Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (6): 1254-1262.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.06.006
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Hypoglycemic mechanism of modified Gegen Qinlian decoction (加味葛根芩连汤) based on regulating the expression and DNA methylation of cholesterol transporters in the adipose tissue of type 2 diabetes mellitus rats
PENG Shuhong1, YANG Lingkun1, LIU Xinyi1, ZHANG Mengyu1, LIN Seqi1, ZHANG Changhua2, XU Guoliang1, ZHU Weifeng3( ), YAO Pengcheng4(
), YAO Pengcheng4( )
)
- 1 Research Center for Differentiation and Development of TCM Basic Theory, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, China
2 School of Pharmacy, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, China
3 State Key Laboratory of Modern Preparation of TCM, Ministry of Education, Nanchang 330004, China
4 Research Center of Natural Resources of Chinese Medicinal Materials and Ethnic Medicine, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, China
-
Received:2024-11-11Accepted:2025-03-27Online:2025-12-15Published:2025-11-24 -
Contact:YAO Pengcheng, Research Center of Natural Resources of Chinese Medicinal Materials and Ethnic Medicine, Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanchang 330004, China, yaopengcheng2001@163.com, Telephone: +86-791-87118109; +86-791-87119060
Prof. ZHU Weifeng, State Key Laboratory of Modern Preparation of TCM, Ministry of Education, Nanchang 330004, China, zwf0322@126.com -
Supported by:Investigation on the Mechanism of Gegen Qinlian Decoction in Lowering Blood Glucose Based on Improving Cholesterol Homeostasis of Lipid Rafts in Adipocytes(82060741);Cause of “Dampness Stagnating in Pi” in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by Overeating High Fat and Sugar Diet Based on Glycerol Transport Which Is Affected by Methylation/Hormones Signal(82160830);Investigation on the Mechanism of Gegen Qinlian Decoction in Lowering Blood Glucose Based on Improving Phosphatidylcholine Biosynthesis in Adipose Tissue(82360799);Relationship between Adipose Tissue and Spleen Image Based on Multivariate Analysis of Modern Literature (No. 2020B0328). Ganpo Juncai-Training Program for Academic and Technical Leaders in Major Disciplines of the Province (Leading Talents-Academic Category)(20232BCJ22022);Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine, First-level Discipline of Integrative Medicine (Jiangxi Province Double First-class Discipline)(zxyylxk20220103);Jiangxi University of Chinese Medicine Science and Technology Innovation Team Development Program(CXTD22007)
Cite this article
PENG Shuhong, YANG Lingkun, LIU Xinyi, ZHANG Mengyu, LIN Seqi, ZHANG Changhua, XU Guoliang, ZHU Weifeng, YAO Pengcheng. Hypoglycemic mechanism of modified Gegen Qinlian decoction (加味葛根芩连汤) based on regulating the expression and DNA methylation of cholesterol transporters in the adipose tissue of type 2 diabetes mellitus rats[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(6): 1254-1262.
share this article
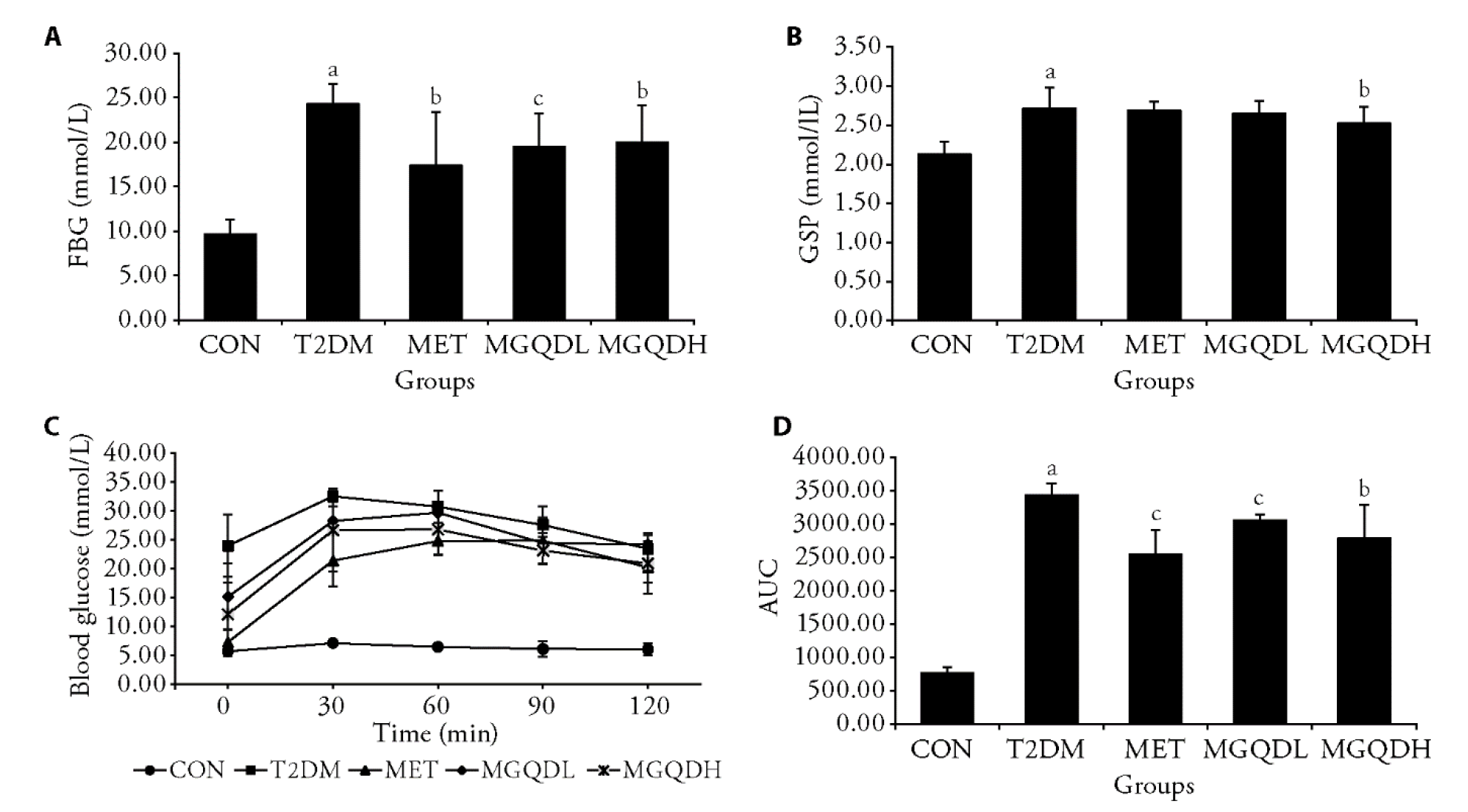
Figure 1 Blood glucose and glucose tolerance test in serum of each group A: FBG; B: GSP; C: glucose tolerance test; D: AUC. CON: normal rats treated with control diet and normal saline; T2DM: diabetic rats treated with high-fat diet and normal saline. MET: diabetic rats treated with high-fat diet and 200 mg·kg?1·d?1 of metformin hydrochloric acid for 14 weeks; MGQDL: diabetic rats treated with high-fat diet and 5 g·kg?1·d?1 of MGQD for 14 weeks; MGQDH: diabetic rats treated with high-fat diet and 10 g·kg?1·d?1 of MGQD for 14 weeks. CON: control; T2DM: type 2 diabetes mellitus; MET: metformin; MGQDL: low-dose Modified Gegen Qinlian decoction; MGQDH: high-dose Modified Gegen Qinlian decoction; FBG: fasting blood glucose; GSP: glycosylated serum protein; AUC: area under curve. The data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to determine if a distribution was normal or not. Statistical differences between treatments were analyzed using a one-way analysis of variance or Mann-Whitney U test (n = 7-10 for FBG and GSP, n = 6 for glucose tolerance test). aP < 0.01 vs the CON group; bP < 0.05, cP < 0.01 vs the T2DM group.
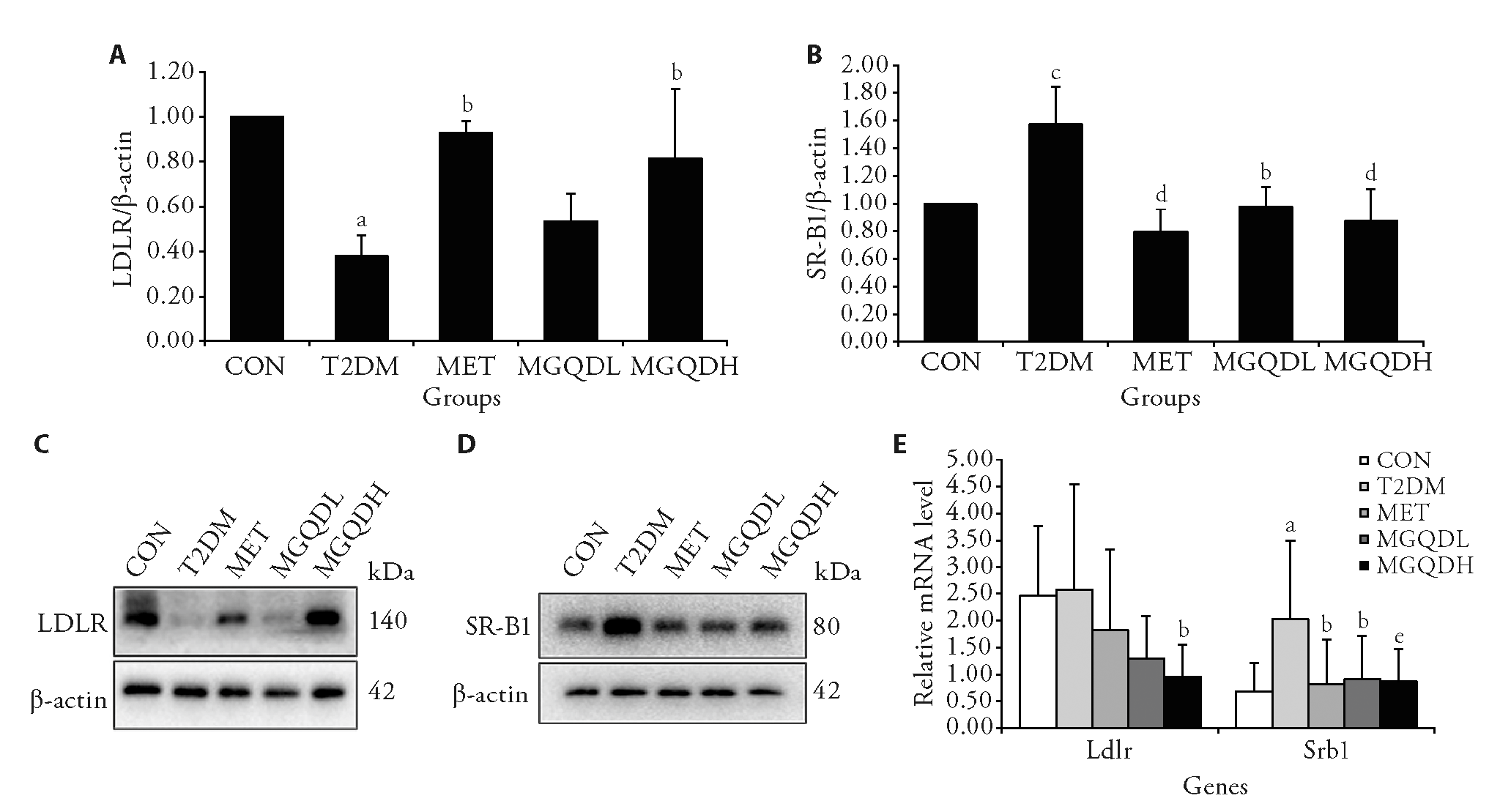
Figure 2 Protein and mRNA levels of LDLR and SR-B1 in eWAT of each group A: relative protein expression of LDLR; B: relative protein expression of SR-B1; C: protein images of LDLR; D: protein images of SR-B1; E: relative mRNA levels of Ldlr and Srb1 were detected by qPCR.CON: normal rats treated with control diet and normal saline; T2DM: diabetic rats treated with high-fat diet and normal saline. MET: diabetic rats treated with high-fat diet and 200 mg·kg?1·d?1 of metformin hydrochloric acid for 14 weeks; MGQDL: diabetic rats treated with high-fat diet and 5 g·kg?1·d?1 of MGQD for 14 weeks; MGQDH: diabetic rats treated with high-fat diet and 10 g·kg?1·d?1 of MGQD for 14 weeks. CON: control; T2DM: type 2 diabetes mellitus; MET: metformin; MGQDL: low-dose modified Gegen Qinlian decoction; MGQDH: high-dose modified Gegen Qinlian decoction; eWAT: epididymal adipose tissue; LDLR: low-density lipoprotein receptor; SR-B1: scavenger receptor class B type 1; Ldlr: the gene encoding LDLR; Srb1: the gene encoding SR-B1; qPCR: quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. The data measured in this research were expressed as mean ± standard deviation. Statistical differences between treatments were analyzed using a one-way analysis of variance (n = 3 for protein levels and n = 5-10 for mRNA levels). aP < 0.01, cP < 0.05 vs the CON group; bP < 0.05, dP < 0.01, and eP = 0.059 vs the T2DM group.
| Group | n | Ldlr | Srb1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CpG | Non-CpG | CpG | Non-CpG | |||
| CON | 6 | 0.56±0.62 | 0.46±0.35 | 0.11±0.27 | 0.33±0.13 | |
| T2DM | 6 | 0.25±0.62 | 0.11±0.12 | 0.30±0.46 | 0.00±0.00b | |
| MET | 6 | 0.32±0.54 | 0.56±0.47a | 0.16±0.39 | 0.21±0.18a | |
| MGQDL | 6 | 0.19±0.46 | 0.32±0.40 | 0.16±0.39 | 0.25±0.23a | |
| MGQDH | 6 | 0.00±0.00 | 0.56±0.39a | 0.00±0.00 | 0.22±0.22a | |
Table 1 Effect of MGQD on methylation level of Ldlr and Srb1 in eWAT of T2DM rats (%,$\bar{x}$ ± s)
| Group | n | Ldlr | Srb1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CpG | Non-CpG | CpG | Non-CpG | |||
| CON | 6 | 0.56±0.62 | 0.46±0.35 | 0.11±0.27 | 0.33±0.13 | |
| T2DM | 6 | 0.25±0.62 | 0.11±0.12 | 0.30±0.46 | 0.00±0.00b | |
| MET | 6 | 0.32±0.54 | 0.56±0.47a | 0.16±0.39 | 0.21±0.18a | |
| MGQDL | 6 | 0.19±0.46 | 0.32±0.40 | 0.16±0.39 | 0.25±0.23a | |
| MGQDH | 6 | 0.00±0.00 | 0.56±0.39a | 0.00±0.00 | 0.22±0.22a | |
| Srb1 | FBG | Cholesterol in eWAT | Srb1 mRNA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P value | P value | P value | P value | P value | P value | |||
| CpG | 0.128 | 0.500 | -0.168 | 0.374 | -0.014 | 0.948 | ||
| Non-CpG | -0.470 | 0.009 | 0.322 | 0.083 | -0.410 | 0.042 | ||
Table 2 Correlation between the methylation level of Srb1 and FBG, cholesterol, and mRNA level in eWAT
| Srb1 | FBG | Cholesterol in eWAT | Srb1 mRNA | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P value | P value | P value | P value | P value | P value | |||
| CpG | 0.128 | 0.500 | -0.168 | 0.374 | -0.014 | 0.948 | ||
| Non-CpG | -0.470 | 0.009 | 0.322 | 0.083 | -0.410 | 0.042 | ||
| 1. | Xu J, Lian FM, Zhao LH, et al. Structural modulation of gut microbiota during alleviation of type 2 diabetes with a Chinese herbal formula. ISME J 2015; 9: 552-62. |
| 2. |
Czech MP. Mechanisms of insulin resistance related to white, beige, and brown adipocytes. Mol Metab 2020; 34: 27-42.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Dugail I, Lay LS, Varret M, Liepvre LX, Dagher G, Ferré P. New insights into how adipocytes sense their triglyceride stores. Is cholesterol a signal? Horm Metab Res 2003; 35: 204-10.
PMID |
| 4. | Lu JC, Chiang YT, Lin YC, et al. Disruption of lipid raft function increases expression and secretion of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in 3T3-L 1 adipocytes. PLoS One 2016; 11: e169005. |
| 5. |
Grzybek M, Palladini A, Alexaki VI, et al. Comprehensive and quantitative analysis of white and brown adipose tissue by shotgun lipidomics. Mol Metab 2019; 22: 12-20.
DOI PMID |
| 6. | Li ZW, Liu XY, Yang LK, et al. Effects of Gegen Qinlian decoction on cholesterol, expression and methylation level of genes encoding key enzymes of cholesterol synthesis in adipose tissue of type 2 diabetic rats. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2025; 43: 173-81. |
| 7. |
Brown MS, Goldstein JL. The SREBP pathway: regulation of cholesterol metabolism by proteolysis of a membrane-bound transcription factor. Cell 1997; 89: 331-40.
DOI PMID |
| 8. | Cheng CM, Geng F, Cheng X, Guo DL. Lipid metabolism reprogramming and its potential targets in cancer. Cancer Commun (Lond) 2018; 38: 27. |
| 9. |
Shen WJ, Azhar S, Kraemer FB. SR-B1: a unique multifunctional receptor for cholesterol influx and efflux. Annu Rev Physiol 2018; 80: 95-116.
DOI URL |
| 10. |
Zhang YZ, Mcgillicuddy FC, Hinkle CC, et al. Adipocyte modulation of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. Circulation 2010; 121: 1347-55.
DOI PMID |
| 11. | Miroshnikova VV, Panteleeva AA, Pobozheva IA, et al. ABCA1 and ABCG 1 DNA methylation in epicardial adipose tissue of patients with coronary artery disease. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 2021; 21: 566. |
| 12. | Liang Y, Yang X, Ma L, et al. Homocysteine-mediated cholesterol efflux via ABCA1 and ACAT1 DNA methylation in THP-1 monocyte-derived foam cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 2013; 45: 220-8. |
| 13. |
Wu Z, Chen L, Hong X, et al. Temporal associations between leukocytes DNA methylation and blood lipids: a longitudinal study. Clin Epigenetics 2022; 14: 132.
DOI PMID |
| 14. | Chen YQ, Gong SF, Huang X, et al. Preliminary study on effect of Gegen Qinlian decoction on enzyme activity, gene expression and methylation level of FASN in adipose tissue of rats with insulin resistance. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2021; 46: 398-405. |
| 15. | Peng SH, Gong SF, Chen YQ, et al. Effect of Gegen Qinlian decoction on methylation and expression of Scd1 gene in adipose tissue of insulin resistant rats and correlations between methylation and physiological and biochemical parameters. Zhong Guo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2022; 47: 3328-38. |
| 16. |
Tong XL, Zhao LH, Lian FM, et al. Clinical observations on the dose-effect relationship of Gegen Qin Lian decoction on 54 out-patients with type 2 diabetes. J Tradit Chin Med 2011; 31: 56-9.
DOI URL |
| 17. |
Liu Y, Huang H, Gao R, Liu Y. Dynamic phenotypes and molecular mechanisms to understand the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy in two widely used animal models of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020; 8: 172.
DOI PMID |
| 18. |
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001; 25: 402-8.
DOI PMID |
| 19. |
Lay SL, Krief S, Farnier C, et al. Cholesterol, a cell size-dependent signal that regulates glucose metabolism and gene expression in adipocytes. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 16904-10.
DOI PMID |
| 20. |
Parpal S, Karlsson M, Thorn H, Strålfors P. Cholesterol depletion disrupts caveolae and insulin receptor signaling for metabolic control via insulin receptor substrate-1, but not for mitogen-activated protein kinase control. J Biol Chem 2001; 276: 9670-8.
DOI PMID |
| 21. | Yang X, Wang ZG, Zhou Y, Liu R, Zhu XD. Effect of modified Gegen Qinlian decoction on the CAP/Cb1/TC10 signaling pathway in the skeletal muscle of type 2 diabetes model rats. Zhong Yi Za Zhi 2021; 62: 2077-83. |
| 22. |
Nohturfft A, Debose-Boyd RA, Scheek S, Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Sterols regulate cycling of SREBP cleavage-activating protein (SCAP) between endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1999; 96: 11235-40.
PMID |
| 23. |
Zelcer N, Hong C, Boyadjian R, Tontonoz P. LXR regulates cholesterol uptake through Idol-dependent ubiquitination of the LDL receptor. Science 2009; 325: 100-4.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Dong Y, Xu Z, Zhang Z, et al. Impaired adipose expansion caused by liver X receptor activation is associated with insulin resistance in mice fed a high-fat diet. J Mol Endocrinol 2017; 58: 141-54.
DOI PMID |
| 25. |
Pettersson AM, Stenson BM, Lorente-Cebrian S, et al. LXR is a negative regulator of glucose uptake in human adipocytes. Diabetologia 2013; 56: 2044-54.
DOI PMID |
| 26. |
Zhang Z, Zhou Y, Lyu Q, et al. Gegen Qinlian decoction modulates atherosclerosis and lipid metabolism through cellular interplay and signaling pathways. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen 2024; 27: 2609-21.
DOI PMID |
| 27. | Hajighasem A, Farzanegi P, Mazaheri Z, Naghizadeh M, Salehi G. Effects of resveratrol, exercises and their combination on Farnesoid X receptor, Liver X receptor and Sirtuin 1 gene expression and apoptosis in the liver of elderly rats with nonalcoholic fatty liver. Peerj 2018; 6: e5522. |
| 28. |
Zhao SP, Wu ZH, Hong SC, Ye HJ, Wu J. Effect of atorvastatin on SR-BI expression and HDL-induced cholesterol efflux in adipocytes of hypercholesterolemic rabbits. Clin Chim Acta 2006; 365: 119-24.
DOI URL |
| 29. |
de Haan W, Bhattacharjee A, Ruddle P, Kang MH, Hayden MR. ABCA1 in adipocytes regulates adipose tissue lipid content, glucose tolerance, and insulin sensitivity. J Lipid Res 2014; 55: 516-23.
DOI PMID |
| 30. |
Robertson KD, Jones PA. DNA methylation: past, present and future directions. Carcinogenesis 2000; 21: 461-7.
DOI PMID |
| 31. |
Fujiwara S, Nagai H, Jimbo H, et al. Gene expression and methylation analysis in melanomas and melanocytes from the same patient: loss of NPM2 expression is a potential immunohistochemical marker for melanoma. Front Oncol 2018; 8: 675.
DOI PMID |
| 32. | Woodcock DM, Crowther PJ, Diver WP. The majority of methylated deoxycytidines in human DNA are not in the CpG dinucleotide. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1987; 145: 888-94. |
| 33. |
Barres R, Osler M E, Yan J, et al. Non-CpG methylation of the PGC-1alpha promoter through DNMT3B controls mitochondrial density. Cell Metab 2009; 10: 189-98.
DOI PMID |
| 34. | Kang S, Lee S, Moon BC, et al. Multi-omics analysis reveals the neuroprotective effect of Atractylodis Rhizoma Alba extract against Parkinson's disease in mouse. J Tradit Chin Med 2024; 44: 1111-7. |
| 35. | Wu JY, Hou L, Zhang XY, Elizabeth G, Gao C, Wang J. Efficacy of Yisui granule on myelodysplastic syndromes in SKM-1 mouse xenograft model through suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Tradit Chin Med 2024; 44: 78-87. |
| 36. | Ding LB, Wang HJ, Li Y, et al. Electroacupuncture stimulating Neixiyan (EX-LE5)and Dubi (ST35)alleviates osteoarthritis in rats induced by anterior cruciate ligament transaction via affecting DNA methylation regulated transcription of miR-146a and miR-140-5p. J Tradit Chin Med 2023; 43: 983-90. |
| 37. | Ishikawa K, Tsunekawa S, Ikeniwa M, et al. Long-term pancreatic beta cell exposure to high levels of glucose but not palmitate induces DNA methylation within the insulin gene promoter and represses transcriptional activity. PLoS One 2015; 10: e115350. |
| 38. | Marra PS, Yamanashi T, Crutchley KJ, et al. Metformin use history and genome-wide DNA methylation profile: potential molecular mechanism for aging and longevity. Aging (Albany NY) 2023; 15: 601-16. |
| [1] | DING Luobin, WANG Huajun, LI Yao, LI Jia, LI Ling, GAO Yangping, GUAN Jian, GENG Weiqiang. Electroacupuncture stimulating Neixiyan (EX-LE5) and Dubi (ST35) alleviates osteoarthritis in rats induced by anterior cruciate ligament transaction via affecting DNA methylation regulated transcription of miR-146a and miR-140-5p [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(5): 983-990. |
| [2] | Joong Sun Kim, Hye-Sun Lim, Byeong Cheol Moon, Mary Jasmin Ang, Sung-Ho Kim, Changjong Moon, Boseok Seong, Yunji Jang, Hyung-Yong Kim, Chul Kim. Epigenetic mechanisms involved in the neuroprotective effect of scorpion extract in a Parkinson's disease murine model based on multi-omics approach [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021, 41(3): 390-396. |
| [3] | Shaodong Chen, Manting Lin, Xiao Zhao, Fan Lu, YujieWang, Shulei Li, BinYan, Haihong Zhou. Effects of Chaiyuwendan decoction on endocannabinoids levels in adipose tissue of rats with chronic stress-induced depression [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2014, 34(01): 96-99. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

