Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1414-1422.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.06.019
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Adjuvant therapy with Traditional Chinese Medicine and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a retrospective cohort study
SHANG Chang1,2,3, LIU Ping1,2,3, HAN Junge1,2,3, ZENG Shuanghui1,2,3, WANG Yue1,2,3, HAN Mei1,2,3, SUN Luying1,2,3( )
)
- 1 Department of Nephropathy and Endocrine, Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 100010, China
2 Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine Metabolic Disease Research Center, Fangshan Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 102400, China
3 Center for Evidence-Based Chinese Medicine, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 102488, China
-
Received:2024-11-25Accepted:2025-03-20Online:2025-12-15Published:2025-11-24 -
Contact:Prof. SUN Luying, Fangshan Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 102400, China. luyingsun@outlook.com, Telephone: +86-10-69314293 -
About author:SHANG Chang and LIU Ping are co-first authors and contributed equally to this work -
Supported by:Industry-University-Research Collaborative Project: the Clinical and Basic Research on Liuzi Yangshen Formula in Preventing and Treating Renal Tubular Injury(HX-DZM-202501)
Cite this article
SHANG Chang, LIU Ping, HAN Junge, ZENG Shuanghui, WANG Yue, HAN Mei, SUN Luying. Adjuvant therapy with Traditional Chinese Medicine and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a retrospective cohort study[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1414-1422.
share this article

Figure 1 Flowchart of patient screening MMC: the metabolic management center; HbA1c: glycated hemoglobin; T1DM: type 1 diabetes mellitus; T2DM: type 2 diabetes mellitus; TCM: Traditional Chinese Medicine.
| Characteristics | Non-TCM (n = 139) | TCM (n = 441) | P value | SMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 57.00 (50.00, 63.00) | 59.00 (51.00, 67.00) | 0.013a | 0.247 |
| Gender [n (%)] | 0.694 | 0.038 | ||
| Male | 67 (48.2) | 221 (50.1) | ||
| Female | 72 (51.8) | 220 (49.9) | ||
| Level of education [n (%)] | 0.321 | 0.097 | ||
| Below high school | 57 (41.0) | 202 (45.8) | ||
| High school or above | 82 (59.0) | 239 (54.2) | ||
| Family history of T2DM [n (%)] | 57 (41.0) | 185 (42.0) | 0.844 | 0.019 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.60 (24.20, 28.60) | 26.60 (24.50, 29.35) | 0.449 | 0.091 |
| Waist (cm) | 93.50 (87.00, 98.50) | 94.50 (88.40, 101.00) | 0.117 | 0.141 |
| VFA (cm2) | 109.00 (85.00, 132.00) | 112.00 (82.50, 140.00) | 0.322 | 0.097 |
| Duration of T2DM (years) | 7.00 (2.00, 14.00) | 7.00 (2.00, 14.00) | 0.526 | 0.013 |
| Tobacco smoking [n (%)] | 0.317 | 0.152 | ||
| No | 108 (77.7) | 322 (73.0) | ||
| Occasionally | 10 (7.2) | 27 (6.1) | ||
| Daily or almost daily | 21 (15.1) | 92 (20.9) | ||
| Alcohol drinking [n (%)] | 0.185 | 0.177 | ||
| No | 93 (66.9) | 287 (65.1) | ||
| Occasionally | 28 (20.1) | 115 (26.1) | ||
| Weekly or almost weekly | 18 (12.9) | 39 (8.8) | ||
| Hypertension [n (%)] | 80 (57.6) | 295 (66.9) | 0.045a | 0.194 |
| Hyperlipidemia [n (%)] | 87 (62.6) | 303 (68.7) | 0.180 | 0.129 |
| CHD [n (%)] | 30 (21.6) | 103 (23.4) | 0.665 | 0.042 |
| Stroke [n (%)] | 6 (4.3) | 26 (5.9) | 0.477 | 0.072 |
| Fatty liver [n (%)] | 30 (21.6) | 100 (22.7) | 0.788 | 0.026 |
| DPN [n (%)] | 45 (32.4) | 136 (30.8) | 0.733 | 0.033 |
| DR [n (%)] | 41 (29.5) | 99 (22.4) | 0.090 | 0.161 |
| Use of antihyperglycemic drug [n (%)] | 0.332 | 0.180 | ||
| None | 15 (10.8) | 65 (14.7) | ||
| OADs | 62 (44.6) | 213 (48.3) | ||
| Insulin | 6 (4.3) | 20 (4.5) | ||
| OADs+insulin | 56 (40.3) | 143 (32.4) | ||
| FPG (mmol/L) | 8.23 (6.74, 10.68) | 8.06 (6.80, 10.03) | 0.840 | 0.038 |
| C peptide (ng/mL) | 2.17 (1.33, 3.08) | 2.21 (1.43, 3.25) | 0.539 | 0.107 |
| ALT (U/L) | 22.00 (15.00, 36.00) | 21.00 (15.00, 30.50) | 0.160 | 0.141 |
| AST (U/L) | 20.00 (17.00, 28.00) | 20.00 (17.00, 25.00) | 0.333 | 0.172 |
| BUN (mmol/L) | 5.36 (4.51, 6.37) | 5.39 (4.46, 6.46) | 0.726 | 0.027 |
| Cr (μmol/L) | 71.00 (59.00, 84.00) | 73.00 (62.85, 85.00) | 0.354 | 0.085 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.53 (0.98, 2.56) | 1.50 (1.03, 2.18) | 0.451 | 0.134 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.83 (3.81, 5.59) | 4.69 (3.79, 5.53) | 0.511 | 0.070 |
| HDL-c (mmol/L) | 1.19 (1.01, 1.44) | 1.20 (1.05, 1.41) | 0.561 | 0.054 |
| LDL-c (mmol/L) | 3.14 (2.37, 3.60) | 2.90 (2.25, 3.61) | 0.515 | 0.064 |
Table 1 Baseline characteristics in the two groups before PS-matching
| Characteristics | Non-TCM (n = 139) | TCM (n = 441) | P value | SMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 57.00 (50.00, 63.00) | 59.00 (51.00, 67.00) | 0.013a | 0.247 |
| Gender [n (%)] | 0.694 | 0.038 | ||
| Male | 67 (48.2) | 221 (50.1) | ||
| Female | 72 (51.8) | 220 (49.9) | ||
| Level of education [n (%)] | 0.321 | 0.097 | ||
| Below high school | 57 (41.0) | 202 (45.8) | ||
| High school or above | 82 (59.0) | 239 (54.2) | ||
| Family history of T2DM [n (%)] | 57 (41.0) | 185 (42.0) | 0.844 | 0.019 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.60 (24.20, 28.60) | 26.60 (24.50, 29.35) | 0.449 | 0.091 |
| Waist (cm) | 93.50 (87.00, 98.50) | 94.50 (88.40, 101.00) | 0.117 | 0.141 |
| VFA (cm2) | 109.00 (85.00, 132.00) | 112.00 (82.50, 140.00) | 0.322 | 0.097 |
| Duration of T2DM (years) | 7.00 (2.00, 14.00) | 7.00 (2.00, 14.00) | 0.526 | 0.013 |
| Tobacco smoking [n (%)] | 0.317 | 0.152 | ||
| No | 108 (77.7) | 322 (73.0) | ||
| Occasionally | 10 (7.2) | 27 (6.1) | ||
| Daily or almost daily | 21 (15.1) | 92 (20.9) | ||
| Alcohol drinking [n (%)] | 0.185 | 0.177 | ||
| No | 93 (66.9) | 287 (65.1) | ||
| Occasionally | 28 (20.1) | 115 (26.1) | ||
| Weekly or almost weekly | 18 (12.9) | 39 (8.8) | ||
| Hypertension [n (%)] | 80 (57.6) | 295 (66.9) | 0.045a | 0.194 |
| Hyperlipidemia [n (%)] | 87 (62.6) | 303 (68.7) | 0.180 | 0.129 |
| CHD [n (%)] | 30 (21.6) | 103 (23.4) | 0.665 | 0.042 |
| Stroke [n (%)] | 6 (4.3) | 26 (5.9) | 0.477 | 0.072 |
| Fatty liver [n (%)] | 30 (21.6) | 100 (22.7) | 0.788 | 0.026 |
| DPN [n (%)] | 45 (32.4) | 136 (30.8) | 0.733 | 0.033 |
| DR [n (%)] | 41 (29.5) | 99 (22.4) | 0.090 | 0.161 |
| Use of antihyperglycemic drug [n (%)] | 0.332 | 0.180 | ||
| None | 15 (10.8) | 65 (14.7) | ||
| OADs | 62 (44.6) | 213 (48.3) | ||
| Insulin | 6 (4.3) | 20 (4.5) | ||
| OADs+insulin | 56 (40.3) | 143 (32.4) | ||
| FPG (mmol/L) | 8.23 (6.74, 10.68) | 8.06 (6.80, 10.03) | 0.840 | 0.038 |
| C peptide (ng/mL) | 2.17 (1.33, 3.08) | 2.21 (1.43, 3.25) | 0.539 | 0.107 |
| ALT (U/L) | 22.00 (15.00, 36.00) | 21.00 (15.00, 30.50) | 0.160 | 0.141 |
| AST (U/L) | 20.00 (17.00, 28.00) | 20.00 (17.00, 25.00) | 0.333 | 0.172 |
| BUN (mmol/L) | 5.36 (4.51, 6.37) | 5.39 (4.46, 6.46) | 0.726 | 0.027 |
| Cr (μmol/L) | 71.00 (59.00, 84.00) | 73.00 (62.85, 85.00) | 0.354 | 0.085 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.53 (0.98, 2.56) | 1.50 (1.03, 2.18) | 0.451 | 0.134 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.83 (3.81, 5.59) | 4.69 (3.79, 5.53) | 0.511 | 0.070 |
| HDL-c (mmol/L) | 1.19 (1.01, 1.44) | 1.20 (1.05, 1.41) | 0.561 | 0.054 |
| LDL-c (mmol/L) | 3.14 (2.37, 3.60) | 2.90 (2.25, 3.61) | 0.515 | 0.064 |
| Characteristics | Non-TCM (n = 133) | TCM (n = 239) | P value | SMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years old) | 57.00 (50.00, 63.50) | 58.00 (50.00, 66.00) | 0.286 | 0.091 |
| Gender [n (%)] | 0.746 | 0.035 | ||
| Male | 65 (48.9) | 121 (50.6) | ||
| Female | 68 (51.1) | 118 (49.4) | ||
| Level of education [n (%)] | 0.420 | 0.087 | ||
| Below high school | 56 (42.1) | 111 (46.4) | ||
| High school or above | 77 (57.9) | 128 (53.6) | ||
| Family history of T2DM [n (%)] | 54 (40.6) | 102 (42.7) | 0.697 | 0.042 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.60 (24.20, 28.70) | 26.50 (24.30, 29.00) | 0.914 | 0.034 |
| Waist (cm) | 93.66 ± 9.52 | 94.40 ± 9.34 | 0.466 | 0.079 |
| VFA (cm2) | 109.00 (84.50, 132.50) | 112.00 (79.00, 136.00) | 0.588 | 0.041 |
| Duration of T2DM (years) | 7.00 (2.50, 13.50) | 8.00 (2.00, 15.00) | 0.891 | 0.035 |
| Tobacco smoking [n (%)] | 0.740 | 0.085 | ||
| No | 102 (76.7) | 175 (73.2) | ||
| Occasionally | 10 (7.5) | 19 (7.9) | ||
| Daily or almost daily | 21 (15.8) | 45 (18.8) | ||
| Alcohol drinking [n (%)] | 0.971 | 0.026 | ||
| No | 89 (66.9) | 157 (65.7) | ||
| Occasionally | 28 (21.1) | 52 (21.8) | ||
| Weekly or almost weekly | 16 (12.0) | 30 (12.6) | ||
| Hypertension [n (%)] | 78 (58.6) | 145 (60.7) | 0.703 | 0.041 |
| Hyperlipidemia [n (%)] | 83 (62.4) | 150 (62.8) | 0.946 | 0.007 |
| CHD [n (%)] | 28 (21.1) | 50 (20.9) | 0.976 | 0.003 |
| Stroke [n (%)] | 6 (4.5) | 12 (5.0) | 0.826 | 0.024 |
| Fatty liver [n (%)] | 28 (21.1) | 53 (22.2) | 0.801 | 0.027 |
| DPN [n (%)] | 43 (32.3) | 71 (29.7) | 0.599 | 0.057 |
| DR [n (%)] | 38 (28.6) | 63 (26.4) | 0.646 | 0.050 |
| Use of antihyperglycemic drug [n (%)] | 0.991 | 0.035 | ||
| None | 15 (11.3) | 25 (10.5) | ||
| OADs | 59 (44.4) | 109 (45.6) | ||
| Insulin | 6 (4.5) | 10 (4.2) | ||
| OADs+insulin | 53 (39.8) | 95 (39.7) | ||
| FPG (mmol/L) | 8.16 (6.74, 10.50) | 8.06 (6.90, 9.98) | 0.773 | 0.002 |
| C peptide (ng/mL) | 2.17 (1.25, 3.07) | 2.03 (1.36, 3.05) | 0.976 | 0.040 |
| ALT (U/L) | 22.00 (15.00, 36.00) | 21.00 (16.00, 31.00) | 0.502 | 0.063 |
| AST (U/L) | 20.00 (16.50, 27.50) | 20.00 (17.00, 26.00) | 0.814 | 0.069 |
| BUN (mmol/L) | 5.38 (4.52, 6.38) | 5.39 (4.48, 6.62) | 0.711 | 0.044 |
| Cr (μmol/L) | 71.00 (62.00, 84.00) | 73.00 (62.00, 86.00) | 0.450 | 0.092 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.51 (0.97, 2.43) | 1.55 (1.08, 2.20) | 0.485 | 0.032 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.81 (3.81, 5.50) | 4.82 (3.82, 5.60) | 0.706 | 0.031 |
| HDL-c (mmol/L) | 1.19 (1.03, 1.45) | 1.20 (1.04, 1.38) | 0.905 | 0.010 |
| LDL-c (mmol/L) | 3.12 (2.37, 3.58) | 2.95 (2.28, 3.69) | 0.785 | 0.025 |
Table 2 Baseline characteristics in the two groups after PS-matching
| Characteristics | Non-TCM (n = 133) | TCM (n = 239) | P value | SMD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years old) | 57.00 (50.00, 63.50) | 58.00 (50.00, 66.00) | 0.286 | 0.091 |
| Gender [n (%)] | 0.746 | 0.035 | ||
| Male | 65 (48.9) | 121 (50.6) | ||
| Female | 68 (51.1) | 118 (49.4) | ||
| Level of education [n (%)] | 0.420 | 0.087 | ||
| Below high school | 56 (42.1) | 111 (46.4) | ||
| High school or above | 77 (57.9) | 128 (53.6) | ||
| Family history of T2DM [n (%)] | 54 (40.6) | 102 (42.7) | 0.697 | 0.042 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 26.60 (24.20, 28.70) | 26.50 (24.30, 29.00) | 0.914 | 0.034 |
| Waist (cm) | 93.66 ± 9.52 | 94.40 ± 9.34 | 0.466 | 0.079 |
| VFA (cm2) | 109.00 (84.50, 132.50) | 112.00 (79.00, 136.00) | 0.588 | 0.041 |
| Duration of T2DM (years) | 7.00 (2.50, 13.50) | 8.00 (2.00, 15.00) | 0.891 | 0.035 |
| Tobacco smoking [n (%)] | 0.740 | 0.085 | ||
| No | 102 (76.7) | 175 (73.2) | ||
| Occasionally | 10 (7.5) | 19 (7.9) | ||
| Daily or almost daily | 21 (15.8) | 45 (18.8) | ||
| Alcohol drinking [n (%)] | 0.971 | 0.026 | ||
| No | 89 (66.9) | 157 (65.7) | ||
| Occasionally | 28 (21.1) | 52 (21.8) | ||
| Weekly or almost weekly | 16 (12.0) | 30 (12.6) | ||
| Hypertension [n (%)] | 78 (58.6) | 145 (60.7) | 0.703 | 0.041 |
| Hyperlipidemia [n (%)] | 83 (62.4) | 150 (62.8) | 0.946 | 0.007 |
| CHD [n (%)] | 28 (21.1) | 50 (20.9) | 0.976 | 0.003 |
| Stroke [n (%)] | 6 (4.5) | 12 (5.0) | 0.826 | 0.024 |
| Fatty liver [n (%)] | 28 (21.1) | 53 (22.2) | 0.801 | 0.027 |
| DPN [n (%)] | 43 (32.3) | 71 (29.7) | 0.599 | 0.057 |
| DR [n (%)] | 38 (28.6) | 63 (26.4) | 0.646 | 0.050 |
| Use of antihyperglycemic drug [n (%)] | 0.991 | 0.035 | ||
| None | 15 (11.3) | 25 (10.5) | ||
| OADs | 59 (44.4) | 109 (45.6) | ||
| Insulin | 6 (4.5) | 10 (4.2) | ||
| OADs+insulin | 53 (39.8) | 95 (39.7) | ||
| FPG (mmol/L) | 8.16 (6.74, 10.50) | 8.06 (6.90, 9.98) | 0.773 | 0.002 |
| C peptide (ng/mL) | 2.17 (1.25, 3.07) | 2.03 (1.36, 3.05) | 0.976 | 0.040 |
| ALT (U/L) | 22.00 (15.00, 36.00) | 21.00 (16.00, 31.00) | 0.502 | 0.063 |
| AST (U/L) | 20.00 (16.50, 27.50) | 20.00 (17.00, 26.00) | 0.814 | 0.069 |
| BUN (mmol/L) | 5.38 (4.52, 6.38) | 5.39 (4.48, 6.62) | 0.711 | 0.044 |
| Cr (μmol/L) | 71.00 (62.00, 84.00) | 73.00 (62.00, 86.00) | 0.450 | 0.092 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.51 (0.97, 2.43) | 1.55 (1.08, 2.20) | 0.485 | 0.032 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 4.81 (3.81, 5.50) | 4.82 (3.82, 5.60) | 0.706 | 0.031 |
| HDL-c (mmol/L) | 1.19 (1.03, 1.45) | 1.20 (1.04, 1.38) | 0.905 | 0.010 |
| LDL-c (mmol/L) | 3.12 (2.37, 3.58) | 2.95 (2.28, 3.69) | 0.785 | 0.025 |
| Item | Good glycemic control | Poor glycemic control | OR (95% CI) | P value | aOR (95% CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 275 (47.4) | 305 (52.6) | ||||
| No-TCM use | 47 (17.1) | 92 (30.2) | 1.00 | , | 1.00 | - |
| TCM use | 228 (82.9) | 213 (69.8) | 0.48 (0.32, 0.71) | <0.001a | 0.47 (0.30, 0.73) | 0.001a |
| Number of cases after PSM | 163 (43.8) | 209 (56.2) | ||||
| No-TCM use | 47 (28.8) | 86 (41.1) | , | , | 1.00 | - |
| TCM use | 116 (71.2) | 123 (58.9) | , | , | 0.60 (0.39, 0.92) | 0.021a |
Table 3 Association between adjuvant TCM therapy and glycemic control among T2DM patients [n (%)]
| Item | Good glycemic control | Poor glycemic control | OR (95% CI) | P value | aOR (95% CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 275 (47.4) | 305 (52.6) | ||||
| No-TCM use | 47 (17.1) | 92 (30.2) | 1.00 | , | 1.00 | - |
| TCM use | 228 (82.9) | 213 (69.8) | 0.48 (0.32, 0.71) | <0.001a | 0.47 (0.30, 0.73) | 0.001a |
| Number of cases after PSM | 163 (43.8) | 209 (56.2) | ||||
| No-TCM use | 47 (28.8) | 86 (41.1) | , | , | 1.00 | - |
| TCM use | 116 (71.2) | 123 (58.9) | , | , | 0.60 (0.39, 0.92) | 0.021a |
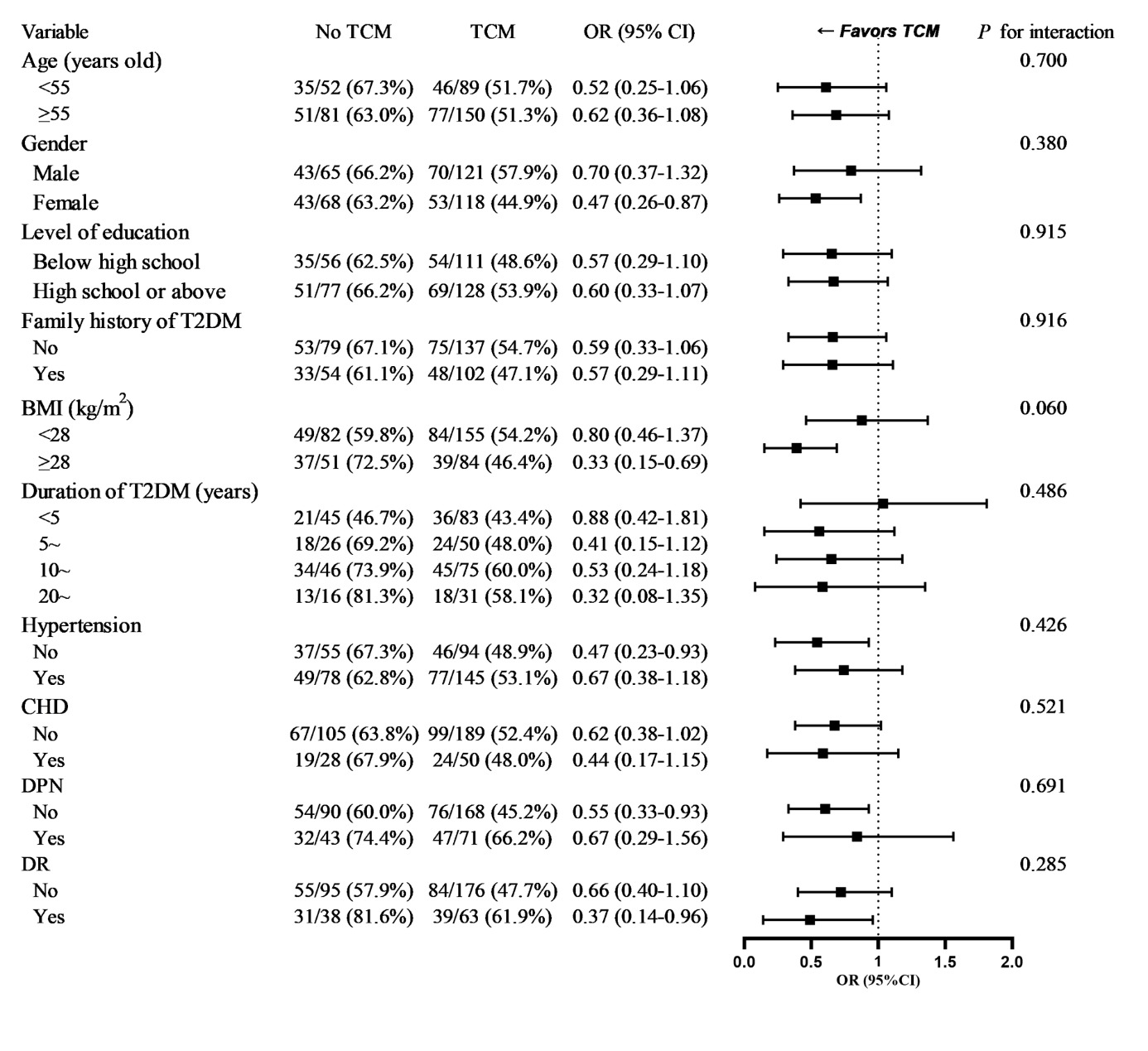
Figure 2 Subgroup analysis evaluating the association between adjuvant TCM therapy and glycemic control BMI: body mass index; CHD: coronary heart disease; CI: confidence interval; DPN: diabetic peripheral neuropathy; DR: diabetic retinopathy; OR: odds ratio; T2DM: type 2 diabetes mellitus; TCM: Traditional Chinese Medicine.
| Item | Good glycemic control | Poor glycemic control | OR (95% CI) | P value | aOR (95% CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 275 (47.4) | 305 (52.6) | ||||
| No-TCM use | 47 (17.1) | 92 (30.2) | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| TCM use, by TCM modalities | ||||||
| CHM alone | 93 (33.8) | 89 (29.2) | 0.49 (0.31, 0.77) | 0.002a | 0.45 (0.27, 0.75) | 0.002a |
| NDT alone | 56 (20.4) | 55 (18.0) | 0.50 (0.30, 0.84) | 0.008a | 0.56 (0.32, 0.99) | 0.047a |
| CHM+NDT | 79 (28.7) | 69 (22.6) | 0.45 (0.28, 0.72) | 0.001a | 0.43 (0.25, 0.74) | 0.002a |
Table 4 Association between different TCM modalities and glycemic control among T2DM patients [n (%)]
| Item | Good glycemic control | Poor glycemic control | OR (95% CI) | P value | aOR (95% CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | 275 (47.4) | 305 (52.6) | ||||
| No-TCM use | 47 (17.1) | 92 (30.2) | 1.00 | - | 1.00 | - |
| TCM use, by TCM modalities | ||||||
| CHM alone | 93 (33.8) | 89 (29.2) | 0.49 (0.31, 0.77) | 0.002a | 0.45 (0.27, 0.75) | 0.002a |
| NDT alone | 56 (20.4) | 55 (18.0) | 0.50 (0.30, 0.84) | 0.008a | 0.56 (0.32, 0.99) | 0.047a |
| CHM+NDT | 79 (28.7) | 69 (22.6) | 0.45 (0.28, 0.72) | 0.001a | 0.43 (0.25, 0.74) | 0.002a |
| 1. |
Ahmad E, Lim S, Lamptey R, Webb DR, Davies MJ. Type 2 diabetes. Lancet 2022; 400: 1803-20.
DOI PMID |
| 2. | International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas, 10th edn online, 2021-12-06, cited 2024-06-07: 5. Available from URL https://wwwdiabetesatlasorg. |
| 3. |
Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2018; 14: 88-98.
DOI PMID |
| 4. | Tu WJ, Xue Y, Nie D. The prevalence and treatment of diabetes in China from 2013 to 2018. JAMA 2022; 327: 1706. |
| 5. |
Zhang Y, Wang W, Ning G. Metabolic management center: an innovation project for the management of metabolic diseases and complications in China. J Diabetes 2019; 11: 11-13.
DOI PMID |
| 6. | Hu J, Zhang F, Li XM, et al. Practice and benefit of national standardized management of type 2 diabetes in Yulin city. Xi'an Jiao Tong Da Xue Xue Bao (Yi Xue Ban) 2023; 44: 836-40. |
| 7. |
Chen YK, Liu TT, Teia FKF, Xie MZ. Exploring the underlying mechanisms of obesity and diabetes and the potential of Traditional Chinese Medicine: an overview of the literature. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2023; 14: 1218880.
DOI URL |
| 8. | Tan Y, Liu S, Huang M, et al. Efficacy and safety of Gegen Qinlian decoction in the treatment of type II diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2023; 14: 1316269. |
| 9. |
Zhang Z, Leng Y, Fu X, et al. The efficacy and safety of dachaihu decoction in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Front Pharmacol 2022; 13: 918681.
DOI URL |
| 10. |
Amatto PPG, Chaves L, Braga GG, Carmona F, Pereira AMS. Effect of Crocus sativus L. (saffron) and crocin in the treatment of patients with type-2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Ethnopharmacol 2024; 319: 117255.
DOI URL |
| 11. | Hong KF, Liu PY, Zhang W, Gui DK, Xu YH. The efficacy and safety of astragalus as an adjuvant treatment for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Integr Complement Med 2024; 30: 11-24. |
| 12. |
Wang Y, Xu GN, Wan RH, et al. Acupuncture in treating obesity combined with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials. Complement Ther Clin Pract 2022; 49: 101658.
DOI URL |
| 13. |
Franklin JM, Pawar A, Martin D, et al. Nonrandomized real-world evidence to support regulatory decision making: process for a randomized trial replication project. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2020; 107: 817-26.
DOI PMID |
| 14. |
Song S, Yanhong Z, Hongyang G, et al. Effectiveness of acupoint application of Xiaozhong Zhitong Tie on diarrhea in patients: a retrospective cohort study in China. J Tradit Chin Med 2023; 43: 809-14.
DOI |
| 15. | Zhou Q, Liu J, Xin L, et al. Association between Traditional Chinese Medicine and osteoarthritis outcome: a 5-year matched cohort study. Heliyon 2024; 10: e26289. |
| 16. |
American Diabetes Association Professional Practice C. 6. Glycemic targets: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022; 45: S83-96.
DOI PMID |
| 17. | Leng Y, Zhou X, Xie Z, et al. Efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine on blood glucose fluctuations in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a protocol of systematic review and Meta-analysis Medicine (Baltimore) 2020; 99: e21904. |
| 18. | Ahmadi S, Rafiey H, Sajjadi H, et al. Trend and pattern of using herbal medicines among people who are aware of their diabetes mellitus: results from National STEPs surveys in 2005 to 2011 in Iran. J Diabetes Metab Disord 2021; 20: 1319-25. |
| 19. |
Ryuk JA, Lixia M, Cao S, Ko BS, Park S. Efficacy and safety of Gegen Qinlian decoction for normalizing hyperglycemia in diabetic patients: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Complement Ther Med 2017; 33: 6-13.
DOI PMID |
| 20. |
Vuksan V, Xu ZZ, Jovanovski E, et al. Efficacy and safety of American ginseng (Panax quinquefolius L.) extract on glycemic control and cardiovascular risk factors in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a double-blind, randomized, cross-over clinical trial. Eur J Nutr 2019; 58: 1237-45.
DOI PMID |
| 21. |
Yang L, Yao D, Yang H, et al. Puerarin protects pancreatic beta-cells in obese diabetic mice via activation of GLP-1R signaling. Mol Endocrinol 2016; 30: 361-71.
DOI PMID |
| 22. | Li X, Geng-Ji JJ, Quan YY, et al. Role of potential bioactive metabolites from Traditional Chinese Medicine for type 2 diabetes mellitus: an overview. Front Pharmacol 2022; 13: 1023713. |
| 23. | Zhu Z, Yu M, Xu M, et al. Baicalin suppresses macrophage JNK-mediated adipose tissue inflammation to mitigate insulin resistance in obesity. J Ethnopharmacol 2024; 332: 118355. |
| 24. | Zhang X, Jia L, Ma Q, et al. Astragalus polysaccharide modulates the gut microbiota and metabolites of patients with type 2 diabetes in an in vitro fermentation model. Nutrients 2024; 16: 1698. |
| 25. |
Liu J, Yao C, Wang Y, Zhao J, Luo H. Non-drug interventions of Traditional Chinese Medicine in preventing type 2 diabetes: a review. Chin Med 2023; 18: 151.
DOI |
| 26. | Chen C, Liu J, Sun M, Liu W, Han J, Wang H. Acupuncture for type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement Ther Clin Pract 2019; 36: 100-12. |
| 27. | Chao M, Wang C, Dong X, Ding M. The effects of Tai Chi on type 2 diabetes mellitus: a Meta-analysis. J Diabetes Res 2018; 2018: 7350567. |
| 28. | Wang XZ, Jin FY, Wang XD. The effects of Tai Chi on glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with diabetes mellitus: a Meta-analysis. Complement Ther Med 2022; 71: 102871. |
| 29. | Wang Y, Yan J, Zhang P, Yang P, Zhang W, Lu M. Tai Chi program to improve glucose control and quality of life for the elderly with type 2 diabetes: a Meta-analysis. Inquiry 2022; 59: 469580211067934. |
| 30. |
Zhang Y, Lin Y, Zhang J, et al. Association between insomnia and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Han Chinese individuals in Shandong province, China. Sleep Breath 2019; 23: 349-54.
DOI PMID |
| 31. |
Sommers T, Mitsuhashi S, Singh P, et al. Prevalence of chronic constipation and chronic diarrhea in diabetic individuals in the United States. Am J Gastroenterol 2019; 114: 135-42.
DOI PMID |
| 32. | Ding C, Zhang J, Lau ESH, et al. Gender differences in the associations between insomnia and glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study. Sleep 2019; 42: zsz014. |
| 33. |
Suarez-Torres I, Garcia-Garcia F, Morales-Romero J, et al. Poor quality of sleep in Mexican patients with type 2 diabetes and its association with lack of glycemic control. Prim Care Diabetes 2023; 17: 155-60.
DOI URL |
| 34. |
Sondrup N, Termannsen AD, Eriksen JN, et al. Effects of sleep manipulation on markers of insulin sensitivity: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Sleep Med Rev 2022; 62: 101594.
DOI URL |
| 35. |
Maloney A, Kanaley JA. Short sleep duration disrupts glucose metabolism: can exercise turn back the clock? Exerc Sport Sci Rev 2024; 52: 77-86.
DOI PMID |
| 36. |
Wei L, Ji L, Miao Y, et al. Constipation in DM are associated with both poor glycemic control and diabetic complications: current status and future directions. Biomed Pharmacother 2023; 165: 115202.
DOI URL |
| 37. |
Su Q, Wang L, Yu H, Li H, Zou D, Ni X. Chinese herbal medicine and acupuncture for insomnia in stroke patients: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Sleep Med 2024; 120: 65-84.
DOI PMID |
| 38. |
Yan L, Liu H, Yan R, Tan L, Tan J, Lei Y. Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine external therapy for functional constipation: a Meta-analysis. Am J Transl Res 2023; 15: 13-26.
PMID |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

