Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1283-1294.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.06.008
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
New approach to overcoming antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus by combining Guanghuoxiang (Herba Pogostemonis) and Penicillin G Sodium treatments
JING Wenguang1, WANG Zhixia2, PI Wenmin2, WU Haonan1,3, LI Minghua1, WANG Penglong2, CHENG Xianlong1, WEI Feng4( )
)
- 1 National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, Beijing 100050, China
2 School of Chinese Pharmacy, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, Beijing 102488, China
3 Faculty of Functional Food and Wine, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang 110016, China
4 National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, Beijing 100050, China
-
Received:2025-04-12Accepted:2025-08-25Online:2025-12-15Published:2025-11-24 -
Contact:WEI Feng, National Institutes for Food and Drug Control, Beijing 100050, China. weifeng@nifdc.org.cn, Telephone: +86-18810035056 -
About author:JING Wenguang and WANG Zhixia are co-first authors and contributed equally to this work -
Supported by:State Key Laboratory of Drug Regulatory Science, Establishment of a Comprehensive Evaluation Method for the Quality of Chinese Medicinal Herbs Pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Benth. and Saposhnikovia divaricata (Turcz) Schischk., Suited to the Characteristics of Traditional Chinese Medicine(2023SKLDRS0101)
Cite this article
JING Wenguang, WANG Zhixia, PI Wenmin, WU Haonan, LI Minghua, WANG Penglong, CHENG Xianlong, WEI Feng. New approach to overcoming antimicrobial resistance of Staphylococcus aureus by combining Guanghuoxiang (Herba Pogostemonis) and Penicillin G Sodium treatments[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1283-1294.
share this article
| No. | Regression equation | R | Linear range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caryophyllene oxide | Y=858X+0.4682 | 0.9992 | 4.76-71.46 g/mL |
| Patchouli alcohol | Y=857.44X+1.0775 | 0.9990 | 4.73-94.64 g/mL |
| Pogostone | Y=2444.5X-5.1023 | 0.9991 | 3.39-50.82 g/mL |
Table 1 Regression equations and linear ranges of each control substance
| No. | Regression equation | R | Linear range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Caryophyllene oxide | Y=858X+0.4682 | 0.9992 | 4.76-71.46 g/mL |
| Patchouli alcohol | Y=857.44X+1.0775 | 0.9990 | 4.73-94.64 g/mL |
| Pogostone | Y=2444.5X-5.1023 | 0.9991 | 3.39-50.82 g/mL |
| No. | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caryophyllene oxide | 2471882 | 2639722 | 2507915 | 2596946 | 2470183 | 2305369 | 1.8203 |
| Patchouli alcohol | 3943481 | 4259755 | 4006344 | 4104033 | 3906534 | 3636020 | 1.7459 |
| Pogostone | 3767505 | 3904119 | 3843637 | 3899166 | 3657586 | 3453915 | 2.7115 |
Table 2 Precision experiment - peak area and peak area ratio RSD
| No. | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caryophyllene oxide | 2471882 | 2639722 | 2507915 | 2596946 | 2470183 | 2305369 | 1.8203 |
| Patchouli alcohol | 3943481 | 4259755 | 4006344 | 4104033 | 3906534 | 3636020 | 1.7459 |
| Pogostone | 3767505 | 3904119 | 3843637 | 3899166 | 3657586 | 3453915 | 2.7115 |
| No. | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caryophyllene oxide | 381858 | 423003 | 375939 | 414591 | 442563 | 538847 | 2.8961 |
| Patchouli alcohol | 13553868 | 15164488 | 13408770 | 14425733 | 15760117 | 18144196 | 2.9788 |
| Pogostone | 1926698 | 2319662 | 2103888 | 2171956 | 2402670 | 2825714 | 2.3107 |
Table 3 Repeatability experiment-peak area and peak area ratio RSD
| No. | S1 | S2 | S3 | S4 | S5 | S6 | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caryophyllene oxide | 381858 | 423003 | 375939 | 414591 | 442563 | 538847 | 2.8961 |
| Patchouli alcohol | 13553868 | 15164488 | 13408770 | 14425733 | 15760117 | 18144196 | 2.9788 |
| Pogostone | 1926698 | 2319662 | 2103888 | 2171956 | 2402670 | 2825714 | 2.3107 |
| No. | 0 h | 2 h | 4 h | 8 h | 12 h | 24 h | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caryophyllene oxide | 381858 | 442246 | 519094 | 698911 | 673852 | 739221 | 4.6254 |
| Patchouli alcohol | 14553868 | 16451970 | 18628266 | 25345087 | 26531630 | 25681622 | 4.9204 |
| Pogostone | 1926698 | 2433963 | 2955132 | 4118752 | 4058584 | 4030975 | 3.0018 |
Table 4 Stability experiment-peak area and peak area ratio RSD
| No. | 0 h | 2 h | 4 h | 8 h | 12 h | 24 h | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caryophyllene oxide | 381858 | 442246 | 519094 | 698911 | 673852 | 739221 | 4.6254 |
| Patchouli alcohol | 14553868 | 16451970 | 18628266 | 25345087 | 26531630 | 25681622 | 4.9204 |
| Pogostone | 1926698 | 2433963 | 2955132 | 4118752 | 4058584 | 4030975 | 3.0018 |
| No. | Average recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Caryophyllene oxide | 103.47% | 2.45% |
| Patchouli alcohol | 92.08% | 2.00% |
| Pogostone | 108.55% | 1.10% |
Table 5 Recovery experiment-average recovery and RSD
| No. | Average recovery (%) | RSD (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Caryophyllene oxide | 103.47% | 2.45% |
| Patchouli alcohol | 92.08% | 2.00% |
| Pogostone | 108.55% | 1.10% |
| Samples | Caryophyllene oxide (%) | Pogostone (%) | Patchouli alcohol (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCB-ZQ | 0.0483 | 0.0123 | 0.4904 |
| PCB-YJ | 0.0592 | 0.0277 | 0.7688 |
Table 6 Contents of caryophyllene oxide, pogostone and bactinol in Guanghuoxiang (Herba Pogostemonis) samples
| Samples | Caryophyllene oxide (%) | Pogostone (%) | Patchouli alcohol (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCB-ZQ | 0.0483 | 0.0123 | 0.4904 |
| PCB-YJ | 0.0592 | 0.0277 | 0.7688 |

Figure 1 Preliminary investigation of the antibacterial effect of Guanghuoxiang (Herba Pogostemonis) A: MIC test of Guanghuoxiang (Herba Pogostemonis) samples (n = 3); B: bacterial plate coating at MIC concentration, B1: control group; B2: PCB-ZQ; B3: PCB-YJ. C: Live/dead bacteria staining after treatment with Guanghuoxiang (Herba Pogostemonis) samples. (Scale bar: 80 μm), C1, C2, C3: control group; C4, C5, C6: PCB-ZQ; C7, C8, C9: PCB-YJ; D: bacterial morphology of Guanghuoxiang (Herba Pogostemonis) samples (scale bar: 1 μm); D1: control group; D2: PCB-ZQ; D3: PCB-YJ.

Figure 2 Removal effect of Guanghuoxiang (Herba Pogostemonis) samples on biofilm. A: The removal effect of Guanghuoxiang (Herba Pogostemonis) samples on biofilm was determined by XTT staining. B: Image of bacterial biofilm after XTT staining, B1: control group; B2: PCB-ZQ; B3: PCB-YJ. C: SEM images of biofilm processed by PCB-ZQ and PCB-YJ (scale: 10 μm), C1, C4: control group; C2, C5: PCB-ZQ; C3, C6: PCB-YJ.

Figure 3 Combination of Guanghuoxiang (Herba Pogostemonis) and PGS A: Test of MIC of PCB-ZQ, PCB-YJ and PGS groups (Horizontal coordinate: top: concentration of Guanghuoxiang (Herba Pogostemonis) samples; bottom: concentration of PGS). B: Results of bacteriostatic rate of PCB-ZQ combined with PGS. C: Results of bacteriostatic rate of PCB-YJ combined with PGS; D: Staining results of live/dead bacteria in each group at 1/4MIC of combine (scale bar 80 μm), D1, D7, D13: control group; D2, D8, D14: PCB-ZQ; D3, D9, D15: PCB-YJ; D4, D10, D16: PGS; D5, D11, D17: P-Z; D6, D12, D18: P-Y. E: Staining results of live/dead bacteria in each group at 1/4MIC of combine (scale bar 20 μm 10 μm 1 μm), E1, E7, E13: control group; E2, E8, E14: PCB-ZQ; E3, E9, E15: PCB-YJ; E4, E10, E16: PGS; E5, E11, E17: P-Z; E6, E12, E18: P-Y.
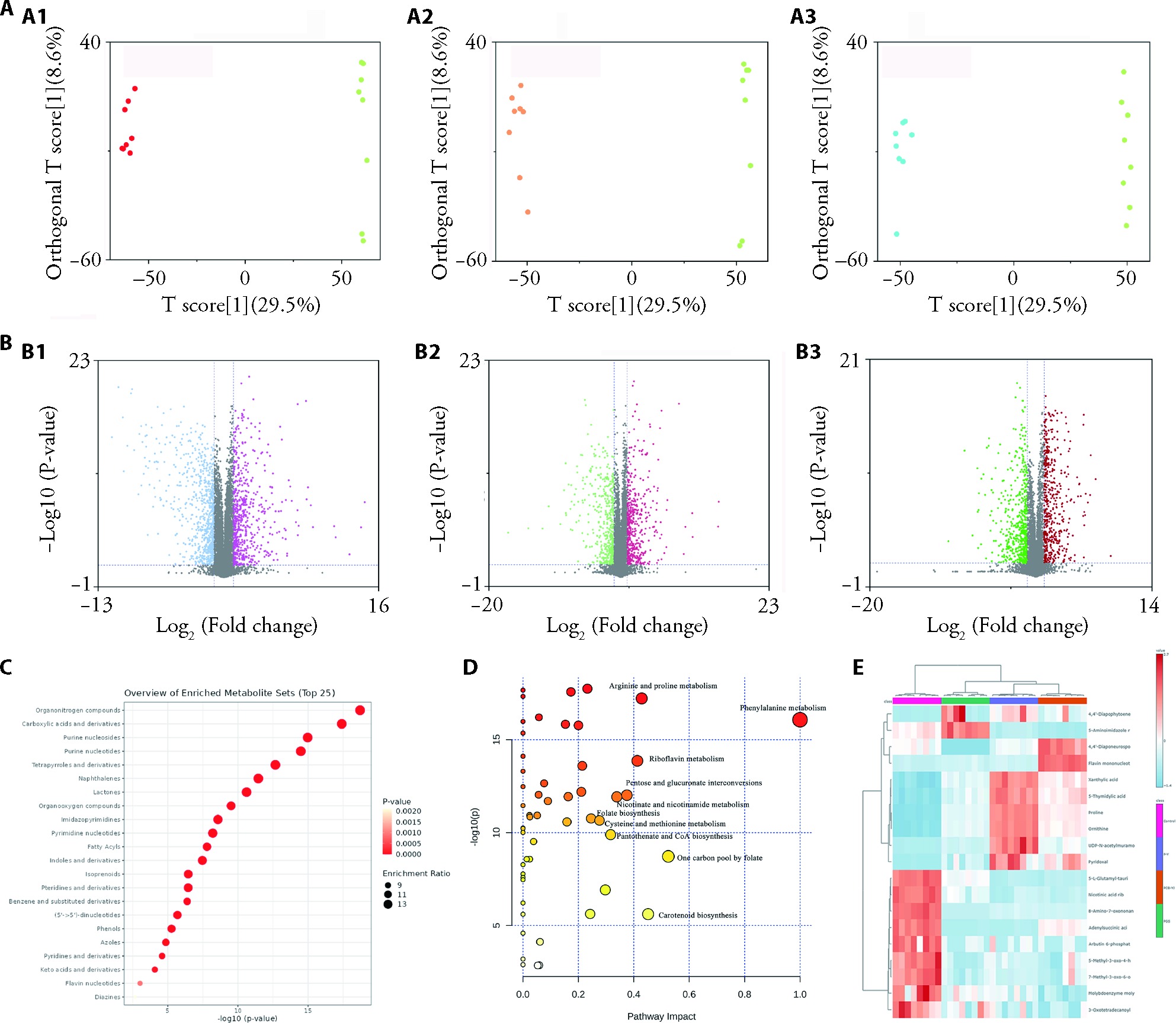
Figure 4 Metabolomic analysis of Control, PGS, PCB-YJ, P-Y A: OPLSDA diagram; A1: P-Y compared to control group; A2: P-Y compared to PGS; A3: P-Y compared to PCB-YJ; B: volcanic maps of each group; B1: P-Y compared to control group; B2: P-Y compared to PGS; B3: P-Y compared to PCB-YJ; C: Major differential metabolites of each group; D: Metabolic pathways; E: Cluster heatmap. Control group: nutrient broth; PGS: Penicillin G Sodium; PCB-YJ: Yangjiang City; P-Y: PGS and PCB-YJ combined. (n = 8).
| Group | PGS | PCB-YJ | P-Y |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolites | Carboxylic acids and derivatives Organooxygen compounds Purine nucleosides Indoles and derivatives Pteridines and derivatives | lmidazopyrimidines Carboxylic acids and derivatives Organooxygen compounds Isoprenoids Indoles and derivatives | Organonitrogen compounds Arboxylic acids and derivatives Purine nucleosides Purine nucleotides Tetrapyrroles and derivatives |
| Metabolic pathways | Purine metabolism Arginine and proline metabolism Biotin metabolism Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis Biosynthesis of various antibiotics Carotenoid biosynthesis Glutathione metabolism | Arginine and proline metabolism Phenylalanine metabolism Riboflavin metabolism Pentose and glucurpnate interconversions Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism |
Table 7 The metabolic pathways of PGS, PCB-YJ and P-Y
| Group | PGS | PCB-YJ | P-Y |
|---|---|---|---|
| Metabolites | Carboxylic acids and derivatives Organooxygen compounds Purine nucleosides Indoles and derivatives Pteridines and derivatives | lmidazopyrimidines Carboxylic acids and derivatives Organooxygen compounds Isoprenoids Indoles and derivatives | Organonitrogen compounds Arboxylic acids and derivatives Purine nucleosides Purine nucleotides Tetrapyrroles and derivatives |
| Metabolic pathways | Purine metabolism Arginine and proline metabolism Biotin metabolism Glyoxylate and dicarboxylate metabolism | Alanine, aspartate and glutamate metabolism Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis Biosynthesis of various antibiotics Carotenoid biosynthesis Glutathione metabolism | Arginine and proline metabolism Phenylalanine metabolism Riboflavin metabolism Pentose and glucurpnate interconversions Nicotinate and nicotinamide metabolism |
| Compound name | KEGG ID | HMDB | PubChem | Control vs PGS | Control vs PCB-YJ | Control vs P-Y | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC | P value | Trend | FC | P value | Trend | FC | P value | Trend | ||||||
| Flavin mononucleotide | C00061 | HMDB0001520 | 643976 | 4.57E+00 | 0.0065285 | up | 6.70E+01 | 3.74E-11 | up | 4.54E+00 | 9.47E-04 | up | ||
| Ornithine | C00077 | HMDB0000214 | 6262 | 2.21E+00 | 2.74E-13 | up | 2.70E+00 | 1.12E-15 | up | 4.17E+00 | 1.03E-17 | up | ||
| Proline | C00148 | HMDB0000162 | 145742 | 2.07E+00 | 1.03E-15 | up | 2.56E+00 | 3.73E-18 | up | 3.80E+00 | 5.72E-18 | up | ||
| Pyridoxal | C00250 | HMDB0001545 | 1050 | 4.46E+01 | 0.011403 | up | 1.54E+02 | 4.60E-04 | up | 2.14E+02 | 1.49E-04 | up | ||
| 5-Thymidylic acid | C00364 | HMDB0001227 | 9700 | 2.14E+00 | 5.67E-09 | up | 2.94E+00 | 3.24E-10 | up | 4.26E+00 | 1.32E-13 | up | ||
| Xanthylic acid | C00655 | HMDB0001554 | 73323 | 2.01E+00 | 6.03E-10 | up | 2.55E+00 | 4.86E-11 | up | 3.73E+00 | 6.71E-14 | up | ||
| 8-Amino-7-oxononanoate | C01092 | METPA0126 | NA | 0.00 | 0.00013789 | down | 7.05E-02 | 1.33E-15 | down | 9.17E-02 | 3.78E-15 | down | ||
| 5-Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide | C03373 | HMDB0001235 | 161500 | 2.11E+00 | 2.50E-08 | up | 4.03E-02 | 2.97E-10 | down | 2.43E-01 | 1.16E-08 | down | ||
| Adenylsuccinic acid | C03794 | HMDB0000536 | 447145 | 9.16E-03 | 7.32E-05 | down | 4.09E-01 | 1.56E-10 | down | 1.64E-02 | 2.83E-04 | down | ||
| UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamyl-6-carboxy-L-lysyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine | C04882 | METPA0553 | NA | 4.77E+00 | 6.24E-08 | up | 9.44E+00 | 1.76E-07 | up | 3.17E+01 | 3.03E-10 | up | ||
| 3-Oxotetradecanoyl-CoA | C05261 | HMDB0003935 | 11966197 | 4.79E-01 | 0.005514 | down | 1.70E-01 | 1.83E-05 | down | 3.07E-01 | 2.08E-04 | down | ||
| UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamyl-6-carboxy-L-lysyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine | C04882 | METPA0553 | NA | 4.77E+00 | 6.24E-08 | up | 9.44E+00 | 1.76E-07 | up | 3.17E+01 | 3.03E-10 | up | ||
| Nicotinic acid ribonucleoside | C05841 | HMDB0006809 | 161234 | 4.73E-01 | 1.43E-10 | down | 3.68E-01 | 1.05E-11 | down | 3.58E-01 | 2.14E-12 | down | ||
| 5-L-Glutamyl-taurine | C05844 | HMDB0004195 | 68759 | 4.44E-01 | 1.56E-12 | down | 2.28E-01 | 1.10E-14 | down | 2.11E-01 | 7.81E-15 | down | ||
| Arbutin 6-phosphate | C06187 | METPA0783 | NA | 1.46E-01 | 1.10E-06 | down | 1.18E-01 | 9.03E-07 | down | 2.00E-01 | 1.23E-05 | down | ||
| 4,4'-Diapophytoene | C16144 | METPA1832 | NA | 7.22E+01 | 0.024326 | up | 3.85E+01 | 5.15E-03 | up | 7.25E+01 | 2.35E-05 | up | ||
| 4,4'-Diaponeurosporenic acid | C16146 | METPA1831 | NA | 0.00 | 1.22E-10 | down | 2.02E+00 | 3.66E-12 | up | 8.67E-01 | 6.39E-11 | down | ||
| 7-Methyl-3-oxo-6-octenoyl-CoA | C16466 | HMDB0060421 | 9549325 | 1.75E-01 | 1.39E-08 | down | 2.52E-01 | 3.05E-06 | down | 2.19E-01 | 7.93E-09 | down | ||
| 5-Methyl-3-oxo-4-hexenoyl-CoA | C16471 | HMDB0060399 | 9549331 | 2.87E-01 | 2.99E-08 | down | 3.51E-01 | 3.63E-06 | down | 3.56E-01 | 2.38E-08 | down | ||
| Molybdoenzyme molybdenum cofactor | C18237 | NA | NA | 4.57E-01 | 0.001064 | down | 1.51E-01 | 1.35E-05 | down | 3.91E-01 | 3.85E-04 | down | ||
Table 8 The same metabolites of Control vs PGS, Control vs PCB-YJ, Control vs P-Y
| Compound name | KEGG ID | HMDB | PubChem | Control vs PGS | Control vs PCB-YJ | Control vs P-Y | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FC | P value | Trend | FC | P value | Trend | FC | P value | Trend | ||||||
| Flavin mononucleotide | C00061 | HMDB0001520 | 643976 | 4.57E+00 | 0.0065285 | up | 6.70E+01 | 3.74E-11 | up | 4.54E+00 | 9.47E-04 | up | ||
| Ornithine | C00077 | HMDB0000214 | 6262 | 2.21E+00 | 2.74E-13 | up | 2.70E+00 | 1.12E-15 | up | 4.17E+00 | 1.03E-17 | up | ||
| Proline | C00148 | HMDB0000162 | 145742 | 2.07E+00 | 1.03E-15 | up | 2.56E+00 | 3.73E-18 | up | 3.80E+00 | 5.72E-18 | up | ||
| Pyridoxal | C00250 | HMDB0001545 | 1050 | 4.46E+01 | 0.011403 | up | 1.54E+02 | 4.60E-04 | up | 2.14E+02 | 1.49E-04 | up | ||
| 5-Thymidylic acid | C00364 | HMDB0001227 | 9700 | 2.14E+00 | 5.67E-09 | up | 2.94E+00 | 3.24E-10 | up | 4.26E+00 | 1.32E-13 | up | ||
| Xanthylic acid | C00655 | HMDB0001554 | 73323 | 2.01E+00 | 6.03E-10 | up | 2.55E+00 | 4.86E-11 | up | 3.73E+00 | 6.71E-14 | up | ||
| 8-Amino-7-oxononanoate | C01092 | METPA0126 | NA | 0.00 | 0.00013789 | down | 7.05E-02 | 1.33E-15 | down | 9.17E-02 | 3.78E-15 | down | ||
| 5-Aminoimidazole ribonucleotide | C03373 | HMDB0001235 | 161500 | 2.11E+00 | 2.50E-08 | up | 4.03E-02 | 2.97E-10 | down | 2.43E-01 | 1.16E-08 | down | ||
| Adenylsuccinic acid | C03794 | HMDB0000536 | 447145 | 9.16E-03 | 7.32E-05 | down | 4.09E-01 | 1.56E-10 | down | 1.64E-02 | 2.83E-04 | down | ||
| UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamyl-6-carboxy-L-lysyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine | C04882 | METPA0553 | NA | 4.77E+00 | 6.24E-08 | up | 9.44E+00 | 1.76E-07 | up | 3.17E+01 | 3.03E-10 | up | ||
| 3-Oxotetradecanoyl-CoA | C05261 | HMDB0003935 | 11966197 | 4.79E-01 | 0.005514 | down | 1.70E-01 | 1.83E-05 | down | 3.07E-01 | 2.08E-04 | down | ||
| UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamyl-6-carboxy-L-lysyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine | C04882 | METPA0553 | NA | 4.77E+00 | 6.24E-08 | up | 9.44E+00 | 1.76E-07 | up | 3.17E+01 | 3.03E-10 | up | ||
| Nicotinic acid ribonucleoside | C05841 | HMDB0006809 | 161234 | 4.73E-01 | 1.43E-10 | down | 3.68E-01 | 1.05E-11 | down | 3.58E-01 | 2.14E-12 | down | ||
| 5-L-Glutamyl-taurine | C05844 | HMDB0004195 | 68759 | 4.44E-01 | 1.56E-12 | down | 2.28E-01 | 1.10E-14 | down | 2.11E-01 | 7.81E-15 | down | ||
| Arbutin 6-phosphate | C06187 | METPA0783 | NA | 1.46E-01 | 1.10E-06 | down | 1.18E-01 | 9.03E-07 | down | 2.00E-01 | 1.23E-05 | down | ||
| 4,4'-Diapophytoene | C16144 | METPA1832 | NA | 7.22E+01 | 0.024326 | up | 3.85E+01 | 5.15E-03 | up | 7.25E+01 | 2.35E-05 | up | ||
| 4,4'-Diaponeurosporenic acid | C16146 | METPA1831 | NA | 0.00 | 1.22E-10 | down | 2.02E+00 | 3.66E-12 | up | 8.67E-01 | 6.39E-11 | down | ||
| 7-Methyl-3-oxo-6-octenoyl-CoA | C16466 | HMDB0060421 | 9549325 | 1.75E-01 | 1.39E-08 | down | 2.52E-01 | 3.05E-06 | down | 2.19E-01 | 7.93E-09 | down | ||
| 5-Methyl-3-oxo-4-hexenoyl-CoA | C16471 | HMDB0060399 | 9549331 | 2.87E-01 | 2.99E-08 | down | 3.51E-01 | 3.63E-06 | down | 3.56E-01 | 2.38E-08 | down | ||
| Molybdoenzyme molybdenum cofactor | C18237 | NA | NA | 4.57E-01 | 0.001064 | down | 1.51E-01 | 1.35E-05 | down | 3.91E-01 | 3.85E-04 | down | ||
| 1. | Sovic J, Segovic S, Pavelic B, et al. Patterns of antibiotic prescription in endodontic therapy in the Republic of Croatia. Antibiotics (Basel) 2024; 13: 645. |
| 2. | Kang J, Yin ZL, Pei FY, et al. Aerobic composting of chicken manure with penicillin G: community classification and quorum sensing mediating its contribution to humification. Bioresour Technol 2022; 35: 127097. |
| 3. |
Huynh D, Tung N, Dam Q, et al. Amoxicillin and penicillin G dosing in pediatric community-acquired pneumococcal pneumonia in the era of conjugate pneumococcal vaccines. Pharmacotherapy 2024; 44: 606-14.
DOI URL |
| 4. |
Ubals M, Nadal-Baron P, Arando M, et al. Oral linezolid compared with benzathine penicillin G for treatment of early syphilis in adults (Trep-AB Study) in Spain: a prospective, open-label, non-inferiority, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Infect Dis 2024; 24: 404-16.
DOI PMID |
| 5. | Hla TK, Osowicki J, Salman S, et al. Study protocol for controlled human infection for penicillin G against Streptococcus pyogenes: a double-blinded, placebo-controlled, randomised trial to determine the minimum concentration required to prevent experimental pharyngitis (the CHIPS trial). BMJ Open 2022; 12: e064022. |
| 6. | Baran A, Kwiatkowska A, Potocki L. Antibiotics and bacterial resistance-a short story of an endless arms race. Int J Mol Sci 2023; 24(6): 5777. |
| 7. | Larsson DGJ, Flach CF. Antibiotic resistance in the environment. Nat Rev Microbiol 2022; 20: 257-69. |
| 8. | Davies J, Davies D. Origins and evolution of antibiotic resistance. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 2010; 74: 417-33. |
| 9. |
Bassetti S, Tschudin-Sutter S, Egli A, Osthoff M. Optimizing antibiotic therapies to reduce the risk of bacterial resistance. Eur J Intern Med 2022; 99: 7-12.
DOI PMID |
| 10. |
Honigsbaum M. Superbugs and us. Lancet 2018; 391: 420.
DOI PMID |
| 11. |
Sharma A, Rodriguez-Morales AJ, Traore T, et al. Globalisation of antibiotic-resistant bacteria at recurring mass gathering events. Lancet 2023; 402: e5-7.
DOI URL |
| 12. |
Willems RPJ, van Dijk K, Vehreschild M, et al. Incidence of infection with multidrug-resistant Gram-negative bacteria and vancomycin-resistant enterococci in carriers: a systematic review and Meta-regression analysis. Lancet Infect Dis 2023; 23: 719-31.
DOI PMID |
| 13. | Patil S, Chen H, Lopes BS, Liu SX, Wen FQ. Multidrug-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae in young children. Lancet Microbe 2023; 4: e69. |
| 14. |
Fursova NK, Fursov MV, Astashkin EI, et al. Multidrug-resistant and extensively drug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii causing nosocomial meningitis in the Neurological Intensive Care Unit. Microorganisms 2023; 11: 2020.
DOI URL |
| 15. | Galar A, Weil AA, Dudzinski DM, Munoz P, Siedner MJ. Methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus prosthetic valve endocarditis: pathophysiology, epidemiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and management. Clin Microbiol Rev 2019; 32: e00041-18. |
| 16. | Jiang JH, Cameron DR, Nethercott C, Aires-de-Sousa M, Peleg AY. Virulence attributes of successful methicillin-resistant Staphy-lococcus aureus lineages. Clin Microbiol Rev 202; 36: e0014822. |
| 17. | Gopikrishnan M, Haryini S, C GPD. Emerging strategies and therapeutic innovations for combating drug resistance in Staphylococcus aureus strains: A comprehensive review. J Basic Microbiol 2024; 64: e2300579. |
| 18. | Mullard A. The deadly burden of drug-resistant bacteria. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2022; 21: 170. |
| 19. |
Antimicrobial Resistance C. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in 2019: a systematic analysis. Lancet 2022; 399: 629-55.
DOI URL |
| 20. |
Collaborators GBDAR. Global burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance 1990-2021: a systematic analysis with forecasts to 2050. Lancet 2024; 404: 1199-226.
DOI URL |
| 21. |
Elbe S, Roemer-Mahler A, Long C. Medical countermeasures for national security: a new government role in the pharmaceuticalization of society. Soc Sci Med 2015; 131: 263-71.
DOI PMID |
| 22. | Lewnard JA, Charani E, Gleason A, et al. Burden of bacterial antimicrobial resistance in low-income and middle-income countries avertible by existing interventions: an evidence review and modelling analysis. Lancet 2024; 403: 2439-54. |
| 23. | Wong F, de la Fuente-Nunez C, Collins JJ. Leveraging artificial intelligence in the Figureht against infectious diseases. Science 2023; 381: 164-70. |
| 24. |
Krell T, Matilla MA. Antimicrobial resistance: progress and challenges in antibiotic discovery and anti-infective therapy. Microb Biotechnol 2022; 15: 70-8.
DOI URL |
| 25. | Barbarossa A, Rosato A, Corbo F, et al. Non-antibiotic drug repositioning as an alternative antimicrobial approach. Antibiotics (Basel) 2022; 11: 816. |
| 26. |
Sikder A, Chaudhuri A, Mondal S, Singh NDP. Recent advances on stimuli-responsive combination therapy against multidrug-resistant bacteria and biofilm. ACS Appl Bio Mater 2021; 4: 4667-83.
DOI PMID |
| 27. |
Theuretzbacher U, Jumde RP, Hennessy A, Cohn J, Piddock LJV. Global health perspectives on antibacterial drug discovery and the preclinical pipeline. Nat Rev Microbiol 2025; 23: 474-90.
DOI |
| 28. |
Ardal C, Balasegaram M, Laxminarayan R, et al. Antibiotic development - economic, regulatory and societal challenges. Nat Rev Microbiol 2020; 18: 267-74.
DOI PMID |
| 29. |
Theuretzbacher U. Market watch: Antibacterial innovation in European SMEs. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2016; 15: 812-3.
DOI PMID |
| 30. | Yang Y, Kessler MGC, Marchan-Rivadeneira MR, Han Y. Combating antimicrobial resistance in the post-genomic era: rapid antibiotic discovery. Molecules 2023; 28: 4183. |
| 31. |
Yang WQ, Li J, Yao ZL, Li M. A review on the alternatives to anti-biotics and the treatment of antibiotic pollution: current development and future prospects. Sci Total Environ 2024; 926: 171757.
DOI URL |
| 32. | Zhu ML, Tse MW, Weller J, Chen JL, Blainey PC. The future of antibiotics begins with discovering new combinations. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2021; 1496: 82-96. |
| 33. | Osman AH, Kotey FCN, Odoom A, et al. The potential of bacteriophage-antibiotic combination therapy in treating infections with multidrug-resistant bacteria. Antibiotics (Basel) 2023; 12: 1329. |
| 34. |
Hernandez-Rodriguez P, Baquero LP. Combination therapy as a strategy to control infections caused by multi-resistant bacteria: current review. Curr Drug Targets 2022; 23: 260-5.
DOI PMID |
| 35. | Wang Q, Lyu YM, Pang J, et al. In vitro and in vivo activity of d-serine in combination with beta-lactam antibiotics against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Acta Pharm Sin B 2019; 9: 496-504. |
| 36. | Abd El-Hamid MI, El-Tarabili RM, Bahnass MM, et al. Partnering essential oils with antibiotics: proven therapies against bovine Staphylococcus aureus mastitis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2023; 13: 1265027. |
| 37. | Weng ZB, Zeng F, Wang MX, et al. Antimicrobial activities of lavandulylated flavonoids in Sophora flavences against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus via membrane disruption. J Adv Res 2024; 57: 197-212. |
| 38. |
Tian XH, Wang PL, Li T, et al. Self-assembled natural phytochemicals for synergistically antibacterial application from the enlightenment of Traditional Chinese Medicine combination. Acta Pharm Sin B 2020; 10: 1784-95.
DOI PMID |
| 39. |
Zhang F, Sun GQ, Zhao R, et al. Zwitterion-modified mxene quantum dot as a nanocarrier for Traditional Chinese Medicine sanguinarine delivery and its application for photothermal-chemotherapy synergistic antibacterial and wound healing. Langmuir 2024; 40: 11381-9.
DOI URL |
| 40. |
Zeng WH, Qian J, Wang Y, Shou MY, Kai GY. Bletilla Striata polysaccharides thermosensitive gel for photothermal treatment of bacterial infection. Int J Biol Macromol 2023; 253: 127430.
DOI URL |
| 41. |
Li JG, Chen XF, Lu TY, et al. Increased activity of beta-lactam antibiotics in combination with carvacrol against MRSA bacteremia and catheter-associated biofilm infections. ACS Infect Dis 2023; 9: 2482-93.
DOI URL |
| 42. | Kim M, Seo Y, Kim SG, et al. Synergistic antibiotic activity of ricini semen extract with oxacillin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics (Basel) 2023; 12: 340. |
| 43. | Peris MC, Martinez A, Ortiz MP, Sheth CC, Veses V. Icariin in combination with amoxycillin-clavulanate and ampicillin, but not vancomycin, increases antibiotic sensitivity and growth inhibition against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antibiotics (Basel) 2022; 11: 233. |
| 44. |
Al-Tawalbeh D, Alkhawaldeh Y, Abu Sawan H, et al. Assessment of carvacrol-antibiotic combinations' antimicrobial activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Front Microbiol 2023; 14: 1349550.
DOI URL |
| 45. |
Jin YS, Lin JX, Shi HQ, et al. The active ingredients in Chinese peony pods synergize with antibiotics to inhibit MRSA growth and biofilm formation. Microbiol Res 2024; 281: 127625.
DOI URL |
| 46. |
Peng XJ, Ang S, Zhang YZ, et al. Chemical constituents with antiproliferative activity from pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Benth. Front Chem 2022; 10: 938851.
DOI URL |
| 47. |
Li D, Xing ZW, Yu TT, et al. Pogostone attenuates adipose tissue inflammation by regulating the adipocyte-macrophage crosstalk via activating SIRT1. Food Funct 2022; 13: 11853-64.
DOI URL |
| 48. |
Jung Ha C, Daehyun K, Kyoungin M, So Young L, Nae Gyu K. Pogostemon cablin extract promotes wound healing through OR2AT4 activation and exhibits anti-inflammatory activity. Current Issues in Molecular Biology 2024; 46: 9136-48.
DOI PMID |
| 49. |
Fan YH, Zhang Q, Zhang W, et al. Inhibitory effects of Patchouli alcohol on the early lifecycle stages of influenza A virus. Front Microbiol 2022; 13: 938868.
DOI URL |
| 50. | Agung Fitri Kusuma S, Asmi Ramdani Lestari S, Moelyono M. GC-MS analysis and anti-malodor activity of Indonesian patchouli leaves essential oil Pogostemon cablin (Blanco) Benth. against Corynebacterium Sp isolate. Res J Chem Environ 2022; 26: 33-40. |
| 51. |
Szewczuk MA, Zych S, Oster N, Karakulska J. Activity of patchouli and tea tree essential oils against Staphylococci Isolated from pyoderma in dogs and their synergistic potential with gentamicin and enrofloxacin. Animals 2023; 13: 1279.
DOI URL |
| 52. |
Zhang QL, Zhang JX, Zhang Y, et al. Antifungal and anti-biofilm activities of patchouli alcohol against Candida albicans. Int J Med Microbiol 2024; 314: 151596.
DOI URL |
| 53. | Peng F, Wan F, Xiong L, et al. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activity of Pogostone. Chin Med J (Engl) 2014; 127: 4001-5. |
| 54. |
Wan F, Peng F, Xiong L, et al. In vitro and in vivo antibacterial activity of patchouli alcohol from pogostemon cablin. Chin J Integr Med 2021; 27: 125-30.
DOI URL |
| 55. |
Li YC, Liang HC, Chen HM, et al. Anti-Candida albicans activity and pharmacokinetics of pogostone isolated from pogostemonis herba. Phytomedicine 2012; 20: 77-83.
DOI URL |
| 56. |
Yu XD, Xie JH, Wang YH, et al. Selective antibacterial activity of patchouli alcohol against Helicobacter pylori based on inhibition of urease. Phytother Res 2015; 29: 67-72.
DOI URL |
| 57. |
Jeong GJ, Khan F, Tabassum N, Cho KJ, Kim YM. Bacterial extracellular vesicles: modulation of biofilm and virulence properties. Acta Biomater 2024; 178: 13-23.
DOI URL |
| 58. | Ranjutha V, Chen Y, Al-Keridis LA, et al. Synergistic antimicrobial activity of ceftriaxone and polyalthia longifolia methanol (MEPL) leaf extract against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and modulation of mecA gene presence. Antibiotics (Basel) 2023; 12: 477. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

