 | 32.7±0.9ab | 32.3±1.5ab | 34.0±1.9ab | 38.0±4.0ab |
| CCI+Tuina | 5 | 52.0±0.7 | 33.7±1.8 | 37.3±1.9c | 40.3±1.8c | 43.4±1.7 |
| CCI+MK-801 | 4 | 51.2±0.8 | 34.6±1.6 | 36.2±1.6 | 41.7±1.4c | 41.2±3.5 |
| CCI+MK-801+Tuina | 5 | 53.0±1.4 | 33.0±1.4 | 36.0±2.2 | 44.0±1.5c | 45.7±3.8d |
| Group | n | Baseline | Day 4 | Day 11 | Day 14 | Day 18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 5 | 12.0±2.7 | 11.6±3.2 | 13.0±2.7 | 12.0±1.2 | 14.0±2.2 |
| Sham | 8 | 11.9±2.6 | 11.2±2.3 | 12.2±3.0 | 11.9±2.6 | 13.1±2.6 |
| CCI | 8 | 13.1±2.6 | 5.0±2.4ab | 3.7±2.0ab | 3.2±1.0ab | 2.2±0.7ab |
| CCI+Tuina | 8 | 11.9±2.9 | 4.7±1.5 | 7.0±1.8c | 8.0±1.1d | 9.0±1.1d |
| CCI+MK-801 | 8 | 14.2±5.6 | 5.5±2.1 | 9.0±1.1d | 9.2±1.0d | 12.5±2.7d |
| CCI+MK-801+Tuina | 8 | 14.5±5.3 | 4.7±2.1 | 9.0±1.1d | 9.4±1.6d | 11.9±2.6d |
Table 2 Time-course changes of PWTs in the hind paw of rats (g, $\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | Baseline | Day 4 | Day 11 | Day 14 | Day 18 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 5 | 12.0±2.7 | 11.6±3.2 | 13.0±2.7 | 12.0±1.2 | 14.0±2.2 |
| Sham | 8 | 11.9±2.6 | 11.2±2.3 | 12.2±3.0 | 11.9±2.6 | 13.1±2.6 |
| CCI | 8 | 13.1±2.6 | 5.0±2.4ab | 3.7±2.0ab | 3.2±1.0ab | 2.2±0.7ab |
| CCI+Tuina | 8 | 11.9±2.9 | 4.7±1.5 | 7.0±1.8c | 8.0±1.1d | 9.0±1.1d |
| CCI+MK-801 | 8 | 14.2±5.6 | 5.5±2.1 | 9.0±1.1d | 9.2±1.0d | 12.5±2.7d |
| CCI+MK-801+Tuina | 8 | 14.5±5.3 | 4.7±2.1 | 9.0±1.1d | 9.4±1.6d | 11.9±2.6d |
| Group | n | Baseline | Day 5 | Day 12 | Day 15 | Day 19 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 5 | 0.80±0.14 | 0.76±0.17 | 0.60±0.14 | 0.62±0.06 | 0.48±0.23 |
| Sham | 8 | 0.83±0.13 | 0.78±0.27 | 0.83±0.20 | 0.75±0.21 | 0.70±0.15 |
| CCI | 8 | 0.88±0.15 | 2.73±0.15ab | 2.85±0.09ab | 2.85±0.03ab | 2.90±0.17ab |
| CCI+Tuina | 8 | 0.83±0.23 | 2.72±0.10 | 2.40±0.17 | 2.15±0.18c | 1.75±0.09c |
| CCI+MK-801 | 8 | 0.95±0.09 | 1.93±0.15c | 1.45±0.14c | 1.30±0.17c | 1.13±0.10c |
| CCI+MK-801+Tuina | 8 | 0.93±0.10 | 1.40±0.11cd | 1.40±0.16c | 1.18±0.20c | 1.05±0.09c |
Table 3 Time-course changes of cold spray scores in the hind paw of rats ($\bar{x}±s$)
| Group | n | Baseline | Day 5 | Day 12 | Day 15 | Day 19 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 5 | 0.80±0.14 | 0.76±0.17 | 0.60±0.14 | 0.62±0.06 | 0.48±0.23 |
| Sham | 8 | 0.83±0.13 | 0.78±0.27 | 0.83±0.20 | 0.75±0.21 | 0.70±0.15 |
| CCI | 8 | 0.88±0.15 | 2.73±0.15ab | 2.85±0.09ab | 2.85±0.03ab | 2.90±0.17ab |
| CCI+Tuina | 8 | 0.83±0.23 | 2.72±0.10 | 2.40±0.17 | 2.15±0.18c | 1.75±0.09c |
| CCI+MK-801 | 8 | 0.95±0.09 | 1.93±0.15c | 1.45±0.14c | 1.30±0.17c | 1.13±0.10c |
| CCI+MK-801+Tuina | 8 | 0.93±0.10 | 1.40±0.11cd | 1.40±0.16c | 1.18±0.20c | 1.05±0.09c |
| Group | n | Glutamate concentrations (ng/mL) | TNF-α level (pg/100 μg) | IL-1β level (pg/100 μg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham | 4 | 726.7±34.5 | 16.4±1.8 | 186.8±11.7 |
| CCI | 4 | 1061.6±85.7a | 26.3±5.6a | 342.7±19.4a |
| CCI+Tuina | 4 | 807.6±14.2b | 16.3±2.0b | 227.1±7.4b |
| CCI+MK-801 | 4 | 865.7±72.8c | 20.1±2.1 | 229.0±8.5b |
| CCI+MK-801+Tuina | 4 | 617.1±22.5bd | 18.3±2.9c | 212.5±11.3b |
Table 4 Glutamate concentrations, TNF-α and IL-1β levels in the SCDH
| Group | n | Glutamate concentrations (ng/mL) | TNF-α level (pg/100 μg) | IL-1β level (pg/100 μg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham | 4 | 726.7±34.5 | 16.4±1.8 | 186.8±11.7 |
| CCI | 4 | 1061.6±85.7a | 26.3±5.6a | 342.7±19.4a |
| CCI+Tuina | 4 | 807.6±14.2b | 16.3±2.0b | 227.1±7.4b |
| CCI+MK-801 | 4 | 865.7±72.8c | 20.1±2.1 | 229.0±8.5b |
| CCI+MK-801+Tuina | 4 | 617.1±22.5bd | 18.3±2.9c | 212.5±11.3b |
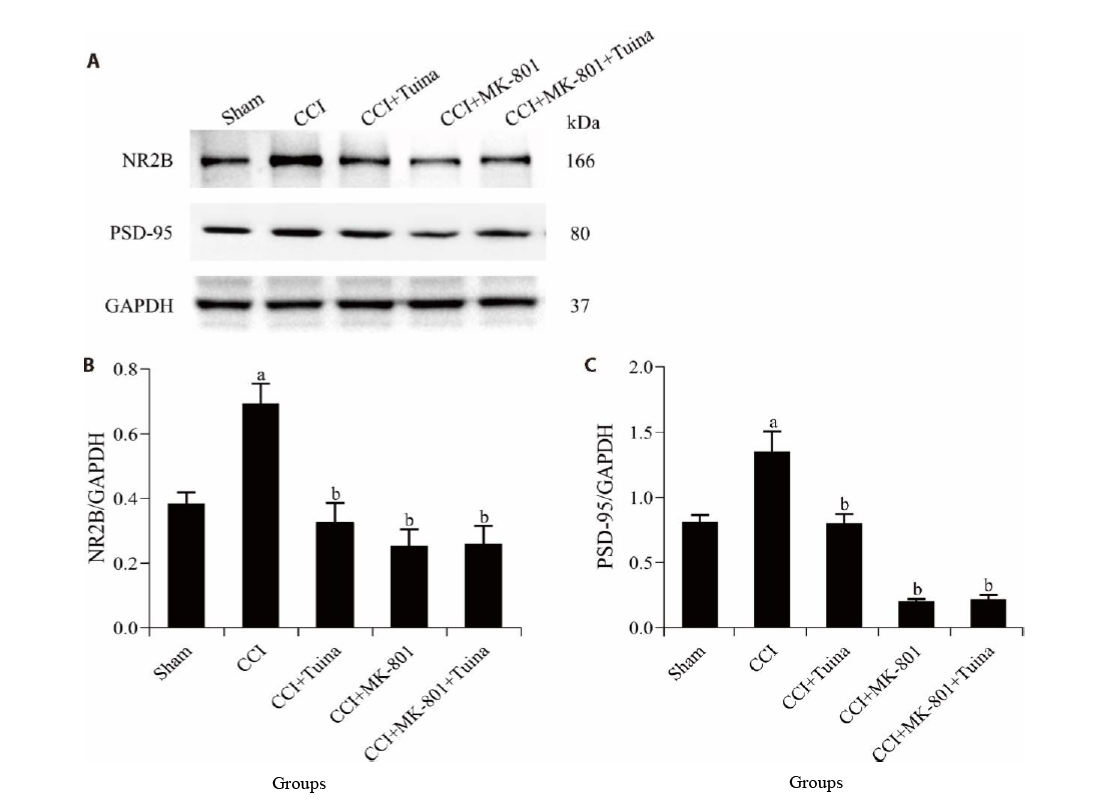
Figure 3 NR2B and PSD-95 protein expression levels in the SCDH A-C: protein expression of NR2B and PSD-95 in the SCDH from rats detected by Western blot. Rats in the sham group were performed with sham surgery without knotting; the CCI group were received chronic constriction injury surgery; the CCI + Tuina group were treat with Tuina manipulation once daily; the CCI + MK-801 group were given intrathecal injection of MK-801 once daily; the CCI + MK-801 + Tuina group, the above two treatments were given once daily. Each group was treated for 14 d. CCI: chronic constriction injury; NR2B: N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B; PSD-95: postsynaptic density protein-95; SCDH: spinal cord dorsal horn. Data were expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 5). aP < 0.01 compared with the sham group; bP < 0.01 compared with the CCI group.
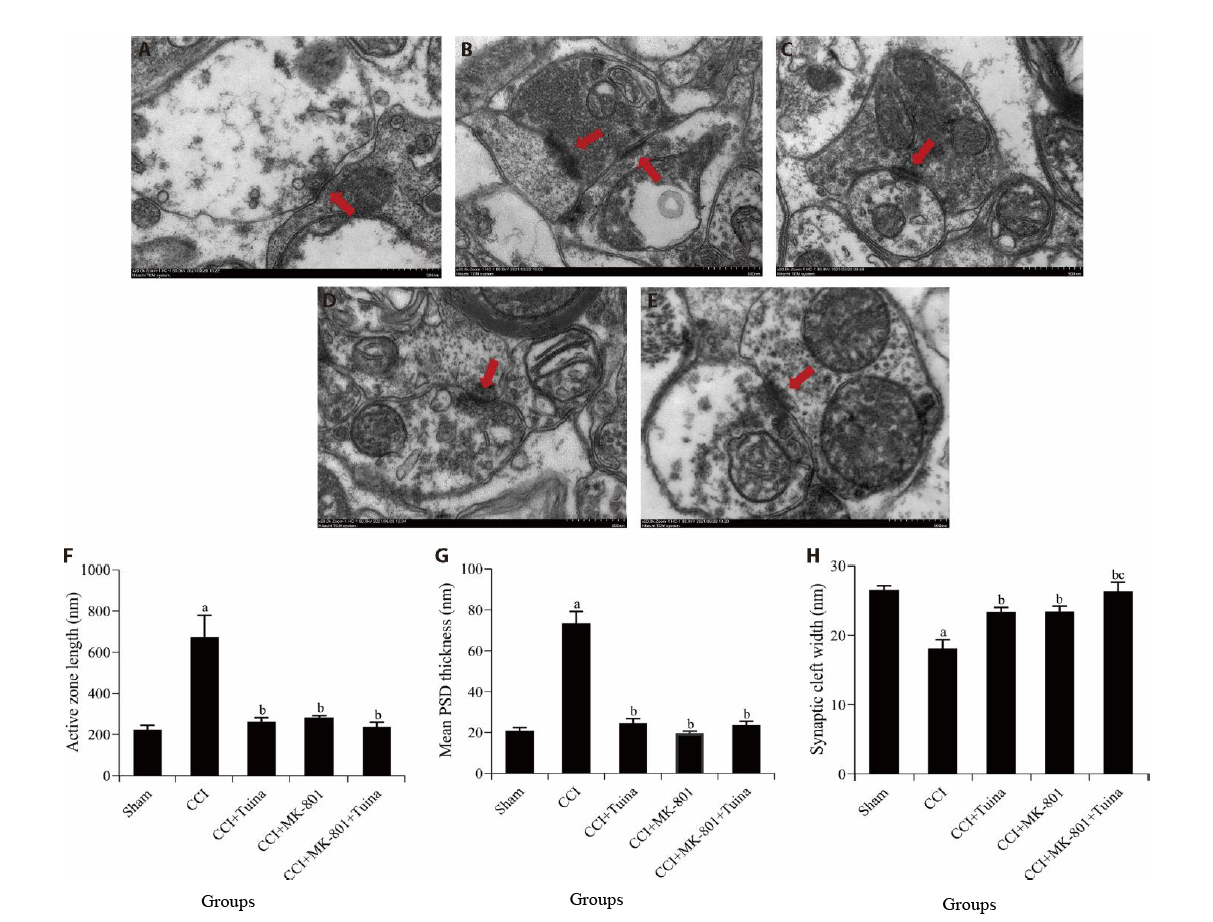
Figure 4 Synaptic ultrastructure changes and quantitative summary of synaptic ultrastructure in the SCDH (Transmission electronic microscopy staining method, × 20 000) The red arrow indicates the synapse. A: sham group; B: CCI group; C: CCI + Tuina group; D: CCI + MK-801 group; E: CCI + MK-801 + Tuina group; F: synaptic active zone length of rats in each group; G: mean PSD thickness of rats in each group; H: synaptic cleft width of rats in each group. Rats in the sham group were performed with sham surgery without knotting; the CCI group were received chronic constriction injury surgery; the CCI + Tuina group were treat with Tuina manipulation once daily; the CCI + MK-801 group were given intrathecal injection of MK-801 once daily; the CCI + MK-801 + Tuina group, the above two treatments were given once daily. Each group was treated for 14 d. SCDH: spinal cord dorsal horn; CCI: chronic constriction injury; PSD: postsynaptic density. Data were expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (n = 3). aP < 0.01 compared with the sham group; bP < 0.01 compared with the CCI group; cP < 0.05 compared with the CCI + MK-801 group.
| Group | n | Active zone length | PSD thickness | Synaptic cleft |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham | 3 | 177.7±45.1 | 22.0±5.4 | 26.1±1.7 |
| CCI | 3 | 541.0±98.9a | 77.9±21.4a | 18.2±4.1a |
| CCI+Tuina | 3 | 232.5±48.1b | 25.0±6.6b | 23.8±0.7b |
| CCI+MK-801 | 3 | 273.5±20.2b | 19.7±3.0b | 23.4±1.8b |
| CCI+MK-801+Tuina | 3 | 205.8±61.2b | 24.5±6.2b | 27.9±2.7bc |
Table 5 Quantitative summary of synaptic ultrastructure in the SCDH (nm)
| Group | n | Active zone length | PSD thickness | Synaptic cleft |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sham | 3 | 177.7±45.1 | 22.0±5.4 | 26.1±1.7 |
| CCI | 3 | 541.0±98.9a | 77.9±21.4a | 18.2±4.1a |
| CCI+Tuina | 3 | 232.5±48.1b | 25.0±6.6b | 23.8±0.7b |
| CCI+MK-801 | 3 | 273.5±20.2b | 19.7±3.0b | 23.4±1.8b |
| CCI+MK-801+Tuina | 3 | 205.8±61.2b | 24.5±6.2b | 27.9±2.7bc |
| 1. | Yu TY. Anmo Tuina Xue. 3rd ed. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College Press, 2012: 3-4. |
| 2. |
Wu Z, Kong L, Zhu Q, et al. Efficacy of Tuina in patients with chronic neck pain: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2019; 20: 1-10.
DOI |
| 3. |
Zhang S, Kong L, Zhu Q, et al. Efficacy of Tuina in patients with chronic low back pain: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials 2020; 21: 1-9.
DOI |
| 4. |
Ai J, Dong Y, Tian Q, et al. Tuina for periarthritis of shoulder: a systematic review protocol. Medicine 2020; 99: e19332.
DOI URL |
| 5. | Smith BH, Hébert HL, Veluchamy A. Neuropathic pain in the community: prevalence, impact, and risk factors. Pain 2020; 161: S127-37. |
| 6. | Yan X, Weng HR. Endogenous interleukin-1β in neuropathic rats enhances glutamate release from the primary afferents in the spinal dorsal horn through coupling with presynaptic N-methyl-D-aspartic acid receptors. J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 30544-57. |
| 7. |
Liao WT, Tseng CC, Chia WT, et al. High-frequency spinal cord stimulation treatment attenuates the increase in spinal glutamate release and spinal miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents in rats with spared nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain. Brain Res Bull 2020; 164: 307-13.
DOI URL |
| 8. |
Alomar SY, Gheit RE, Enan ET, et al. Novel mechanism for memantine in attenuating diabetic neuropathic pain in mice via downregulating the spinal HMGB1/TRL4/NF-kB inflammatory axis. Pharmaceuticals 2021; 14: 307.
DOI URL |
| 9. | Duarte RV, Nevitt S, McNicol E, et al. Systematic review and Meta-analysis of placebo/sham controlled randomised trials of spinal cord stimulation for neuropathic pain. Pain 2020; 161: 24-35. |
| 10. |
Berger JV, Knaepen L, Janssen SPM, et al. Cellular and molecular insights into neuropathy-induced pain hypersensitivity for mechanism-based treatment approaches. Brain Res Rev 2011; 67: 282-310.
DOI PMID |
| 11. | Peterson CD, Kitto KF, Verma H, et al. Agmatine requires GluN2B-containing NMDA receptors to inhibit the development of neuropathic pain. Mol Pain 2021; 17: 17448069211029171. |
| 12. |
Kuner R, Flor H. Structural plasticity and reorganisation in chronic pain. Nat Rev Neurosci 2017; 18: 20-30.
DOI |
| 13. | Bittar A, Jun J, La JH, et al. Reactive oxygen species affect spinal cell type-specific synaptic plasticity in a model of neuropathic pain. Pain 2017; 158: 2137-46. |
| 14. | Liang F, Liu M, Fu X, et al. Dexmedetomidine attenuates neuropathic pain in chronic constriction injury by suppressing NR2B, NF-κB, and iNOS activation. Saudi Pharm J 2017; 25: 649-54. |
| 15. |
Lu L, Pan C, Chen L, et al. AMPK activation by peri-sciatic nerve administration of ozone attenuates CCI-induced neuropathic pain in rats. J Mol Cell Biol 2017; 9: 132-43.
DOI PMID |
| 16. |
Loftis JM, Janowsky A. The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR2B: localization, functional properties, regulation, and clinical implications. Pharmacol Ther 2003; 97: 55-85.
DOI URL |
| 17. |
Li S, Cao J, Yang X, et al. NR2B phosphorylation at tyrosine 1472 in spinal dorsal horn contributed to N‐methyl‐D‐aspartate‐induced pain hypersensitivity in mice. J Neurosci Res 2011; 89: 1869-76.
DOI URL |
| 18. | Wang XY, Zhou HR, Wang S, et al. NR2B-Tyr phosphorylation regulates synaptic plasticity in central sensitization in a chronic migraine rat model. J Headache Pain 2018; 19: 1-15. |
| 19. |
Qu XX, Cai J, Li MJ, et al. Role of the spinal cord NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the development of neuropathic pain. Exp Neurol 2009; 215: 298-307.
DOI URL |
| 20. | Wang J, Qiao Y, Yang RS, et al. The synergistic effect of treatment with triptolide and MK-801 in the rat neuropathic pain model. Mol Pain 2017; 13: 1744806917746564. |
| 21. |
Xu F, Zhao X, Liu L, et al. Perturbing NR2B-PSD-95 interaction relieves neuropathic pain by inactivating CaMKII-CREB signaling. Neuroreport 2017; 28: 856-63.
DOI PMID |
| 22. |
Wang Z, Chen Z, Yang J, et al. Treatment of secondary brain injury by perturbing postsynaptic density protein-95-NMDA receptor interaction after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 2019; 39: 1588-601.
DOI URL |
| 23. |
Borja BB, Shroff H, Upadhyay H, et al. Probing synaptic signaling with optogenetic stimulation and genetically encoded calcium reporters. Methods Mol Biol 2021; 2191: 109-34.
DOI PMID |
| 24. | Huang LE, Guo SH, Thitiseranee L, et al. N-methyl D-aspartate receptor subtype 2B antagonist, Ro 25-6981, attenuates neuropathic pain by inhibiting postsynaptic density 95 expression. Sci Rep 2018; 8: 1-9. |
| 25. | Bennett GJ, Xie YK. A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen in man. Pain 1988; 33: 87-107. |
| 26. |
Gui X, Wang H, Wu L, et al. Botulinum toxin type A promotes microglial M2 polarization and suppresses chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain through the P2X7 receptor. Cell Biosci 2020; 10: 1-10.
DOI |
| 27. |
Jiang H, Yu X, Ren X, et al. Electroacupuncture alters pain-related behaviors and expression of spinal prostaglandin E_2 in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Tradit Chin Med 2016; 36: 85-91.
DOI URL |
| 28. |
Roh DH, Yoon SY, Seo HS, et al. Intrathecal injection of carbenoxolone, a gap junction decoupler, attenuates the induction of below-level neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Neurol 2010; 224: 123-32.
DOI URL |
| 29. | Rivlin AS, Tator CH. Objective clinical assessment of motor function after experimental spinal cord injury in the rat. J Neurosurg 1977; 47: 577-81. |
| 30. | Li MJ, Liu LY, Chen L, et al. Chronic stress exacerbates neuropathic pain via the integration of stress-affect-related information with nociceptive information in the central nucleus of the amygdala. Pain 2017; 158: 717-39. |
| 31. | Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, et al. Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 1994; 53: 55-63. |
| 32. |
Vissers K, Meert T. A behavioral and pharmacological validation of the acetone spray test in gerbils with a chronic constriction injury. Anesth Analg 2005; 101: 457-64.
DOI PMID |
| 33. | Chen J, Joshi SK, DiDomenico S, et al. Selective blockade of TRPA1 channel attenuates pathological pain without altering noxious cold sensation or body temperature regulation. Pain 2011; 152: 1165-72. |
| 34. | Park CH, Kim HW, Rhyu IJ, et al. How to get well-preserved samples for transmission electron microscopy. J Vis Exp 2016; 46: 188-92. |
| 35. |
Güldner FH, Ingham CA. Increase in postsynaptic density material in optic target neurons of the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus after bilateral enucleation. Neurosci Lett 1980; 17: 27-31.
DOI PMID |
| 36. |
Jones DG, Devon RM. An ultrastructural study into the effects of pentobarbitone on synaptic organization. Brain Res 1978; 147: 47-63.
PMID |
| 37. | Wu Q, Yue J, Lin L, et al. Electroacupuncture may alleviate neuropathic pain via suppressing P2X7R expression. Mol Pain 2021; 17: 1744806921997654. |
| 38. |
Peng B, Lin J, Shang Y, et al. Plasticity in the synaptic number associated with neuropathic pain in the rat spinal dorsal horn: a stereological study. Neurosci Lett 2010; 486: 24-8.
DOI PMID |
| 39. | Xu Q, Liu T, Chen S, et al. The cumulative analgesic effect of repeated electroacupuncture involves synaptic remodeling in the hippocampal CA 3 region. Neural Regen Res 2012; 7: 1378-85. |
| 40. | Luo H, Li Y, Shi X, et al. Ginsenoside Rd improves behavioral impairment of rats with acute plateau status by modulating synaptic plasticity. Chin Herb Med 2019; 11: 438-41. |
| 41. | Chen LC, Lin ZG, Chen SQ, et al. Effect of Dianan massage on expression of PKC and P2X3 in dorsal root ganglion of CCI rats. Fu Jian Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2020; 54: 291-4. |
| 42. | Lin ZG, Wang JZ, Zhao D, et al. Effects of kneading manipulation method of massage on gait and gastrocnemius of rats with chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2020; 35: 927-31. |
| 43. |
Osikowicz M, Mika J, Przewlocka B. The glutamatergic system as a target for neuropathic pain relief. Exp Physiol 2013; 98: 372-84.
DOI PMID |
| 44. |
Sung B, Lim G, Mao J. Altered expression and uptake activity of spinal glutamate transporters after nerve injury contribute to the pathogenesis of neuropathic pain in rats. J Neurosci 2003; 23: 2899-910.
PMID |
| 45. | Kawasaki Y, Zhang L, Cheng JK, et al. Cytokine mechanisms of central sensitization: distinct and overlapping role of interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-α in regulating synaptic and neuronal activity in the superficial spinal cord. J Neurosci 2008; 28: 5189-94. |
| 46. |
Guo W, Wang H, Watanabe M, et al. Glial-cytokine-neuronal interactions underlying the mechanisms of persistent pain. J Neurosci 2007; 27: 6006-18.
PMID |
| 47. |
Deng M, Chen SR, Pan HL. Presynaptic NMDA receptors control nociceptive transmission at the spinal cord level in neuropathic pain. Cell Mol Life Sci 2019; 76: 1889-99.
DOI PMID |
| 48. | Gao YH, Chen SP, Wang JY, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture at different acupoints on the pain behavior and NMDA receptor 2 B subunit mRNA and protein expression and phosphorylation level in the cervical spinal cord in rats with thyroid regional pain. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu 2009; 34: 376-82. |
| 49. |
D'Mello R, Marchand F, Pezet S, et al. Perturbing PSD-95 interactions with NR2B-subtype receptors attenuates spinal nociceptive plasticity and neuropathic pain. Mol Ther 2011; 19: 1780-92.
DOI PMID |
| 50. | Lin TB, Lai CY, Hsieh MC, et al. Neuropathic allodynia involves spinal neurexin-1β-dependent neuroligin-1/postsynaptic density-95/NR2B cascade in rats. Anesthesiology 2015; 123: 909-26. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

