Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1040-1047.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.05.010
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effect of Jiegeng (Radix Platycodi) on Jingjie (Herba Schizonepetae Tenuifoliae) “Yin-Jing” into the lungs based on pharmacokinetics
ZHANG Yuanmei1,2, LIU Heqing1,2, WANG Shaowen1,2, WANG Lele1,2, GAO Yawen1,2, SUN Rui1,2, TANG Jihui1,2( )
)
- 1 School of Pharmacy, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, China
2 Inflammation and Immune Mediated Diseases Laboratory of Anhui Province, Anhui Institute of Innovative Drugs, Research and Industrialization of New Drug Release Technology Joint Laboratory of Anhui Province, School of Pharmacy, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, China
-
Received:2024-09-02Accepted:2025-01-13Online:2025-10-15Published:2025-09-15 -
Contact:Prof. TANG Jihui, School of Pharmacy, Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230032, China. tangjh@ahmu.edu.cn,Telephone: +86-551-65161176 -
Supported by:Key Laboratory of Xin’an Medicine Open Project Fund (Anhui University of Chinese Medicine) Ministry of Education: Study on the Material Basis and Mechanism of the Buoyance of Jingjie (Herba Schizonepetae Tenuifoliae) Loaded with Jiegeng (Radix Platycodi) of Traditional Chinese Medicine(2020xayx02);Drug Regulatory Scientific Research Key Project: Establishment of a New Dissolution Method Based on Drug Absorption and its Application in Drug Quality Monitoring (AHYJ-KJ-202206, Central of Regulatory Science for Medical Products, Anhui Province);Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Anhui Province of China: to Explore the Effect and Mechanism of Immune Escape Nanopreparation Based on "Dont eat me" Signal on Tumor Photodynamic Therapy(2308085MH308)
Cite this article
ZHANG Yuanmei, LIU Heqing, WANG Shaowen, WANG Lele, GAO Yawen, SUN Rui, TANG Jihui. Effect of Jiegeng (Radix Platycodi) on Jingjie (Herba Schizonepetae Tenuifoliae) “Yin-Jing” into the lungs based on pharmacokinetics[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(5): 1040-1047.
share this article
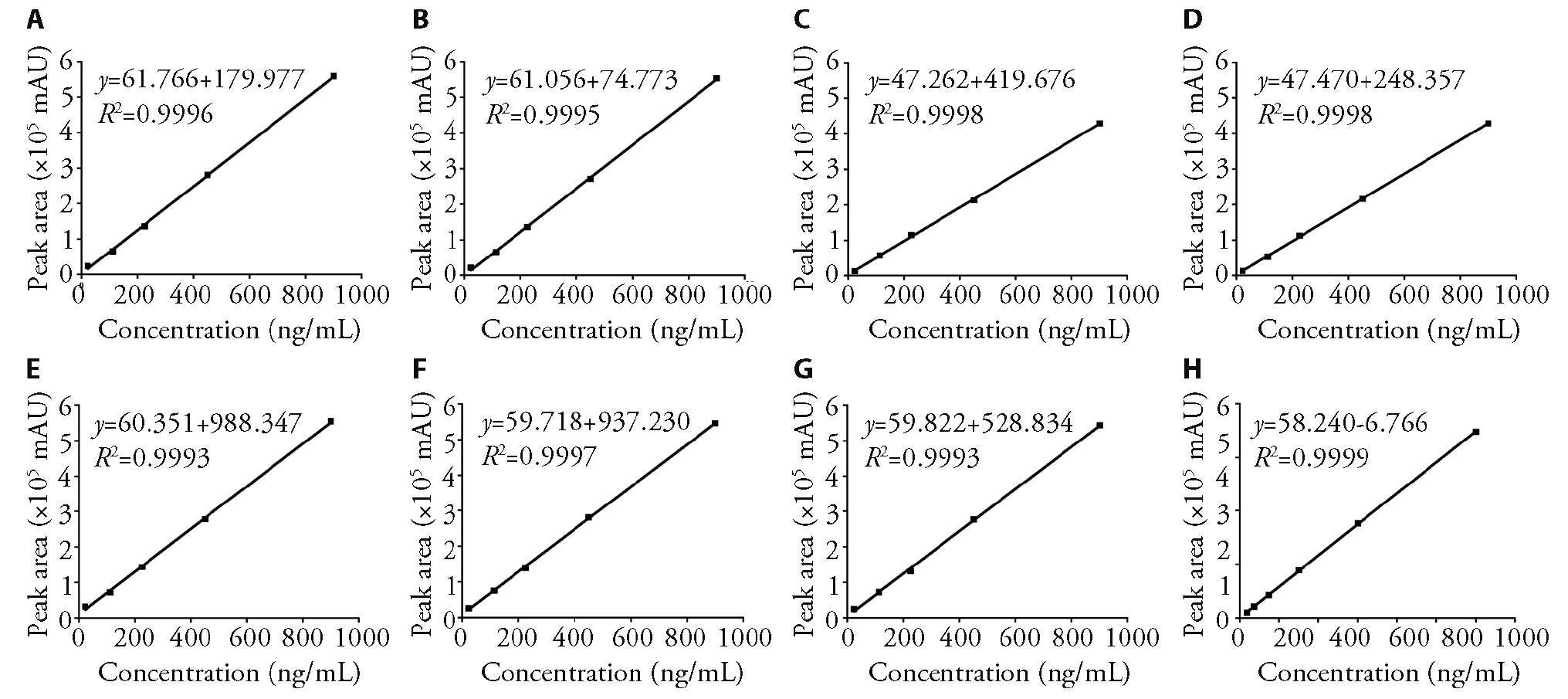
Figure 1 Representative chromatograms of rat heart, liver, spleen, lungs, kidneys, small intestine, testicles plasma and blank blood with after the addition of pulegone A: rat heart; B: rat liver; C: rat spleen; D: rat lungs; E: rat kidneys; F: rat small intestine; G: rat testicles plasma; H: rat blank blood.
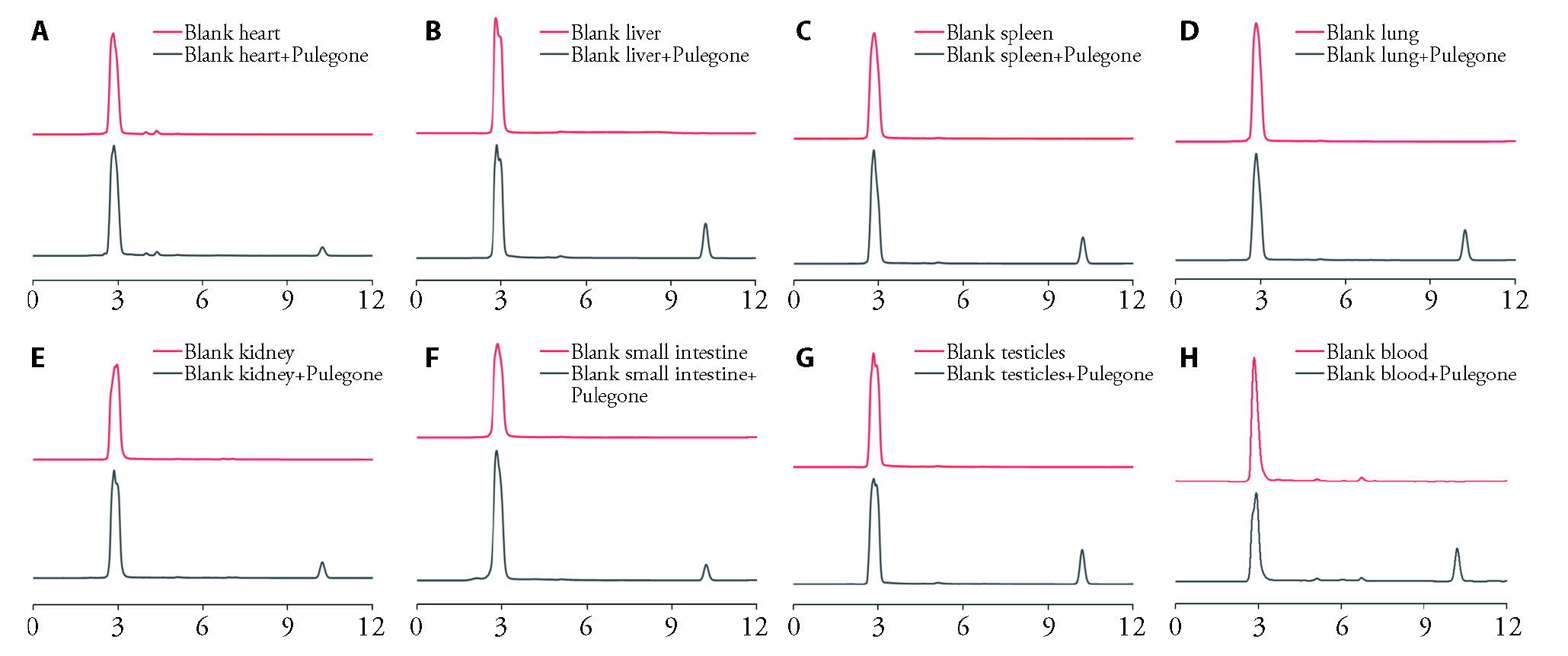
Figure 2 Summary of standard curves, correlation coefficients, and linear ranges for pulegone A: rat heart; B: rat liver; C: rat spleen; D: rat lungs; E: rat kidneys; F: rat small intestine; G: rat testicles plasma; H: rat blood.
| Tissue | Concentration (ng/mL) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Heart | 22.5 | 104.2±10.2 |
| 225.0 | 94.9±9.6 | |
| 900.0 | 89.4±3.3 | |
| Liver | 22.5 | 96.6±10.7 |
| 225.0 | 85.2±5.6 | |
| 900.0 | 84.0±5.1 | |
| Spleen | 22.5 | 101.1±5.2 |
| 225.0 | 100.8±4.2 | |
| 900.0 | 104.5±3.8 | |
| Lung | 22.5 | 94.4±9.6 |
| 225.0 | 93.2±1.7 | |
| 900.0 | 101.7±1.7 | |
| Kindey | 22.5 | 102.7±9.6 |
| 225.0 | 110.5±6.8 | |
| 900.0 | 85.8±3.5 | |
| Small intestine | 22.5 | 104.3±7.1 |
| 225.0 | 83.1±1.4 | |
| 900.0 | 88.2±6.3 | |
| Testicles | 22.5 | 97.3±1.4 |
| 225.0 | 109.2±1.9 | |
| 900.0 | 86.7±5.0 | |
| Blood | 187.5 | 97.0±1.6 |
| 750.0 | 107.1±2.1 | |
| 3000.0 | 97.9±3.5 |
Table 1 Sample recoveries of high, medium, and low pulegone concentrations in various tissues and plasma (n = 3, x - ± s)
| Tissue | Concentration (ng/mL) | Recovery (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Heart | 22.5 | 104.2±10.2 |
| 225.0 | 94.9±9.6 | |
| 900.0 | 89.4±3.3 | |
| Liver | 22.5 | 96.6±10.7 |
| 225.0 | 85.2±5.6 | |
| 900.0 | 84.0±5.1 | |
| Spleen | 22.5 | 101.1±5.2 |
| 225.0 | 100.8±4.2 | |
| 900.0 | 104.5±3.8 | |
| Lung | 22.5 | 94.4±9.6 |
| 225.0 | 93.2±1.7 | |
| 900.0 | 101.7±1.7 | |
| Kindey | 22.5 | 102.7±9.6 |
| 225.0 | 110.5±6.8 | |
| 900.0 | 85.8±3.5 | |
| Small intestine | 22.5 | 104.3±7.1 |
| 225.0 | 83.1±1.4 | |
| 900.0 | 88.2±6.3 | |
| Testicles | 22.5 | 97.3±1.4 |
| 225.0 | 109.2±1.9 | |
| 900.0 | 86.7±5.0 | |
| Blood | 187.5 | 97.0±1.6 |
| 750.0 | 107.1±2.1 | |
| 3000.0 | 97.9±3.5 |
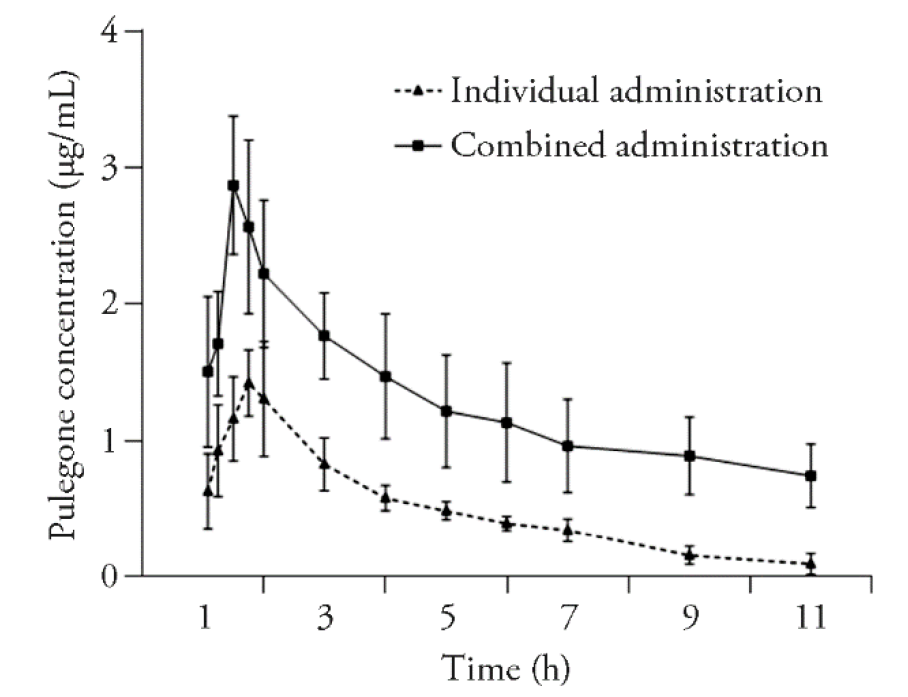
Figure 3 Blood concentration-time profiles of pulegone after individual and combined administration Individual administration: SD rats were treated with the volatile oil and aqueous extract of ST. Combined administration: SD rats were treated with the volatile oil and aqueous extract of ST and aqueous extract of RP. Pulegone 300 mg/kg, ST aqueous extract 852 mg/kg and RP aqueous extract 443 mg/kg. Statistical analyses were measured using Student’s t-test for two groups. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation (n = 6). SD: Sprague-Dawley; ST: Jingjie (Herba Schizonepetae Tenuifoliae); RP: Jiegeng (Radix Platycodi).
| Parameter | Individual administration | Combined administration |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax (mg/L) | 1.82±0.45 | 2.76±0.52 |
| Tmax (h) | 0.81±0.10 | 0.55±0.11 |
| T1/2 (h) | 3.21±0.97 | 5.85±2.40 |
| AUC0→10 (mg·L?1·h?1) | 5.35±0.78 | 12.55±2.87 |
| AUC0→∞ (mg·L?1·h?1) | 31.80±8.65 | 122.86±36.65 |
| CL (L·h?1·kg?1) | 48.74±7.23 | 19.20±5.97 |
| MRT (h) | 3.38±0.21 | 3.86±0.26 |
| Ke (h?1) | 0.23±0.06 | 0.13±0.04 |
Table 2 Pharmacokinetic parameters after administration of pulegone alone and in combination (n = 6, x - ± s)
| Parameter | Individual administration | Combined administration |
|---|---|---|
| Cmax (mg/L) | 1.82±0.45 | 2.76±0.52 |
| Tmax (h) | 0.81±0.10 | 0.55±0.11 |
| T1/2 (h) | 3.21±0.97 | 5.85±2.40 |
| AUC0→10 (mg·L?1·h?1) | 5.35±0.78 | 12.55±2.87 |
| AUC0→∞ (mg·L?1·h?1) | 31.80±8.65 | 122.86±36.65 |
| CL (L·h?1·kg?1) | 48.74±7.23 | 19.20±5.97 |
| MRT (h) | 3.38±0.21 | 3.86±0.26 |
| Ke (h?1) | 0.23±0.06 | 0.13±0.04 |
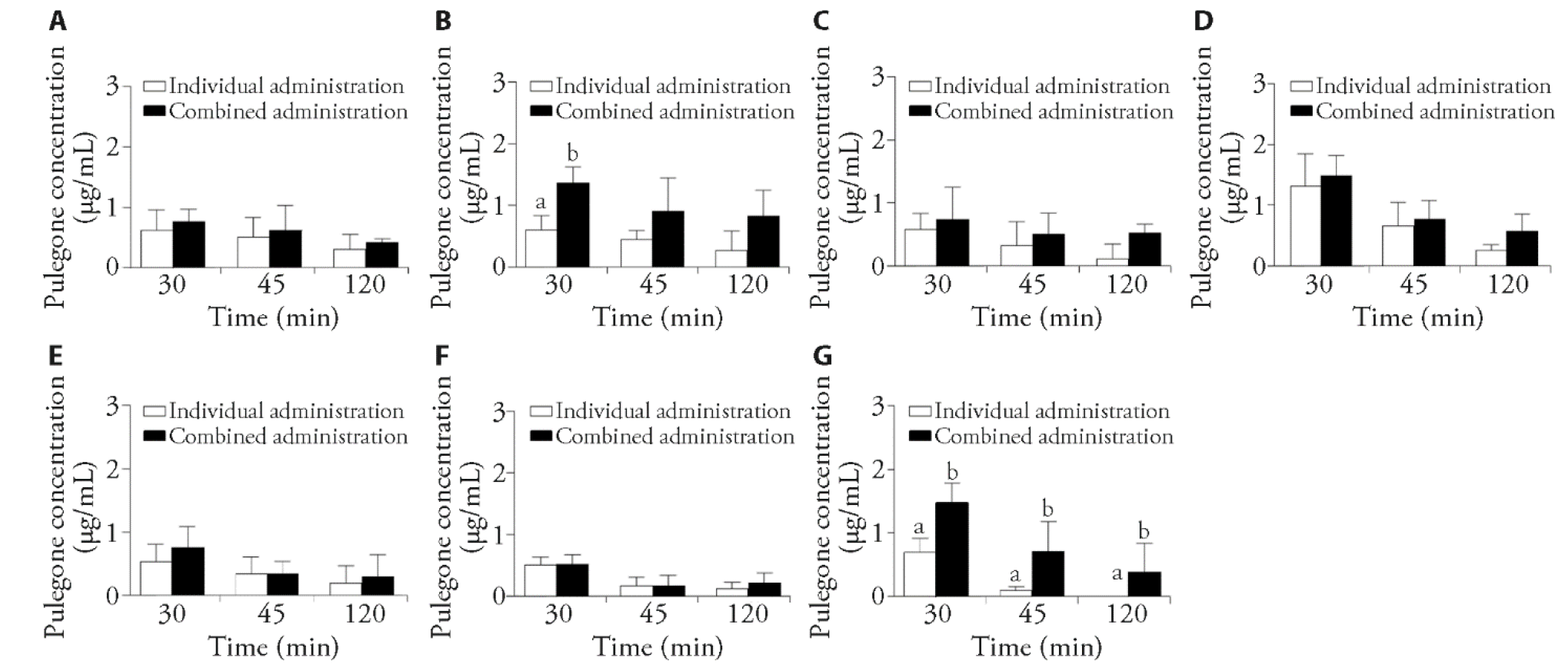
Figure 4 Concentration of pulegone in various tissues at 30, 45 and 120 min after administration of pulegone alone and in combination (n = 6, x - ± s) A: heart tissue; B: liver tissue; C: spleen tissue; D: kidney tissue; E: small intestine tissue; F: testicles tissue; G: lung tissue. Individual administration: SD rats were treated with the volatile oil and aqueous extract of ST. Combined administration: SD rats were treated with the volatile oil and aqueous extract of ST and aqueous extract of RP. Pulegone 300 mg/kg, ST aqueous extract 852 mg/kg and RP aqueous extract 443 mg/kg. SD: Sprague-Dawley; ST: Jingjie (Herba Schizonepetae Tenuifoliae); RP: Jiegeng (Radix Platycodi). Compared with combined administration, aP < 0.05; compared with individual administration, bP < 0.05, was considered statistically.
| 1. | Gao M, Ding ML lei ZQ, et al. Research progress of Jingfangbaidu powder and its Chinese patent medicine preparation. Zhong Yao Yao Li Yu Lin Chuang 2023; 39: 112-8. |
| 2. | Li MM, Yu HY, Zhou YD. Analyzing the characteristics and academic features of Xin'an medicine. Zhong Yi Xue Bao 2023; 38: 756-61. |
| 3. | Committee SP. Chinese Pharmacopoeia. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020: 243-5. |
| 4. | Yu X, Chai J, Kong X, Bai C, Liang J, Kuang H. Insight of "Yin-Jing" medical property of Ligusticum Chuanxiong Hort. via pharmacokinetics and tissue distributions by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry. J Ethnopharmacol 2023; 314: 116569. |
| 5. | Zhao X, Zhou M. Review on chemical constituents of Schizonepeta tenuifolia Briq. and their pharmacological effects. Molecules 2022; 27: 5249. |
| 6. | Zhang M. Ideas and methods of preventing and treating influenza with Traditional Chinese Medicine. Jinnan: Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016: 1-209. |
| 7. | Zhou K, Zhou T. Experience of clearing knots and eliminating carbuncle in treating acne. Liaoning Zhong Yi Yao Da Xue Xue Bao 2012; 14: 26-7. |
| 8. | Ye AJ, Shao H, Zhang BH, Yang LP. Clinical analysis of the use of proprietary Chinese medicines in Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China: Part I. Zhong Guo Yi Yuan Yong Yao Ping Jia Yu Fen Xi 2022; 22: 1517-21. |
| 9. |
Farzaei MH, Bahramsoltani R, Ghobadi A, Farzaei F, Najafi F. Pharmacological activity of Mentha longifolia and its phytoconstituents. J Tradit Chin Med 2017; 37: 710-20.
PMID |
| 10. | Lee YH, Wang CM, Liu PY, et al. Volatile Oils of Nepeta tenuifolia (Jing Jie) as an alternative medicine against multidrug-resistant pathogenic microbes. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol 2018; 2018: 8347403. |
| 11. |
Yu S, Chen Y, Zhang L, Shan M, Tang Y, Ding A. Quantitative comparative analysis of the bio-active and toxic constituents of leaves and spikes of Schizonepeta tenuifolia at different harvesting times. Int J Mol Sci 2011; 12: 6635-44.
DOI PMID |
| 12. | Guo C, Su Y, Wang H, Cao M, Diao N, Liu Z. A novel saponin liposomes based on the couplet medicines of Platycodon grandiflorum-Glycyrrhiza uralensis for targeting lung cancer. Drug Deliv 2022; 29: 2743-50. |
| 13. | Hu YZ, Bi ZL. An analysis of the pharmacological mechanism of priming in Traditional Chinese Medicine prescriptions. Xian Dai Zhong Yao Yan Jiu Yu Shi Jian 1997; 11: 63-4. |
| 14. | Shi C, Li Q, Zhang X. Platycodin D protects human fibroblast cells from premature senescence induced by H2O2 through improving mitochondrial biogenesis. Pharmacology 2020; 105: 598-608. |
| 15. | Kim T, Song I, Lee H, Lim J, Cho E. Platycodin D, a triterpenoid sapoinin from Platycodon grandiflorum, ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 2012; 50: 4254-9. |
| 16. |
Guo R, Zhao M, Liu H, et al. Uncovering the pharmacological mechanisms of Xijiao Dihuang decoction combined with Yinqiao powder in treating influenza viral pneumonia by an integrative pharmacology strategy. Biomed Pharmacother 2021; 141: 111676.
DOI PMID |
| 17. | Pan Y, Wang J, Hu J, et al. Characteristics and achievements of the Xin'an Medical School. Zhong Yi Yao Za zhi 2018; 5: 328-34. |
| 18. | Fan R, He HY, Tang T, Cui HJ. Long-term effects of Qingfei Paidu decoction (清肺排毒汤) in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 acute pneumonia after treatment:a protocol for systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Tradit Chin Med 2023; 43: 1068-71. |
| 19. | Wang YW, Wang J, Ye M. Ten famous Xin'an recipes. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2013; 28: 3600-5. |
| 20. | Nie D, Wang J, Wang X, et al. Study on medication characteristics and data mining of 464 cases of pulmonary diseases in Xinan Wang's internal medicine. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2019; 44: 2397-402. |
| 21. |
Flamini G, Cioni PL, Puleio R, Morelli I, Panizzi L. Antimicrobial activity of the essential oil of Calamintha nepeta and its constituent pulegone against bacteria and fungi. Phytother Res 1999; 13: 349-51.
DOI PMID |
| 22. |
Moorthy B, Madyastha P, Madyastha KM. Hepatotoxicity of pulegone in rats: its effects on microsomal enzymes, in vivo. Toxicology 1989; 55: 327-37.
PMID |
| 23. |
Chen LJ, Lebetkin EH, Burka LT. Comparative disposition of (R)-(+)-pulegone in B6C3F1 mice and F344 rats. Drug Metab Dispos 2003; 31: 892-9.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Khojasteh-Bakht SC, Chen W, Koenigs LL, Peter RM, Nelson SD. Metabolism of (R)-(+)-pulegone and (R)-(+)-menthofuran by human liver cytochrome P-450s: evidence for formation of a furan epoxide. Drug Metab Dispos 1999; 27: 574-80.
PMID |
| 25. | Fang L, Tang WK, Cheng HY, Li DW. Progress of the mechanism of action of Traditional Chinese Medicine in leading upward and its brain-targeted preparations. Zhong Cao Yao 2023; 54: 3312-21. |
| 26. | Steven LCT, Yi GX. Discussion on relevance and studies of prescription compatibility in Chinese medicine. Zhong Guo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2020; 27: 788-93. |
| 27. | Li ZH, Wang YW, Sun J. Appreciation of the characteristics of Wang key's medicines for the treatment of cold and flu. Guo Ji Zhong Yi Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2017; 29: 472-4. |
| 28. | Zhang W, Li M, Du W, et al. Tissue distribution and anti-lung cancer effect of 10-hydroxycamptothecin combined with Platycodonis Radix and Glycyrrhizae Radix et Rhizoma. Molecules 2019; 24: 2068. |
| 29. | Yan D, Ma B, Shi R, Wang T, Ma Y. Involvement of herb-herb interactions in the influences of Radix Scutellaria and Coptis Chinensis on the bioavailability of the anthraquinones form Rhei Rhizoma in rats. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 2015; 40: 103-10. |
| 30. | Mao Y, Peng L, Kang A, Xie T, Xu J. Influence of Jiegeng on pharmacokinetic properties of flavonoids and saponins in Gancao. Molecules 2017; 22: 1587. |
| 31. | Chen WC, Liang XY, Xie LY, et al. Comparative study on the pharmacokinetics of paeoniflorin, white peony root water extract, and Taohong Siwu decoction after oral administration in rats. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 2023; 48: 301-10. |
| 32. | Yin XY, Fang XM. A literature study on the historical changes in the efficacy and clinical application of platycodon grandiflorum. Zhong Hua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2021: 167-76. |
| 33. |
Xu C, Sun G, Yuan G, Wang R, Sun X. Effects of platycodin D on proliferation, apoptosis and PI3K/Akt signal pathway of human glioma U251 cells. Molecules 2014; 19: 21411-23.
DOI PMID |
| 34. | Li J, Wang S, Tian F, Zhang SQ, Jin H. Advances in pharmacokinetic mechanisms of transporter-mediated herb-drug interactions. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2022; 15: 1126. |
| 35. | Wu BL, Ling P, Gao Y. Regulation of hepatic CYP450 enzyme activity and mRNA expression in rats by aqueous extracts of Ziziphi jujuba, Polygonum multiflorum and Platycodon grandiflorum. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi 2011; 17: 235-9. |
| 36. | He XW, Li XY, Sun R. Progress in the study of chemical composition of mint based on efficacy and toxicity. Zhong Yao Xue 2011; 8: 746-9. |
| 37. | Li W, Qi Y, Wang Z. In vitro antitumor activity of Platycodonopsis saponins. Zhong Yao Yao Li Yu Lin Chuang 2009; 25: 37-40. |
| 38. |
Zhang L, Zhu L, Wang Y, et al. Characterization and quantification of major constituents of Xue Fu Zhu Yu by UPLC-DAD-MS/MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2012; 62: 203-9.
DOI PMID |
| 39. |
Nyakudya E, Jeong JH, Lee NK, Jeong YS. Platycosides from the Roots of Platycodon grandiflorum and Their Health Benefits. Prev Nutr Food Sci 2014; 19: 59-68.
DOI PMID |
| 40. | Shen F, Wu W, Zhang M, et al. Micro-PET imaging demonstrates 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl platycodigenin as an effective metabolite affects permeability of cell membrane and improves dosimetry of [18F]-phillygenin in lung tissue. Front Pharmacol 2019; 10: 1020. |
| 41. | Yau LF, Huang H, Tong TT, et al. Characterization of deglycosylated metabolites of platycosides reveals their biotransformation after oral administration. Food Chem 2022; 393: 133383. |
| 42. | Tang Z, Hou Y, Hu X, et al. Metabolite identification and pharmacokinetic study of platycodi radix (Jiegeng). Rsc Advances 2017; 7: 37459-66. |
| 43. | Zhang M, Ye L, Huang H, et al. Micelles self-assembled by 3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl latycodigenin enhance cell membrane permeability, promote antibiotic pulmonary targeting and improve anti-infective efficacy. J Nanobiotechnology 2020; 18: 140. |
| 44. | Lin LY, Li XC. Plasma pharmacokinetic studies on the rat plasma drug metabolism of hummermintone. pharmacognosy 2022; 34: 23-6. |
| [1] | LI Xiuyan, LUO Yuting, WANG Jinhui, DU Zhimin. Formulation, characterization and in vivo and in vitro evaluation of aloe-emodin-loaded solid dispersions for dissolution enhancement [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(1): 54-62. |
| [2] | Fan Wentao, Huang Yuwei, Wang Lisheng, Liao Weiguo, Li Zhou, Wu Yinai, Liao Fengyun, Yu Jianye, Liu Qiang. Effect of stimulating the acupoints Feishu (BL 13) and Dazhui (GV14) on transdermal uptake of sinapine thiocyanate in asthma gel [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 37(04): 503-509. |
| [3] | Abdullah Mohammed AI-Mohizea, Mohammad Raish, Abdul Ahad, Fahad Ibrahim AI-Jenoobi, Mohd Aftab Alam. Pharmacokinetic interaction of Acacia catechu with CYP1A substrate theophylline in rabbits [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 35(05): 588-593. |
| [4] | Wang Jiannong, Jiang Junjie, Xie Yanming, Wei Xu, Li Jianpeng, Duan Jingli, Xiong Xin. Effect of naringenin in Qianggu capsule on population pharmacokinetics in Chinese women with primary osteoporosis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 35(02): 141-153. |
| [5] | Wang Xiuli, Gao Wei, Sun Mao. Pharmacokinetic investigation on nteraction between hydrophilic lithospermic acid B and lipophilic tanshinone IIA in rats:an experimental study [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 35(02): 206-210. |
| [6] | Bai Jinxia, Han Jin, Chen Hongge, Shen Baode, Xu He, Dai Ling, Shen Chengying, Yuan Hailong. Daily administration times of Canhuang tablet based on a pharmacodynamic/pharmacokinetic model in jaundiced rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 35(01): 84-89. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

