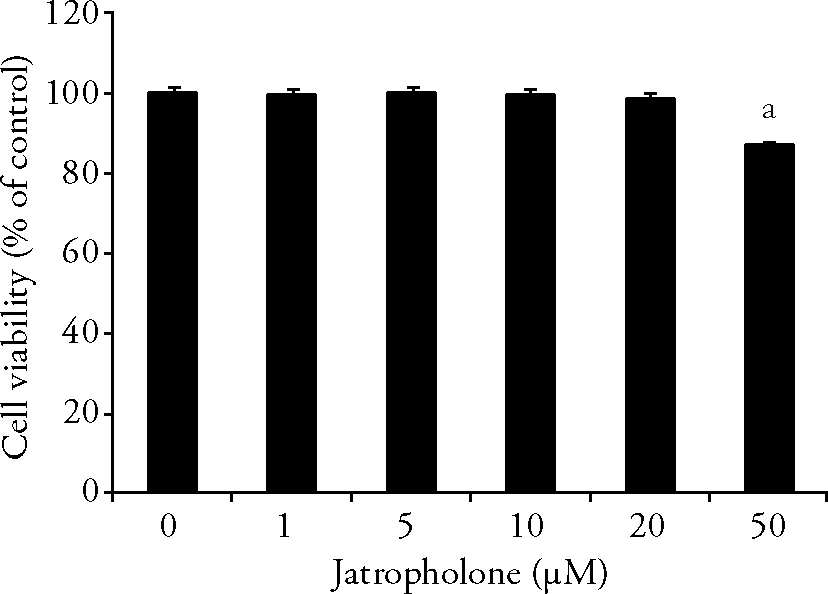
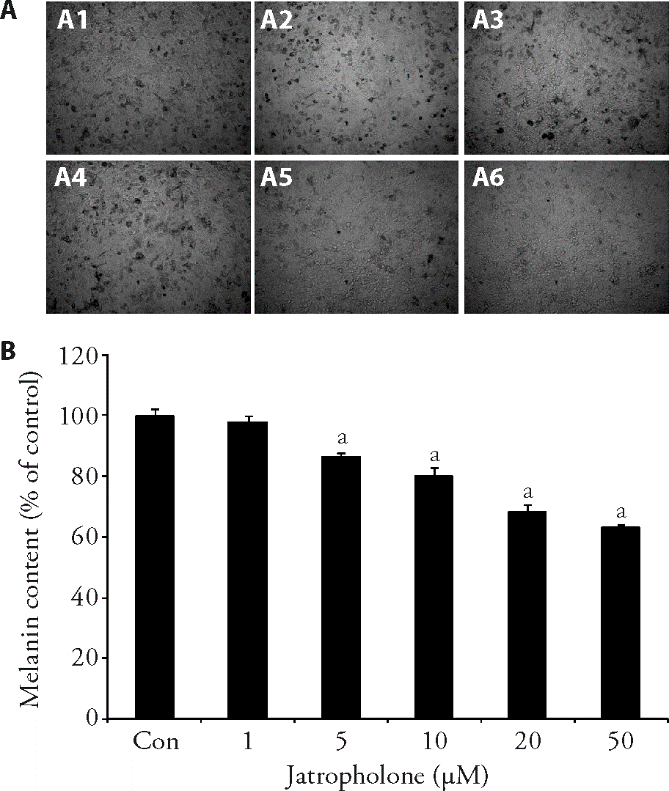
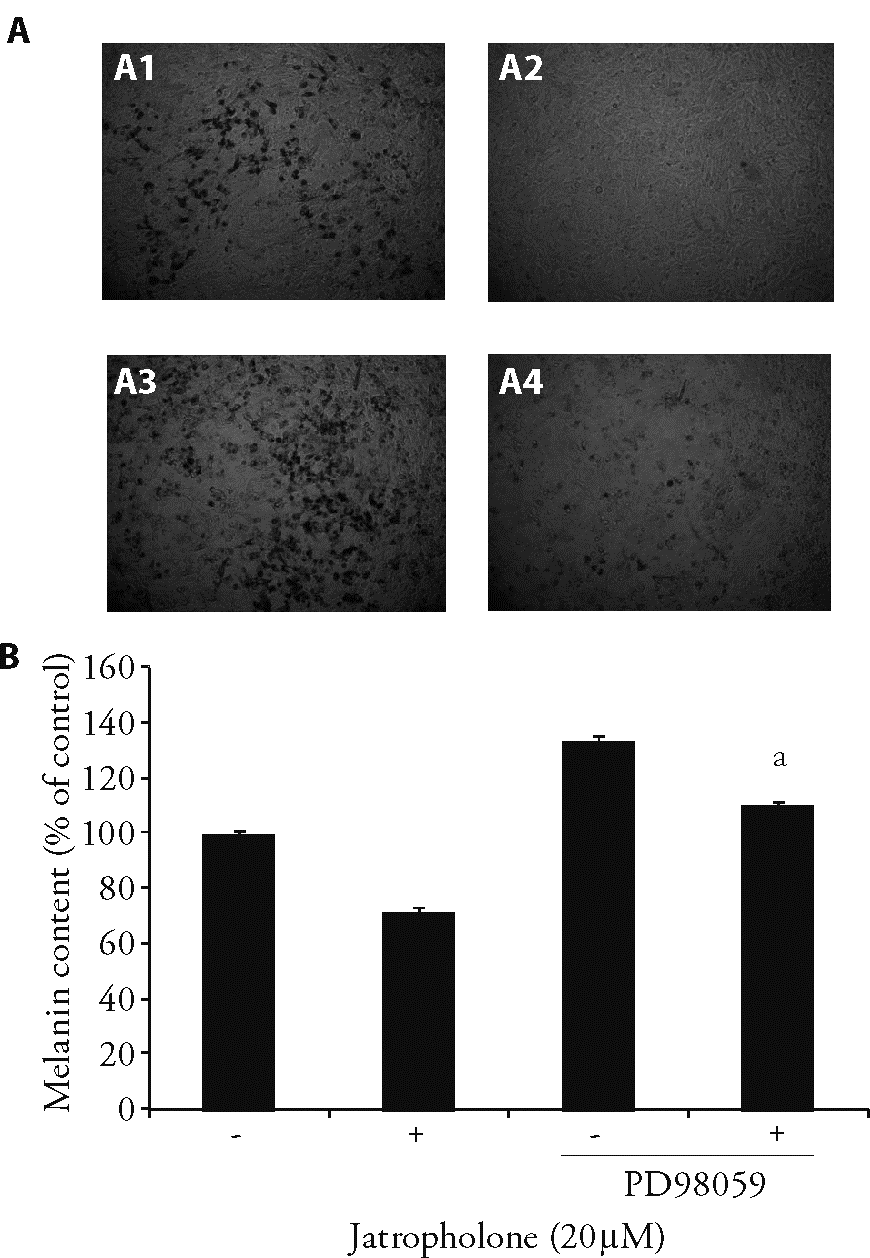
| 1. |
Othman AR, Abdullah N, Ahmad S, et al. Elucidation of in-vitro anti-inflammatory bioactive compounds isolated from Jatropha curcas L. plant root. BMC Complement Altern Med 2015; 15: 11.
|
| 2. |
Huang JD, Zhang C, Xu WJ, et al. New lathyrane diterpenoids with anti-inflammatory activity isolated from the roots of Jatropha curcas L. J Ethnopharmacol 2021; 268: 113673.
|
| 3. |
Sabandar CW, Ahmat N, Jaafar FM, Sahidin I. Medicinal property, phytochemistry and pharmacology of several Jatropha species (Euphorbiaceae): a review. Phytochemistry 2013; 85: 7-29.
DOI
PMID
|
| 4. |
Thomas R, Sah NK, Sharma PB. Therapeutic biology of Jatropha curcas: a mini review. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 2008; 9: 315-24.
|
| 5. |
Liu JQ, Yang YF, Li XY, et al. Cytotoxicity of naturally occurring rhamnofolane diterpenes from Jatropha curcas. Phytochemistry 2013; 96: 265272.
|
| 6. |
Pertino M, Schmeda-Hirschmann G, Rodriguez JA, Theoduloz C. Gastroprotective effect and cytotoxicity of semisynthetic jatropholone derivatives. Planta Medica 2007; 73: 1095-100.
PMID
|
| 7. |
D'Mello SA, Finlay GJ, Baguley BC, Askarian-Amiri ME. Signaling pathways in melanogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 2016; 17: 1144.
|
| 8. |
Kim S, Kim M, Choi Y, et al. Down-regulation of tyrosinase, TRP-1, TRP-2 and MITF expressions by citrus press-cakes in murine B16 F10 melanoma. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2013; 3: 617-22
|
| 9. |
Sanchez-Ferrer A, Rodriguez-Lopez JN, Garcia-Canovas F, Garcia-Carmona F. Tyrosinase: a comprehensive review of its mechanism. Biochim Biophys Acta 1995; 1247: 1-11.
|
| 10. |
Chen T, Zhao B, Liu Y, et al. MITF-M regulates melanogenesis in mouse melanocytes. J Dermatol Sci 2018; 90: 253-62.
DOI
PMID
|
| 11. |
Shin JS, Cho JH, Lee H, et al. Dual hypopigmentary effects of punicalagin via the ERK and Akt pathways. Biomed Pharmacother 2017; 92: 122-7.
|
| 12. |
Kim DS, Lee HK, Park SH, et al. Terrein inhibits keratinocyte proliferation via ERK inactivation and G2/M cell cycle arrest. Exp Dermatol 2008; 17: 312-7.
|
| 13. |
Kim DS, Park SH, Kwon SB, et al. Sphingosylphosphorylcholine-induced ERK activation inhibits melanin synthesis in human melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res 2006; 19: 146-53.
|
| 14. |
Kim SY, Hahn HG, Nam KD, et al. A derivative of 2-aminothiazole inhibits melanogenesis in B16 mouse melanoma cells via glycogen synthase kinase 3beta phosphorylation. J Pharm Pharmacol 2011; 63: 1031-6.
|
| 15. |
Bellei B, Flori E, Izzo E, et al. GSK3beta inhibition promotes melanogenesis in mouse B16 melanoma cells and normal human melanocytes. Cell Signal 2008; 20: 1750-61.
DOI
PMID
|
| 16. |
Kim DS, Park SH, Kwon SB, et al. Sphingosylphosphorylcholine inhibits melanin synthesis via pertussis toxin-sensitive MITF degradation. J Pharm Pharmacol 2010; 62: 181-7.
|
| 17. |
Costin GE, Hearing VJ. Human skin pigmentation: melanocytes modulate skin color in response to stress. FASEB J 2007; 21: 976-94.
|
| 18. |
Solano F. Photoprotection and skin pigmentation: melanin-related molecules and some other new agents obtained from natural sources. Molecules 2020; 25: 1537.
|
| 19. |
Burlando B, Clericuzio M, Cornara L. Moraceae plants with tyrosinase inhibitory activity: a review. Mini Rev Med Chem 2017; 17: 108-21.
DOI
PMID
|
| 20. |
Kumari S, Tien Guan Thng S, Kumar Verma N, Gautam HK. Melanogenesis Inhibitors. Acta Derm Venereol 2018; 98: 924-31.
|
| 21. |
Kim DS, Hwang ES, Lee JE, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate decreases melanin synthesis via sustained ERK activation and subsequent MITF degradation. J Cell Sci 2003; 116: 1699-706.
|
| 22. |
Kim JY, Lee EJ, Ahn Y, et al. A chemical compound from fruit extract of Juglans mandshurica inhibits melanogenesis through p-ERK-associated MITF degradation. Phytomedicine 2019; 57: 57-64.
DOI
PMID
|
| 23. |
Higuchi K, Kawashima M, Ichikawa Y, Imokawa G. Sphingosylphosphorylcholine is a melanogenic stimulator for human melanocytes. Pigment Cell Res 2003; 16: 670-8.
|
| 24. |
Kim DS, Kim SY, Lee JE, et al. Sphingosine-1-phosphate-induced ERK activation protects human melanocytes from UVB-induced apoptosis. Arch Pharm Res 2003; 26: 739-46.
|
 )
)