Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2025, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 747-758.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.04.005
• Original Articles • Previous Articles Next Articles
Huayu Qutan formula (化瘀祛痰方) can improve platelet aggregation in acute coronary syndrome rats by regulating gut microbes to drive trimethylamine/flavin containing monooxygenase 3/trimethylamine N-oxide pathway
ZHANG Ni1( ), CHEN Yanxi2, JIA Lianqun3, LI Xinya2, MA Yixin4
), CHEN Yanxi2, JIA Lianqun3, LI Xinya2, MA Yixin4
- 1 Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110032, China
2 First Clinical College, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, China
3 Department of Biochemistry, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, China
4 Chinese Medicine Innovation Engineering Technology Center, Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110847, China
-
Received:2024-07-16Accepted:2024-11-29Online:2025-08-15Published:2025-07-25 -
Contact:ZHANG Ni -
About author:Dr. ZHANG Ni, Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Hospital of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shenyang 110032, China. zhang_ni1993@163.com,Telephone: +86-24-82961932
-
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China Project: based on the Theory of “the Heart is in Harmony with the Small Intestine” to Explore the Influence and Mechanism of Gut Microbes on High Platelet Reactivity of Acute Coronary Syndrome with Phlegm and Blood Stasis Syndrome(82104841);Education Department of Liaoning Province Young Science and Technology Talents "Seedling" Project: to Explore the Effect and Mechanism of Huayu Qutan Formula on Platelet Function in Acute Coronary Syndrome Patients with Phlegm and Blood Stasis Syndrome after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention based on Intestinal Microbiome(L202039)
Cite this article
ZHANG Ni, CHEN Yanxi, JIA Lianqun, LI Xinya, MA Yixin. Huayu Qutan formula (化瘀祛痰方) can improve platelet aggregation in acute coronary syndrome rats by regulating gut microbes to drive trimethylamine/flavin containing monooxygenase 3/trimethylamine N-oxide pathway[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2025, 45(4): 747-758.
share this article

Figure 1 Effect of Huayu Qutan formula on myocardial ischemia in ACS rats A1: the electrocardiogram of CON group rats; A2: the electrocardiogram of ACS group rats; A3: the electrocardiogram of HYQT group rats; A4: the electrocardiogram of FJYZ group rats; A5: the electrocardiogram of LH group rats; B1: the HE staining of myocardial tissue in CON group rats; B2: the HE staining of myocardial tissue in ACS group rats; B3: the HE staining of myocardial tissue in HYQT group rats; B4: the HE staining of myocardial tissue in FJYZ group rats; B5: the HE staining of myocardial tissue in LH group rats; C1: the serum TG levels in rats; C2: the serum TC levels in rats; C3: the serum LDL-C levels in rats; C4: the serum HDL-C levels in rats. CON: treated only with physiological saline; ACS: treated with a high-fat diet and an intraperitoneal injection of isoproterenol (45 mg/kg); HYQT: treated with Huayu Qutan formula of equivalent dose according to the body surface area ratio between humans and rats for 28 d; FJYZ: treated with fecal bacteria extract of 15.197 g/kg for 28 d; LH: treated with Huayu Qutan formula and fecal bacteria extract of 15.197 g/kg for 28 d. ACS: acute coronary syndrome; TC: cholesterol; TG: triglyceride; LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HE: hematoxylin-eosin staining; ANOVA: analysis of variance. One-way ANOVA, data are presented as mean ± standard deviation, n = 15. Compared with the CON group, aP < 0.01; compared with the ACS group, bP <0.01; compared with the HYQT group, cP < 0.01; compared with the FJYZ group, dP < 0.01.
| Group | n | PLT (109/L) | MARAA (%) | MARADP (%) | CD62p (ng/mL) | PAC-1 (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 15 | 194.930±3.035 | 35.270±7.294 | 38.270±4.621 | 4.497±0.539 | 0.333±0.029 |
| ACS | 15 | 213.070±12.826a | 99.400±5.235a | 79.000±3.836a | 7.171±0.603a | 0.457±0.023a |
| HYQT | 15 | 210.270±12.959a | 49.270±6.902ab | 52.270±7.860ab | 5.994±0.425ab | 0.398±0.025ab |
| FJYZ | 15 | 213.070±8.730a | 53.070±4.574ab | 48.800±4.229ab | 5.708±0.614ab | 0.385±0.031ab |
| LH | 15 | 210.670±11.331a | 50.200±5.596ab | 48.600±6.905ab | 5.556±0.622abc | 0.344±0.029bcd |
Table 1 Effects of Huayu Qutan formula on platelet, platelet aggregation rate, and platelet activation markers in ACS rats ($\bar{x} \pm s$)
| Group | n | PLT (109/L) | MARAA (%) | MARADP (%) | CD62p (ng/mL) | PAC-1 (ng/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CON | 15 | 194.930±3.035 | 35.270±7.294 | 38.270±4.621 | 4.497±0.539 | 0.333±0.029 |
| ACS | 15 | 213.070±12.826a | 99.400±5.235a | 79.000±3.836a | 7.171±0.603a | 0.457±0.023a |
| HYQT | 15 | 210.270±12.959a | 49.270±6.902ab | 52.270±7.860ab | 5.994±0.425ab | 0.398±0.025ab |
| FJYZ | 15 | 213.070±8.730a | 53.070±4.574ab | 48.800±4.229ab | 5.708±0.614ab | 0.385±0.031ab |
| LH | 15 | 210.670±11.331a | 50.200±5.596ab | 48.600±6.905ab | 5.556±0.622abc | 0.344±0.029bcd |
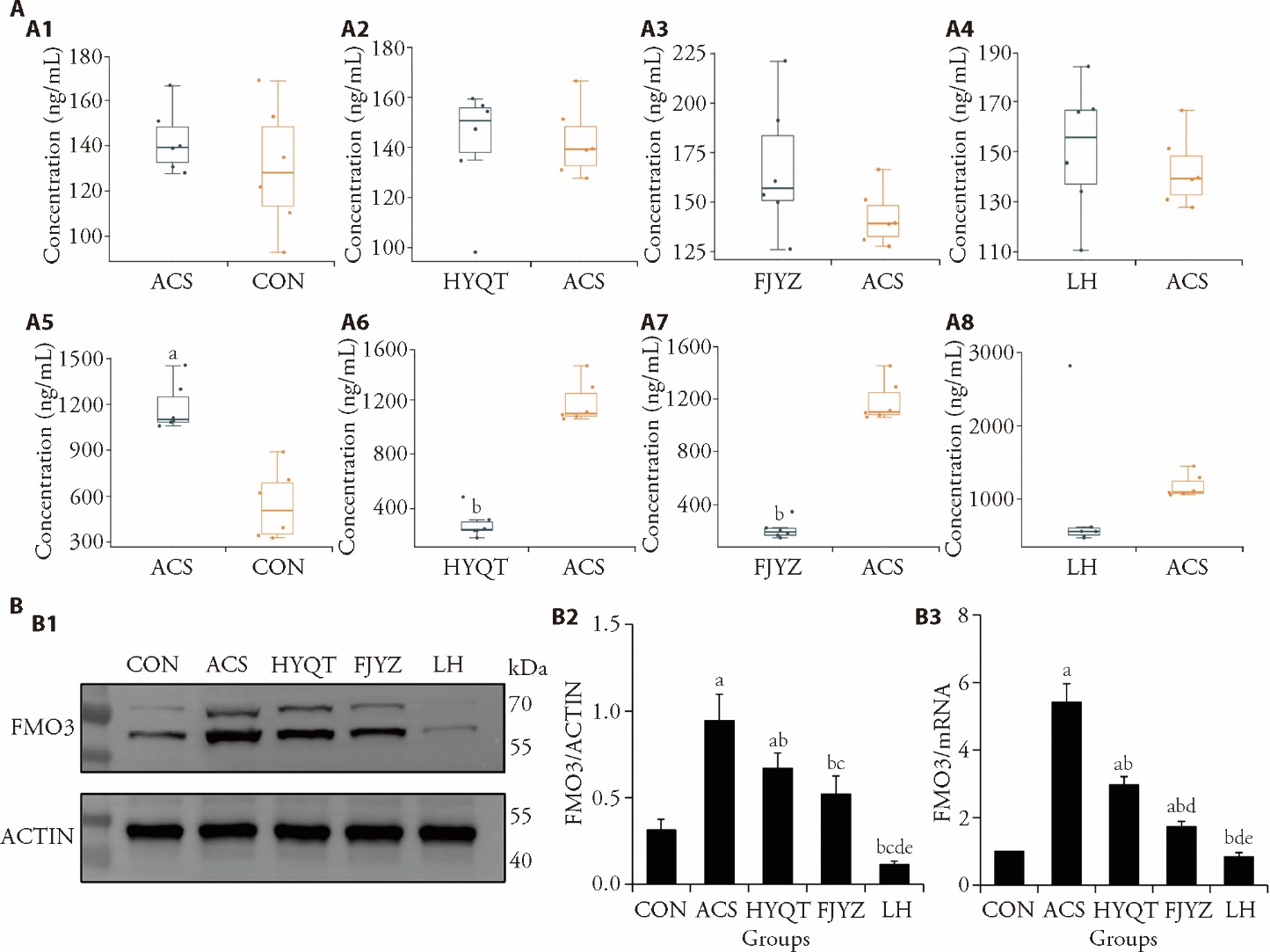
Figure 2 Regulation of the TMA/FMO3/TMAO pathway by Huayu Qutan formula in ACS rats A1: comparison of TMA concentration between the ACS and CON groups; A2: comparison of TMA concentration between the HYQT and ACS groups; A3: comparison of TMA concentration between the FJYZ and ACS groups; A4: comparison of TMA concentration between the LH and ACS groups; A5: comparison of TMAO concentration between the ACS and CON groups; A6: comparison of TMAO concentration between the HYQT and ACS groups; A7: comparison of TMAO concentration between the FJYZ and ACS groups; A8: comparison of TMAO concentration between the LH and ACS groups; B1: FMO3 and Actin protein expression bands; B2: the expression levels of the FMO3 protein; B3: the expression levels of the FMO3 gene. CON: treated only with physiological saline; ACS: treated with a high-fat diet and an intraperitoneal injection of isoproterenol (45 mg/kg); HYQT: treated with Huayu Qutan formula of equivalent dose according to the body surface area ratio between humans and rats for 28 d; FJYZ: treated with fecal bacteria extract of 15.197 g/kg for 28 d; LH: treated with Huayu Qutan formula and fecal bacteria extract of 15.197 g/kg for 28 d. TMA: trimethylamine; TMAO: trimethylamine N-oxide; FMO3: flavin containing monooxygenase 3; ACS: acute coronary syndrome; ANOVA: analysis of variance. A: quantile analysis, n = 6; B: one-way ANOVA, data are presented as mean ± standard deviation, B2: n = 3, B3: n = 9. Compared with the CON group, aP < 0.01; compared with the ACS group, bP < 0.01; compared with the CON group, cP < 0.05; compared with the HYQT group, dP < 0.01; compared with the FJYZ group, eP < 0.01.
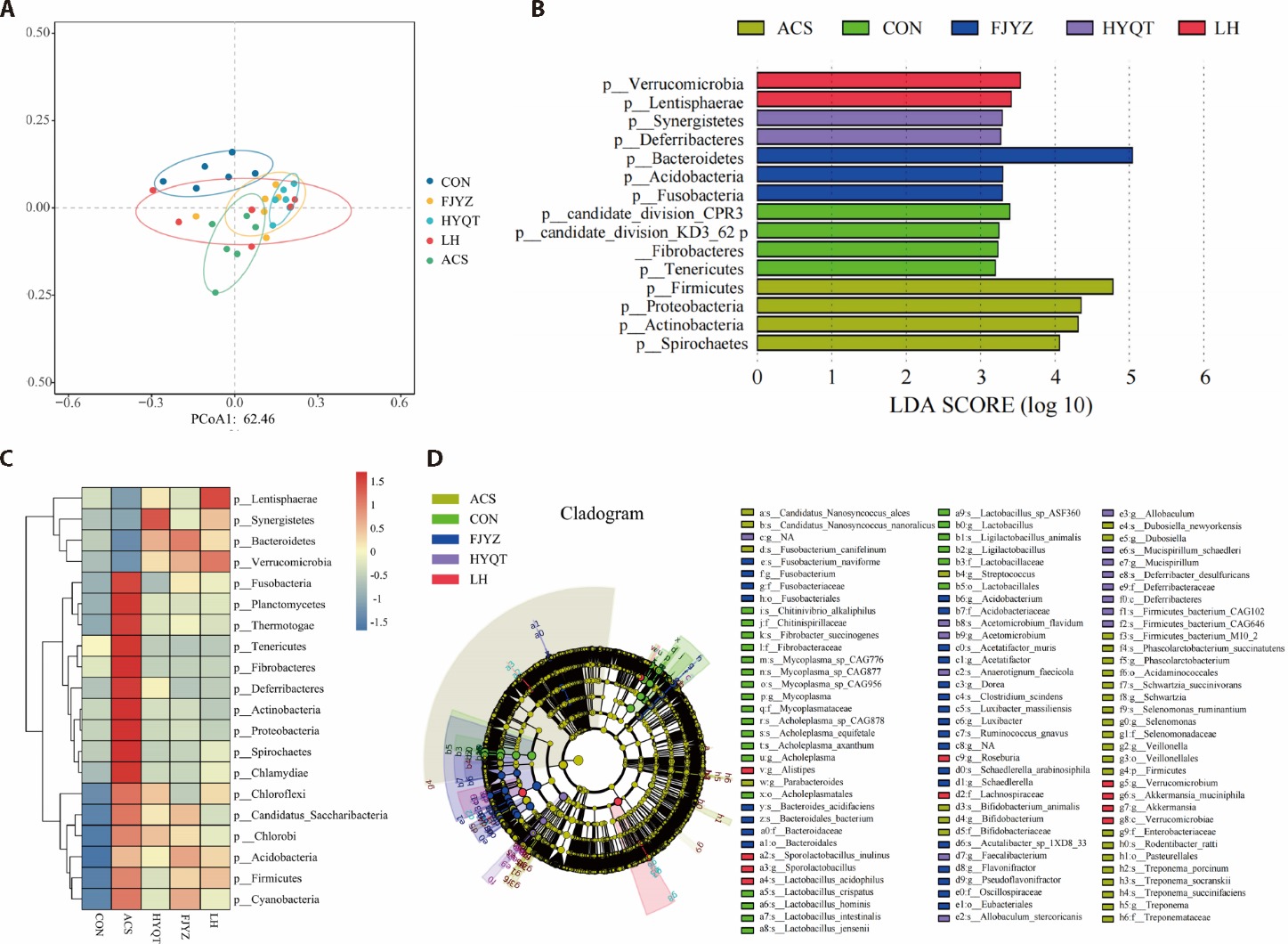
Figure 3 Effect of Huayu Qutan formula on the metagenomic distribution characteristics of ACS rats A: PCoA analysis reveals significant differences in the composition and structure of gut microbiota among the groups. B: the LDA cluster tree highlights key classification differences at the phylum level among the five groups and identifies 15 bacterial phyla with notable differences. C: the cluster heatmap displays species with significant differences between groups according to wilcoxon analysis. D: the cladogram demonstrates important differences in gut microbiota at each taxonomic level. CON: treated only with physiological saline; ACS: treated with a high-fat diet and an intraperitoneal injection of isoproterenol (45 mg/kg); HYQT: treated with Huayu Qutan formula of equivalent dose according to the body surface area ratio between humans and rats for 28 d; FJYZ: treated with fecal bacteria extract of 15.197 g/kg for 28 d; LH: treated with Huayu Qutan formula and fecal bacteria extract of 15.197 g/kg for 28 d. ACS: acute coronary syndrome; PCoA: principal coordinates analysis; LDA: linear discriminant analysis.

Figure 4 Effect of Huayu Qutan formula on the KEGG pathway for gut microbiota of ACS rats A: Wilcoxon analysis highlights KEGG pathways with significant differences among groups; B: stamp analysis identifies KEGG pathways with significant differences among groups; B1: between the ACS and CON groups; B2: between the HYQT and ACS groups; B3: between the FJYZ and ACS groups; B4: between the LH and ACS groups; C: network analysis illustrates the correlations between gut microbiota and KEGG pathway. CON: treated only with physiological saline; ACS: treated with a high-fat diet and an intraperitoneal injection of isoproterenol (45 mg/kg); HYQT: treated with Huayu Qutan formula of equivalent dose according to the body surface area ratio between humans and rats for 28 d; FJYZ: treated with fecal bacteria extract of 15.197 g/kg for 28 d; LH: treated with Huayu Qutan formula and fecal bacteria extract of 15.197 g/kg for 28 d. KEGG: Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; ACS: acute coronary syndrome.
| 1. |
Gach O, El HZ, Lancellotti P. Acute coronary syndrome. Rev Med Liege 2018; 73: 243-50.
PMID |
| 2. | Wang L, Jin Y. Noncoding RNAs as biomarkers for acute coronary syndrome. Biomed Res Int 2020; 2020: 3298696. |
| 3. | Sabouret P, Spadafora L, Fischman D, et al. De-escalation of antiplatelet therapy in patients with coronary artery disease: time to change our strategy? Eur J Intern Med 2023; 110: 1-9. |
| 4. | Kwon O, Park DW. Antithrombotic therapy after acute coronary syndromes or percutaneous coronary interventions in east asian populations. JACC Asia 2022; 2: 1-18. |
| 5. | Pedersen OB, Pasalic L, Nissen PH, Grove EL, Kristensen SD, Hvas AM. Flow cytometric assessment of changes in platelet reactivity after acute coronary syndrome: a systematic review. Semin Thromb Hemost 2022; 48: 542-51. |
| 6. | Alenazy FO, Thomas MR. Novel antiplatelet targets in the treatment of acute coronary syndromes. Platelets 2021; 32: 15-28. |
| 7. | Wongsalap Y, Kengkla K, Wilairat P, Ratworawong K, Saokaew S, Wanlapakorn C. Efficacy and safety of different dual antiplatelet strategies in patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: a systematic review and network Meta-analysis. Chronic Dis Transl Med 2023; 9: 299-308. |
| 8. | De Luca L, Gragnano F, Calabrò P, Huber K. Balancing benefits and risks of oral antiplatelet strategies in patients with coronary artery diseases: an evolving issue. Curr Probl Cardiol 2023; 48: 102025. |
| 9. |
Jacob S, Kosaka Y, Bhatlekar S, et al. Mitofusin-2 regulates platelet mitochondria and function. Circ Res 2024; 134: 143-61.
DOI PMID |
| 10. | Solari FA, Krahn D, Swieringa F, et al. Multi-omics approaches to study platelet mechanisms. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2023; 73: 102253. |
| 11. | Ravera S, Signorello MG, Panfoli I. Platelet metabolic flexibility: a matter of substrate and location. Cells 2023; 12: 1802. |
| 12. |
Kong H, Cen J, Yang X, et al. Research progress in the relationship between trimethylamine oxide and coronary heart disease. Altern Ther Health Med 2024; 30: 220-7.
PMID |
| 13. | Chen B, Patel S, Bao L, Nadeem D, Krittanawong C. Pro-inflammatory food, gut microbiota, and cardiovascular and pancreatic diseases. Biomolecules 2024; 14: 210. |
| 14. | Fang J, Yu CH, Li XJ, et al. Gut dysbiosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic implications. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2022; 12: 997018. |
| 15. | Piccioni A, de Cunzo T, Valletta F, et al. Gut microbiota and environment in coronary artery disease. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021; 18: 4242. |
| 16. | Xie Z, Liu X, Huang X, et al. Remodelling of gut microbiota by berberine attenuates trimethylamine N-oxide-induced platelet hyperreaction and thrombus formation. Eur J Pharmacol 2021; 911: 174526. |
| 17. | Zhang F, Wu LB, Hu L, et al. Study on the central neural pathway and the relationship between the heart and small intestine via a dual neural tracer. PLoS One 2022; 17: e0277644. |
| 18. | Anonymous (compiled during Warring States to Western Han Dynasty). Huang Di Nei Jing. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013: 14. |
| 19. | Qin JM (Ming dynasty), Qin HS (Qing dynasty, Supplement). Zheng Yin Mai Zhi. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2023: 3. |
| 20. | Yi M, Dai X, Li Q, Zhao Y, Nie S, Wang D. 1H-NMR-based metabolomics study on coronary heart disease with blood-stasis syndrome and phlegm syndrome. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban 2021; 46: 591-600. |
| 21. |
Liu R, Jiang LJ, Yang Y, et al. Study on syndrome differentiation strategy of phlegm and blood stasis syndromes of coronary heart disease based on expert consultation on medical cases. Ann Palliat Med 2021; 10: 9940-52.
DOI PMID |
| 22. | Galli M, Andreotti F, Sabouret P, Gragnano F. 2023 ESC guidelines on ACS: what is new in antithrombotic therapy? Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother 2023; 9: 595-6. |
| 23. |
Heemskerk JWM, West J. Emerging technologies for understanding platelet diversity. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2022; 42: 540-52.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Van der Meijden PEJ, Heemskerk JWM. Platelet biology and functions: new concepts and clinical perspectives. Nat Rev Cardiol 2019; 16: 166-79.
DOI PMID |
| 25. | Fei YX, Wang SQ, Yang LJ, et al. Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Danshen) extract attenuates permanent cerebral ischemia through inhibiting platelet activation in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 2017; 207: 57-66. |
| 26. |
Li L, Chen H, Shen A, et al. Ligustrazine inhibits platelet activation via suppression of the Akt pathway. Int J Mol Med 2019; 43: 575-82.
DOI PMID |
| 27. |
Zhang D, Qiao W, Zhao Y, Fang H, Xu D, Xia Q. Curdione attenuates thrombin-induced human platelet activation: β1-tubulin as a potential therapeutic target. Fitoterapia 2017; 116: 106-15.
DOI PMID |
| 28. |
Zhu W, Gregory JC, Org E, et al. Gut microbial metabolite TMAO enhances platelet hyperreactivity and thrombosis risk. Cell 2016; 165: 111-24.
DOI PMID |
| 29. |
Hasan RA, Koh AY, Zia A. The gut microbiome and thromboembolism. Thromb Res 2020; 189: 77-87.
DOI PMID |
| 30. | Emonds JJ, Ringel C, Reinicke M, et al. Influence of trimethylamine N-Oxide on platelet activation. Nutrients 2022; 14: 3261. |
| 31. |
Nam HS. Gut microbiota and ischemic stroke: the role of trimethylamine N-Oxide. J Stroke 2019; 21: 151-59.
DOI PMID |
| 32. | Canyelles M, Borràs C, Rotllan N, Tondo M, Escolà-Gil JC, Blanco-Vaca F. Gut microbiota-derived TMAO: a causal factor promoting atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease? Int J Mol Sci 2023; 24: 1940. |
| 33. |
Ivashkin VT, Kashukh YA. Impact of L-carnitine and phosphatidylcholine containing products on the proatherogenic metabolite TMAO production and gut microbiome changes in patients with coronary artery disease. Vopr Pitan 2019; 88: 25-33.
DOI PMID |
| 34. |
Ge X, Zheng L, Zhuang R, et al. The gut microbial metabolite trimethylamine N-Oxide and hypertension risk: a systematic review and dose-response Meta-analysis. Adv Nutr 2020; 11: 66-76.
DOI PMID |
| 35. | Duttaroy AK. Role of gut microbiota and their metabolites on atherosclerosis, hypertension and human blood platelet function: a review. Nutrients 2021; 13: 144. |
| 36. | Massey W, Osborn LJ, Banerjee R, et al. Flavin-containing monooxygenase 3 (FMO3) is critical for dioxin-induced reorganization of the gut microbiome and host insulin sensitivity. Metabolites 2022; 12: 364. |
| 37. |
Zhang WQ, Wang YJ, Zhang A, et al. TMA/TMAO in hypertension: novel horizons and potential therapies. J Cardiovasc Transl Res 2021; 14: 1117-24.
DOI PMID |
| 38. |
Zhang Y, Wang Y, Ke B, Du J. TMAO: how gut microbiota contributes to heart failure. Transl Res 2021; 228: 109-25.
DOI PMID |
| 39. |
Tang WH, Wang Z, Li XS, et al. Increased trimethylamine N-Oxide portends high mortality risk independent of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Chem 2017; 63: 297-306.
DOI PMID |
| 40. |
Witkowski M, Weeks TL, Hazen SL. Gut microbiota and cardiovascular disease. Circ Res 2020; 127: 553-70.
DOI PMID |
| 41. | Verhaar BJH, Prodan A, Nieuwdorp M, Muller M. Gut microbiota in hypertension and atherosclerosis: a review. Nutrients 2020; 12: 2982. |
| 42. | Khan I, Khan I, Jianye Z, et al. Exploring blood microbial communities and their influence on human cardiovascular disease. J Clin Lab Anal 2022; 36: e24354. |
| 43. | Cui L, Zhao T, Hu H, Zhang W, Hua X. Association study of gut flora in coronary heart disease through high-throughput sequencing. Biomed Res Int 2017; 2017: 3796359. |
| 44. |
Sanchez-Alcoholado L, Castellano-Castillo D, Jordan-Martinez L, et al. Role of gut microbiota on cardiometabolic parameters and immunity in coronary artery disease patients with and without type-2 diabetes mellitus. Front Microbiol 2017; 8: 1936.
DOI PMID |
| 45. | Peng Y, Zhang N, Li WJ, et al. Correlations of changes in inflammatory factors, glucose and lipid metabolism indicators and adiponectin with alterations in intestinal flora in rats with coronary heart disease. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2020; 24: 10118-25. |
| 46. |
Peeling RW, Mabey D, Chen XS, Garcia PJ. Syphilis. Lancet 2023; 402: 336-46.
DOI PMID |
| 47. | Mathur H, Beresford TP, Cotter PD. Health benefits of lactic acid bacteria (LAB) fermentates. Nutrients 2020; 12: 1679. |
| 48. | Martín R, Rios-Covian D, Huillet E, et al. Faecalibacterium: a bacterial genus with promising human health applications. FEMS Microbiol Rev 2023; 47: fuad039. |
| 49. | Yang HT, Jiang ZH, Yang Y, et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii as a potential antiatherosclerotic microbe. Cell Commun Signal 2024; 22: 54. |
| 50. | Wang H, Reddy ST, Fogelman AM. The role of gut-derived oxidized lipidsand bacterial lipopolysaccharide in systemic infammation and atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Lipidol 2022; 33: 277-82. |
| 51. | Zheng Z, Lyu W, Ren Y, et al. Allobaculum involves in the modulation of intestinal ANGPTLT 4 expression in mice treated by high-fat diet. Front Nutr 2021; 8: 690138. |
| 52. | Park S, Kim I, Han SJ, et al. Oral porphyromonas gingivalis infection affects intestinal microbiota and promotes atherosclerosis. J Clin Periodontol 2023; 50: 1553-67. |
| 53. | Herp S, Durai Raj AC, Salvado Silva M, Woelfel S, Stecher B. The human symbiont mucispirillum schaedleri: causality in health and disease. Med Microbiol Immunol 2021; 210: 173-79. |
| 54. | Li Y, Luan Y, Yue X, et al. Effects of codonopis bulleynana forest ex diels on deferribacteres in constipation predominant intestine tumor: differential analysis. Saudi J Biol Sci 2019; 26: 395-401. |
| 55. |
Corredor Z, Suarez-Molina A, Fong C, Cifuentes-C L, Guauque-Olarte S. Presence of periodontal pathogenic bacteria in blood of patients with coronary artery disease. Sci Rep 2022; 12: 1241.
DOI PMID |
| 56. | Lledós M, Prats-Sánchez L, Llucià-Carol L, et al. Ischaemic stroke patients present sex differences in gut microbiota. Eur J Neurol 2023; 30: 3497-506. |
| 57. |
Kuhn KA, Schulz HM, Regner EH, et al. Bacteroidales recruit IL-6-producing intraepithelial lymphocytes in the colon to promote barrier integrity. Mucosal Immunol 2018; 11: 357-68.
DOI PMID |
| 58. | Zhao N, Wang Y, Ma Y, et al. Jia-Wei-Si-Miao-Yong-An decoction modulates intestinal flora and metabolites in acute coronary syndrome model. Front Cardiovasc Med 2023; 9: 1038273. |
| 59. | Burakova I, Smirnova Y, Gryaznova M, et al. The effect of short-term consumption of lactic acid bacteria on the gut microbiota in obese people. Nutrients 2022; 14: 3384. |
| 60. |
Zhang T, Li Q, Cheng L, Buch H, Zhang F. Akkermansia muciniphila is a promising probiotic. Microb Biotechnol 2019; 12: 1109-25.
DOI PMID |
| 61. | Jian H, Liu Y, Wang X, Dong X, Zou X. Akkermansia muciniphila as a next-generation probiotic in modulating human metabolic homeostasis and disease progression: a role mediated by gut-liver-brain axes? Int J Mol Sci 2023; 24: 3900. |
| 62. | Cani PD, Depommier C, Derrien M, Everard A, de Vos WM. Akkermansia muciniphila: paradigm for next-generation beneficial microorganisms. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2022; 19: 625-37. |
| 63. |
Xing YQ, Li JX, Yuan YL, Mao TY. The combination of gut microbiota-depleted treatment and fecal microbiota transplantation is an important strategy to verify the efficacy of traditional Chinese medicine though modulation of gut dysbiosis. J Tradit Chin Med 2024; 44: 222-3.
DOI |
| [1] | Liu Chao, Duan Lian, Huang Mingyan, Li Jun, Xiong Xingjiang, Chen Guang, He Haoqiang, Zhang Zhenpeng, Wang Jie. Effectiveness and safety of Suxiao Jiuxin pill in treating acute coronary syndrome: a systematic review and Meta-analysis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2020, 40(4): 518-529. |
| [2] | Chen Cen, Wang Fengqin, Xiao Wen, Xia Zhining, Hu Guang, Wan Jianbo, Yang Fengqing. Effect on platelet aggregation activity: extracts from 31 Traditional Chinese Medicines with the property of activating blood and resolving stasis [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2017, 37(01): 64-75. |
| [3] | Peng Wang, Qunxing Wang, Chunhua Luo, Chao Tan, Xiaohui Yuan. Iridoid glycosides extracted from Zhizi(Fructus Gardeniae)decrease collagen-induced platelet aggregation and reduce carotid artery thrombosis in an invivo rat model [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2013, 33(04): 531-534. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

