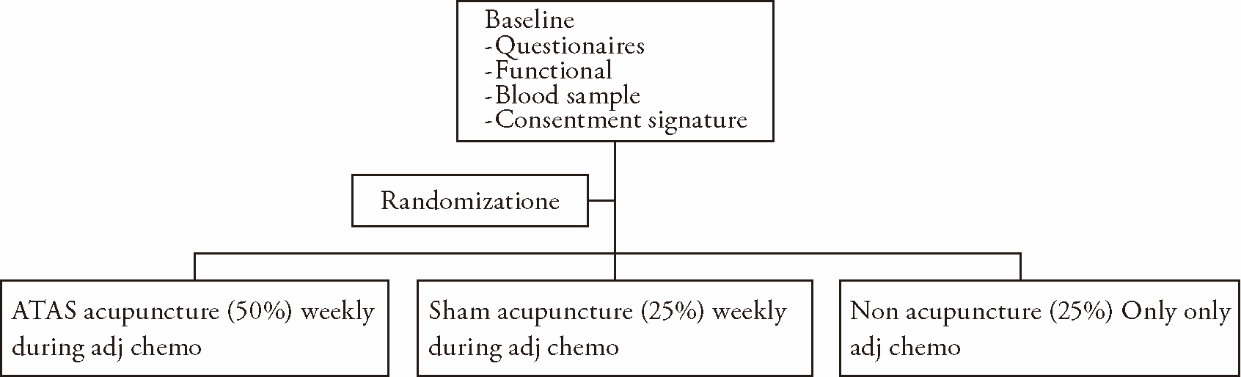
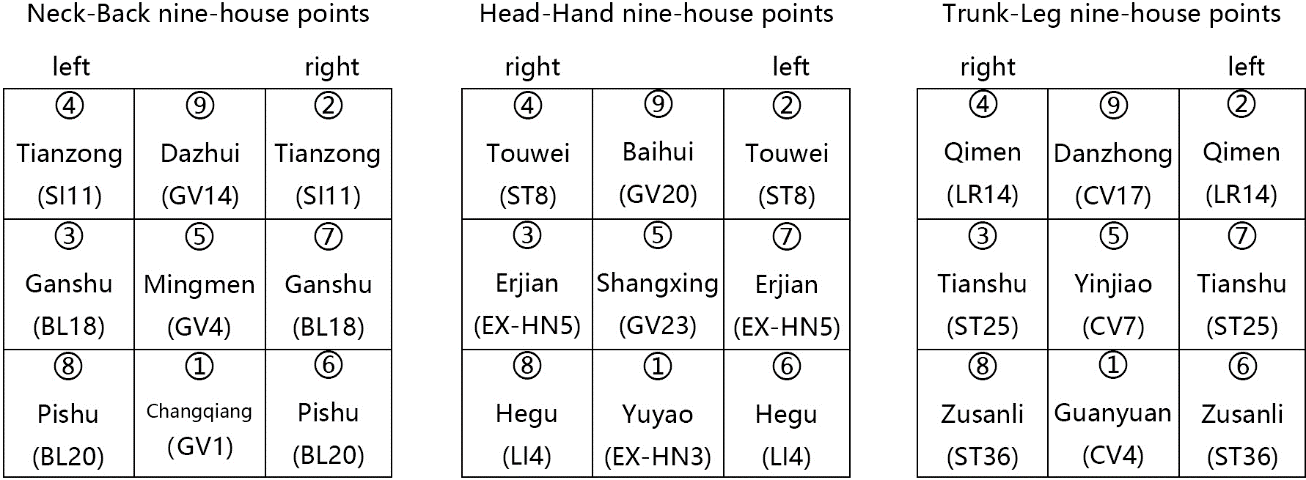
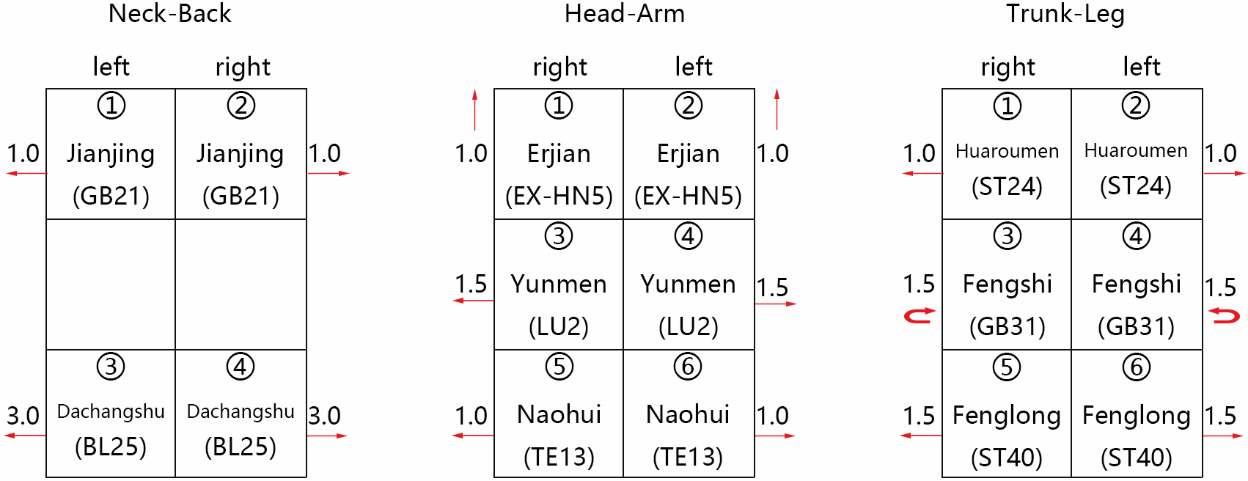
| [1] |
LI Menghan, WANG Yu, RAN Dawei, YANG Xinming, DENG Shizhe, SHI Lei, MENG Zhihong.
Effects of anterior sciatic nerve acupuncture on lower limb paralysis after cerebral infarction: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 205-211.
|
| [2] |
LI Chaoran, YANG Yan, FENG Chuwen, LI Heng, QU Yuanyuan, WANG Yulin, WANG Delong, WANG Qingyong, GUO Jing, SHI Tianyu, SUN Xiaowei, WANG Xue, HOU Yunlong, SUN Zhongren, YANG Tiansong.
Integrated 'omics analysis for the gut microbiota response to moxibustion in a rat model of chronic fatigue syndrome
[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1176-1189.
|
| [3] |
DAI Zeqi, LIAO Xing, GUAN Yueyue, ZENG Zixiu, TANG Jun, HU Jing.
Bloodletting puncture in the treatment of acute ischemic stroke: protocol for a mixed-method study of a multi-center randomized controlled trial and focus group
[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(6): 1259-1267.
|
| [4] |
YANG Yuqing, CHEN Yuhuan, LI Chunxiao, LING Xiao, WANG Panpan, GUO Jing, ZHANG Yingying.
Effectiveness and safety of Pingxiao capsule (平消胶囊) as adjuvant therapy in treatment of breast cancer: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 851-859.
|
| [5] |
TANG Wenjuan, HU Yu, ZHU Man, DONG Mingzhi, LIU Tieming, SARWAR Ammar, ZHAN Yingzhuan, ZHANG Yanmin.
Pingxiao capsule (平消胶囊) inhibits lung metastasis of triple-negative breast cancer and sensitizes breast cancer to radiotherapy
[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 897-905.
|
| [6] |
GUO Ziliang, QIAN Qingyuan, LI Xiaolin, ZHU Yuting, REN Jun, LI Maoxing.
Efficacy of verbascoside, echinacoside, crenatoside on altitude-induced fatigue in rats and possible mechanism
[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 934-943.
|
| [7] |
YOU Jianyu, LI Haiyan, XIE Dingyi, CHEN Mingren, CHEN Rixin.
Efficacy of acupuncture therapy for post-stroke fatigue: a systematic review and Meta-analysis
[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(1): 27-33.
|
| [8] |
ZHOU Ziyi, WAN Can, ZHAO Yuanqi, LIU Xiangzhe, GAO Ying, AN Hongwei, LI Lejun, ZHANG Huili, YU Xiaofei, ZHANG Xinchun, WANG Huijuan, SHI Qing, WEI Chunhua, CHEN Jie, HUANG Wenguo, CHEN Junbin, GAO Ying, HU Mingzhe, CAI Yefeng.
Efficacy and safety of a sequential treatment with clearing heat and eliminating phlegm and tonifying Qi and activating blood circulation in treating acute ischemic stroke: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(4): 604-610.
|
| [9] |
LIU Ying, ZOU Wen, XIAN Qingfei, DENG Xin, ZHANG Fuchun, WANG Li, LI Yonghong, LUN Wenhui, WANG Jian.
Efficacy and safety of Mianyi granules (+mianyi+) for reversal of immune nonresponse following antiretroviral therapy of human immunodeficiency virus-1: a randomized, double-blind, multi-center, placebo-controlled trial
[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(3): 432-438.
|
| [10] |
MA Tingting, WU Jie, YANG Lijie, FENG Fen, YANG Huilin, ZHANG Jinhua, ZHONG Yanjin, NING Qing, HUANG Lirong, LIN Youbing, YAN Jue, CHEN Guiquan, HOU Tianshu, WANG Li, REN Yuanfang, TAN Jing.
Ginger-indirect moxibustion plus acupuncture versus acupuncture alone for chronic fatigue syndrome: a randomized controlled trial
[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 242-249.
|
| [11] |
WEI Meng, LI Yu, XIONG Chan, LIU Yefang, LIANG Fanrong, MAO Bing, MIAO Tiwei, HUANG Ying, ZHU Yijing, FU Juanjuan.
Mechanisms of immune regulation for acupuncture on chronic respiratory diseases
[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 42(2): 314-320.
|
| [12] |
ZHU Manjing, XIE Su, XIE Qing, ZHU Jiulong, HUANG Yazhen.
Effecacy of Biejia(Carapax Trionycis) and Ezhu(Rhizoma Curcumae Phaeocaulis) couplet medicine on epithelial-mesenchymal transition, invasion and migration of MDA-MB-231 triple negative breast cancer cells via PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(6): 853-861.
|
| [13] |
ZHAO Shuai, TAN Jun, YU Hengmei, TIAN Ying, WU Youfang, LUO Rui, GUO Jianjun.
In vivo and in vitro antiproliferative and antimetastatic effects of hemolymph of Aspongopus chinensis Dallas on breast cancer cells
[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(4): 523-529.
|
| [14] |
ZHANG Zhouji, ZHANG Ming, WU Xiaoting, CUI Qing, GUO Yijun.
Zhengyuan capsule(正元胶囊)for the treatment of cancer-related fatigue in lung cancer patients undergoing operation:a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(3): 485-490.
|
| [15] |
Zhang Ning, Zhou Chao, Wang Lifu, He Tingting, Wang Yao, Wang Yan, Bai Yunfeng, Li Jun, Xiao Xiaohe, Gong Man.
Effectiveness and safety of Chinese herbal medicines for hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure: study protocol for a multicenter randomized controlled trial
[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(6): 1052-1059.
|
 ), Jean-Pierre Armand1, ZHU Miansheng7, JU Liya5(
), Jean-Pierre Armand1, ZHU Miansheng7, JU Liya5( )
)