Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (2): 322-328.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20221121.001
• Original articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Efficacy of electroacupunture at Zusanli (ST36) on jumping-injured muscle based on transcriptome sequencing and genes analysis
HAN Rui1, CHANG Junzhao2, LIU Qianqian1, LIU Haitao3, LI Junwei1( )
)
- 1 School of Physical Education and Sport, Henan University, Kaifeng 475001, China
2 Kidney Department, Xindu Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu 610500, China
3 Intensive Care Unit, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine; Diagnostics Faculty, the Third School of Clinical Medicine of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450053, China
-
Received:2022-01-11Accepted:2022-04-01Online:2023-04-15Published:2023-03-14 -
Contact:LI Junwei, Intensive Care Unit, the Third Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine; Diagnostics Faculty, the Third School of Clinical Medicine of Henan University of Chinese Medicine; Zhengzhou 450053, China. Zhongqihuang@163.com. Telephone: + 86-371- 22866474 -
Supported by:Science and Technology Department of Henan Province: Effect Mechanisms of Acupuncture to Promote the Repair of Injured Skeletal Muscle(212102310260);Study on the Relationship between Hspb7 Protein and JAK/STAT Pathway and Electroacupuncture Intervention in Muscle Injury based on mRNA-Seq Analysis(222102320072);Science and Technology Bureau of Kaifeng: the Effect of Platelet Plasma Injection on Patellar Tendon Fibrosis(2003006)
Cite this article
HAN Rui, CHANG Junzhao, LIU Qianqian, LIU Haitao, LI Junwei. Efficacy of electroacupunture at Zusanli (ST36) on jumping-injured muscle based on transcriptome sequencing and genes analysis[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(2): 322-328.
share this article

Figure 1 Ultra-microstructure of gastrocnemius muscle from four groups A-D: images of the group NC, JI, EA, and NEA, respectively (2.0 μM,× 2.5k). NC: normal control group; JI: jumping-induced muscle injury model group; EA: JI with electroacupuncture stimulation treatment group; NEA: JI with non-electroacupuncture stimulation group; black arrow: M line malalignment; white arrow: Z line malalignment; green arrow: swollen mitochondria; blue arrows: autophagosome; yellow arrows: mitochondrial vacuoles; red arrows: normal mitochondria with different shapes.

Figure 2 Targeting key genes of the jumping-injured muscle in response to electroacupuncture at Zusanli (ST36) A: MA plot showing differentially expressed mRNA level; B: Go annotation of differentially expressed genes; C: KEGG enrichment for differentially expressed genes; D: interaction network prediction of Hspb7 protein in rats. red dots: upregulated genes; green dots: downregulated genes. FPKM: fragments per kilobase million; FC: fold change; KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
| Gene ID | Gene Name | FDR | log2FC | Regulated (JI vs EA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSRNOG00000029079 | Hspb7 | 1.37E-99 | 1.558272 | up |
| ENSRNOG00000014815 | Myoz2 | 1.31E-47 | 1.041293 | up |
Table 1 Transcriptome analysis results of target genes
| Gene ID | Gene Name | FDR | log2FC | Regulated (JI vs EA) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSRNOG00000029079 | Hspb7 | 1.37E-99 | 1.558272 | up |
| ENSRNOG00000014815 | Myoz2 | 1.31E-47 | 1.041293 | up |
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'-3') | Product lengths (bp) | Tm (℃) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-GAPDH-S | CTGGAGAAACCTGCCAAGTATG | 138 | 60 | |
| R-GAPDH-A | GGTGGAAGAATGGGAGTTGCT | |||
| R-Hspb7-S | CGGGGGACAAGGAAACATCA | 182 | 60 | |
| R-Hspb7-A | CTGGTAGCTGGCACTTGTGA | |||
| R- Myoz2-S | GACTTCGAACGACTGCTGCTAAC | 164 | 60 | |
| R- Myoz2-A | TCTGACTCTGGCATAGTGACATCTT | |||
Table 2 Primer sequences of factors to improve regeneration and repair
| Primer name | Primer sequence (5'-3') | Product lengths (bp) | Tm (℃) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R-GAPDH-S | CTGGAGAAACCTGCCAAGTATG | 138 | 60 | |
| R-GAPDH-A | GGTGGAAGAATGGGAGTTGCT | |||
| R-Hspb7-S | CGGGGGACAAGGAAACATCA | 182 | 60 | |
| R-Hspb7-A | CTGGTAGCTGGCACTTGTGA | |||
| R- Myoz2-S | GACTTCGAACGACTGCTGCTAAC | 164 | 60 | |
| R- Myoz2-A | TCTGACTCTGGCATAGTGACATCTT | |||
| Group | n | Hspb7 | Myoz2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| JI | 3 | 1.00±0.28 | 1.00±0.84 |
| EA | 3 | 1.88±0.46a | 3.51±0.87a |
| P value | 0.048 | 0.023 |
Table 3 Effects of electroacupunture at Zusanli (ST36) on mRNA expressions of injured muscle ($\bar{x}\pm s$)
| Group | n | Hspb7 | Myoz2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| JI | 3 | 1.00±0.28 | 1.00±0.84 |
| EA | 3 | 1.88±0.46a | 3.51±0.87a |
| P value | 0.048 | 0.023 |
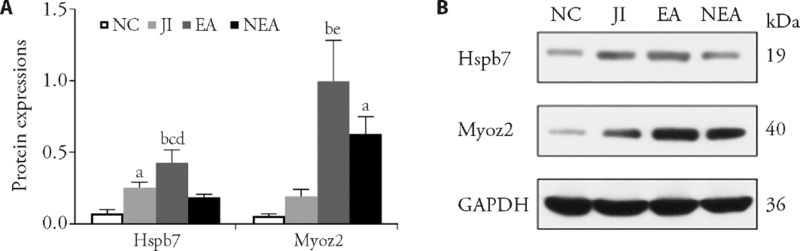
Figure 3 Expressions of target proteins in rats After confirming that transcriptome sequencing results are accurate and reliable, expressions of Hspb7 and Myoz2 proteins were detected in gastrocnemius. A: The fold change in relative expression of target proteins to the internal control protein was shown. Data are represented as the mean ± standard deviation for three experiments per group. Compared with the NC group, aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01; compared with the JI group, cP < 0.05, eP < 0.01; compared with the NEA group, dP < 0.05. B: Target protein bands were shown by using Western blotting. GAPDH used as an internal control. NC: normal control group; JI: jumping-induced muscle injury model group; EA: JI with electroacupuncture stimulation treatment group; NEA: JI with non-electroacupuncture stimulation group; Hspb7: heat shock protein beta-7; Myoz2: Myozenin2; GAPDH: glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
| 1. | Kim W, Kim J, Park HS, et al. Development of microfluidic stretch system for studying recovery of damaged skeletal muscle cells. Micromachines (Basel) 2018; 9: 671. |
| 2. |
Relaix F, Zammit PS. Satellite cells are essential for skeletal muscle regeneration: the cell on the edge returns centre stage. Development 2012; 139: 2845-56.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Brooks SV. Current topics for teaching skeletal muscle physiology. Adv Physiol Educ 2003; 27: 171-82.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Vickers AJ, Vertosick EA, Lewith G, et al. Acupuncture Trialists' Collaboration. Acupuncture for chronic pain: update of an individual patient data meta-analysis. J Pain 2018; 19: 455-74.
DOI PMID |
| 5. |
Bassett AJ, Ahlmen A, Rosendorf JM, et al. The biology of sex and sport. JBJS Rev 2020; 8: e0140.
DOI URL |
| 6. |
Cross KM, Gurka KK, Saliba S, et al. Comparison of thigh muscle strain occurrence and injury patterns between male and female high school soccer athletes. J Sport Rehabil 2018; 27: 451-9.
DOI PMID |
| 7. |
Ross JL, Queme LF, Lamb JE, et al. Sex differences in primary muscle afferent sensitization following ischemia and reperfusion injury. Biol Sex Differ 2018; 9: 2.
DOI PMID |
| 8. |
Liu H, Gao F, Liang X, et al. Pathogenesis and development of patellar tendon fibrosis in a rabbit overuse model. Am J Sports Med 2020; 48: 1141-50.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Laumonier T, Menetrey J. Muscle injuries and strategies for improving their repair. J Exp Orthop 2016; 3: 15.
DOI PMID |
| 10. |
Yin CS, Jeong HS, Park HJ, et al. A proposed transpositional acupoint system in a mouse and rat model. Res Vet Sci 2008; 84: 159 -65.
DOI PMID |
| 11. | Zou D, Chen Y, Liu T, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture at "Weizhong" (BL40) on morphology and expression of CK and IL-17 in rats with bupivacaine-induced multifidus muscle injury. Zhong Guo Zhen Jiu 2017; 37: 971-6. |
| 12. | Zhongren Li. Experimental acupuncture. 2nd ed. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2007: 206-11. |
| 13. |
Zininga T, Ramatsui L, Shonhai A. Heat shock proteins as immuno-modulants. Molecules 2018; 23: 2846.
DOI URL |
| 14. |
Mymrikov EV, Seit-Nebi AS, Gusev NB. Large potentials of small heat shock proteins. Physiol Rev 2011; 91: 1123-59.
DOI PMID |
| 15. |
Koike N, Hatano Y, Ushimaru T. Heat shock transcriptional factor mediates mitochondrial unfolded protein response. Curr Genet 2018; 64: 907-17.
DOI PMID |
| 16. |
Mymrikov EV, Seit-Nebi AS, Gusev NB. Large potentials of small heat shock proteins. Physiol Rev 2011; 91: 1123-59.
DOI PMID |
| 17. |
Kennedy D, Mnich K, Samali A. Heat shock preconditioning protects against ER stress-induced apoptosis through the regulation of the BH3-only protein BIM. FEBS Open Bio 2014; 4: 813-21.
DOI PMID |
| 18. |
Taylor RP, Benjamin IJ. Small heat shock proteins: a new classification scheme in mammals. J Mol Cell Cardiol 2005; 38: 433-44.
DOI PMID |
| 19. |
Muranova LK, Shatov VM, Bukach OV, et al. Cardio-vascular heat shock protein (cvHsp, HspB7), an unusual representative of small heat shock protein family. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2021; 86: S1-11.
DOI |
| 20. |
Jin C, Shuai T, Tang Z. HSPB7 regulates osteogenic differentiation of human adipose derived stem cells via ERK signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther 2020; 11: 450.
DOI |
| 21. |
Rüdebusch J, Benkner A, Poesch A, et al. Dynamic adaptation of myocardial proteome during heart failure development. PLoS One 2017; 12: e0185915.
DOI URL |
| 22. | Juo LY, Liao WC, Shih YL, et al. HSPB7 interacts with dimerized FLNC and its absence results in progressive myopathy in skeletal muscles. J Cell Sci 2016; 129: 1661-70. |
| 23. |
Wu T, Mu Y, Bogomolovas J, et al. HSPB7 is indispensable for heart development by modulating actin filament assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2017; 114: 11956-61.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Sun X, Li X, Jia H, et al. Effect of heat-shock protein B7 on oxidative stress in adipocytes from preruminant calves. J Dairy Sci 2019; 102: 5673-85.
DOI PMID |
| 25. |
Yin H, Price F, Rudnicki MA. Satellite cells and the muscle stem cell niche. Physiol Rev 2013; 93: 23-67.
DOI PMID |
| 26. |
Cosentino M, Musarò A. Mechanisms regulating muscle regeneration: insights into the interrelated and time-dependent phases of tissue healing. Cells 2020; 9: 1297.
DOI URL |
| 27. | Li YF, Zhu GY, Ma Y, et al. Expression and prognosis of MYOZ2 in gastric cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2018; 22: 5920-27. |
| 28. | Wu YQ, Li WX, Yang S, et al. Myoz2 promoted adipogenic differentiation of C3H10T1/2 Cells by negatively regulating the expression of TCAP. Zhong Guo Sheng Wu Hua Xue Yu Fen Zi Sheng Wu Xue Bao 2021; 37: 380-90. |
| 29. |
Wang H, Zhu Z, Wang H, et al. Characterization of different expression patterns of calsarcin-1 and calsarcin-2 in porcine muscle. Gene 2006; 374: 104-11.
PMID |
| 30. |
Hoffman A, Taleski G, Sontag E. The protein serine/threonine phosphatases PP2A, PP1 and calcineurin: a triple threat in the regulation of the neuronal cytoskeleton. Mol Cell Neurosci 2017; 84: 119-31.
DOI PMID |
| 31. |
La G, Zhou M, Lim JY, et al. Proteomics and transcriptomics analysis reveals clues into the mechanism of the beneficial effect of electrical stimulation on rat denervated gastrocnemius muscle. Cell Physiol Biochem 2019; 52: 769-86.
DOI PMID |
| 32. |
Lee FX, Houweling PJ, North KN, et al. How does α-actinin-3 deficiency alter muscle function? Mechanistic insights into ACTN3, the 'gene for speed'. Biochim Biophys Acta 2016; 1863: 686-93.
DOI PMID |
| 33. |
Wang YN, Yang WC, Li PW, et al. Myocyte enhancer factor 2A promotes proliferation and its inhibition attenuates myogenic differentiation via myozenin 2 in bovine skeletal muscle myoblast. PLoS One 2018; 13: e0196255.
DOI URL |
| [1] | ZHANG Qiongzhi, FU Tingting, DAI Jianing, ZHOU Zhinan, SHEN Cuizhen. Sodium Danshensu promotes the healing of stage 2 pressure injury wounds in ischemia/reperfusion injury rat models: possible regulation of apoptosis and inflammatory response [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(4): 571-580. |
| [2] | Chi Ho Lee, Jeong June Choi, Joo Hye Sim, Younmin Shin, Seung-Joon Oh, Ji-Hyang Gu, Hyun Ju Ha, Dong Hwi Jeon, Eun-Jung Lee, Min-Seok Oh. Gyejibokryeong-Hwan improves recovery of injured muscles in mouse model of muscle contusion [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(3): 406-413. |
| [3] | Guo Yan, Lu Juan, Liang Jingrong, Zhao Ruili, Xu Jing, Zhang Wei, Park Kibeum, Zhu Shipeng, Chen Huan, Ma Liangxiao. Effect of acupuncture at Renying(ST 9) on gene expression profile of hypothalamus in spontaneously hypertensive rats [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2018, 38(02): 227-241. |
| [4] | Wang Yili, Tian Yuanxiang, Zhao Jianxin, Xu Lei. Effect of electroacupuncture on gene expression in calcium signaling pathway in hippocampal cells in mice with cerebral ischemia reperfusion [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 37(02): 252-260. |
| [5] | Chen Longhui, Yang Zemin, Chen Weiwen, Li Ruliu, Lin Chuanquan, Guan Lihua, Zhu Zhangzhi, Chen Ruifang, Li Saimei, Zhao Lingbo, Zeng Jinhao, Wang Jianhua. Differential expression of immune-related genes between healthy volunteers and type 2 diabetic patients with spleen-deficiency pattern [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 35(06): 646-652. |
| [6] | Guo Yan, Xie Xiaojia, Guo Changqing, Wang Zhaoyang, Liu Qingguo. Effect of electro-acupuncture on gene expression in heart of rats with stress-induced pre-hypertension based on gene chip technology [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2015, 35(03): 285-294. |
| [7] | Bingbing Han, Shijun Wang, Lin Li, YuanWang, Haijun Zhao. Gene expression profiling of rat livers with Yin-deficiency-heat syndrome [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(03): 378-383. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

