Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2024, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 1017-1023.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20240828.007
Previous Articles Next Articles
Relative exchangeable copper, a high-quality biomarker for differentiation of Traditional Chinese Medicine syndrome in Wilson’s disease
DING Yufeng1, YANG Wenming1( ), CHENG Yuan1, YANG Yulong1, ZHU Jun2, LU Yachun2, FANG Xiang1, ZHANG Jing1(
), CHENG Yuan1, YANG Yulong1, ZHU Jun2, LU Yachun2, FANG Xiang1, ZHANG Jing1( )
)
- 1 Department of Neurology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China
2 Department of clinical laboratory, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China
-
Received:2023-06-11Accepted:2023-11-27Online:2024-10-15Published:2024-09-11 -
Contact:YANG Wenming, Department of Neurology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China. yangwm8810@126.com;ZHANG Jing, Department of Neurology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, China. zj5125115@163.com Telephone: +86-551-62838522; +86-15357950670 -
Supported by:Research on the Neuroprotective Mechanism of the Gandouling based on the Regulation of Long Non-coding Ribonucleic Acid Maternally Expressed Gene 3 and Targets Gene Forkhead Box O1 through the Way of Autophagy in Wilson Disease(82104783);Study on Mechanism of Xin’an Medical Gubenpeiyuan Prescription Treating Wilson’s Disease based on Enterohepatic Axis and Enterobrain Axis Pathway(U22A20366);2019 Project of Building Evidence based Practice Capacity for Traditional Chinese Medicine(2019XZZX-NB001);Mechanism Study on the Regulation of Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor-gamma Coactivator-1alpha/Sirtuin-3/Mitochondrial Axis to Maintain Hippocampal Synaptic Homeostasis to Improve Cognitive Impairment in Wilson’s Disease by Qingre Lidan JieDu Prescription(2008085MH264);Mitofusin 2 Mediates the Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum-MAMs-mitochondria Regulation of Synaptic Homeostasis in Wilson’s Disease Neurons and the Mechanism of Qingre Lidan Jiedu Prescription Intervention(2208085MH271)
Cite this article
DING Yufeng, YANG Wenming, CHENG Yuan, YANG Yulong, ZHU Jun, LU Yachun, FANG Xiang, ZHANG Jing. Relative exchangeable copper, a high-quality biomarker for differentiation of Traditional Chinese Medicine syndrome in Wilson’s disease[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(5): 1017-1023.
share this article
| Item | WD group (n = 78) | N-WD group (n = 32) | HC group (n = 37) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 24±8 | 22±8 | 24±7 |
| Female [n (%)] | 32 (41.03) | 14 (43.75) | 20 (54.05) |
| Time since first symptoms (months) | 14±8 | 8±7 | -- |
| Neurologic symptoms at diagnosis [n (%)] | 54 (69.23) | -- | -- |
| Kayser-Fleischer corneal rings [n (%)] | 73 (93.59) | -- | 0 (0.00) |
| Serum ceruloplasmin (< 200 mg/L) | 77 (98.72) | 5 (15.63) | 12 (32.43) |
| Dominant mutations [n (%)] | |||
| c.2333G>T (R778L, exon 8) | 24 (30.77) | -- | 14 (37.84) |
| c.2975C>T (P992L, exon 13) | 11 (14.10) | -- | 6 (16.22) |
| c.2621C>T (A874V, exon 11) | 6 (7.69) | -- | 3 (8.11) |
Table 1 Characteristics of the study population
| Item | WD group (n = 78) | N-WD group (n = 32) | HC group (n = 37) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 24±8 | 22±8 | 24±7 |
| Female [n (%)] | 32 (41.03) | 14 (43.75) | 20 (54.05) |
| Time since first symptoms (months) | 14±8 | 8±7 | -- |
| Neurologic symptoms at diagnosis [n (%)] | 54 (69.23) | -- | -- |
| Kayser-Fleischer corneal rings [n (%)] | 73 (93.59) | -- | 0 (0.00) |
| Serum ceruloplasmin (< 200 mg/L) | 77 (98.72) | 5 (15.63) | 12 (32.43) |
| Dominant mutations [n (%)] | |||
| c.2333G>T (R778L, exon 8) | 24 (30.77) | -- | 14 (37.84) |
| c.2975C>T (P992L, exon 13) | 11 (14.10) | -- | 6 (16.22) |
| c.2621C>T (A874V, exon 11) | 6 (7.69) | -- | 3 (8.11) |
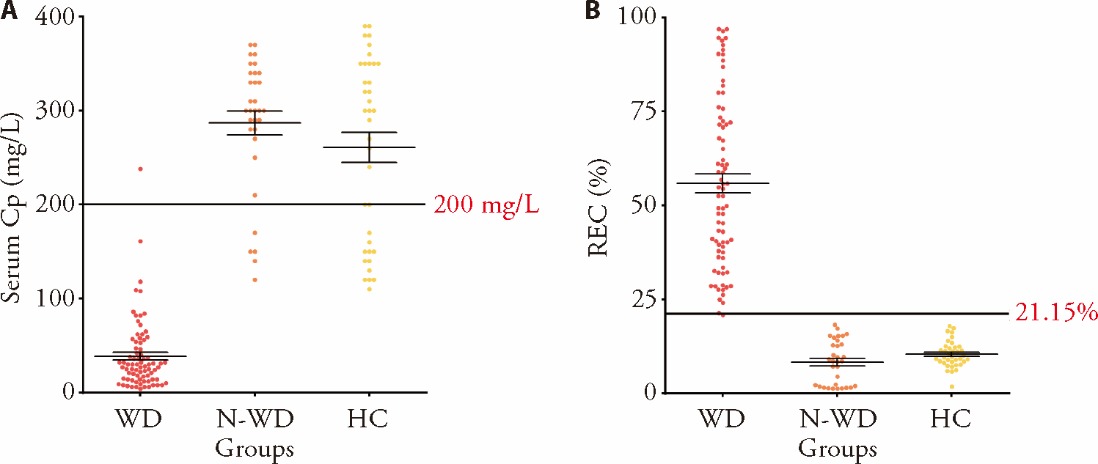
Figure 1 Comparison of the REC ratios and serum Cp levels in WD, non-Wilsonian liver diseases, and heterozygous ATP7B carriers A: comparison of the serum copper levels in WD, non-Wilsonian liver diseases, and heterozygous ATP7B carriers. B: comparison of the REC ratios in WD, non-Wilsonian liver diseases, and heterozygous ATP7B carriers. WD group (n = 78), N-WD group (n = 32), HC group (n = 37). WD: Wilson’s disease; N-WD: non-Wilsonian liver diseases; HC: heterozygous ATP7B carriers; REC: relative exchangeable copper; Cp: ceruloplasmin. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation using one-way analysis of variance.
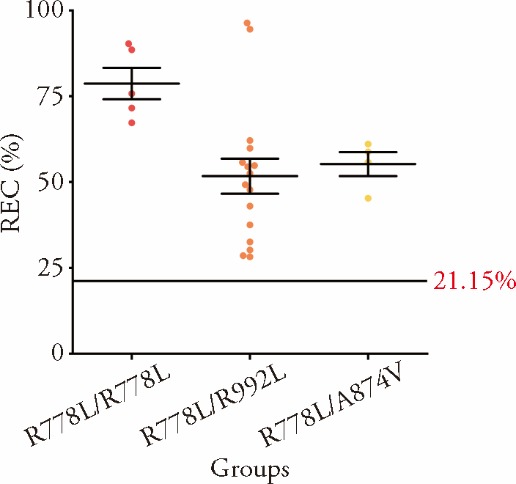
Figure 2 Comparison of the REC ratios in different ATP7B mutational sites in WD R778L/R778L (n = 5), R778L/R992L (n = 16), and A874V/ R778L (n = 4). REC: relative exchangeable copper; WD: Wilson’s disease. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation using one-way analysis of variance.
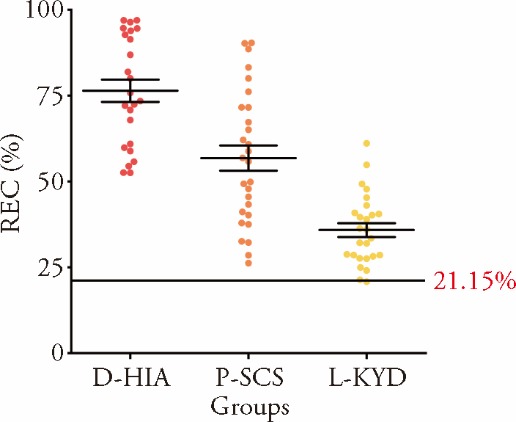
Figure 3 Comparison of the REC ratios in different TCM syndromes D-HIA group (n = 24), P-SCS group (n = 28), L-KYD group (n = 26). REC: relative exchangeable copper; TCM: Traditional Chinese Medicine; D-HIA: Dampness-heat internal accumulation syndrome; P-SCS: Phlegm-stasis combination syndrome; L-KYD: Liver-kidney Yin deficiency syndrome. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation using one-way analysis of variance.
| Subregion | D-HIA group (n = 17) | P-SCS group (n = 23) | L-KYD group (n = 18) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Left PUT-VA | 0.27±0.11 | 0.14±0.07 | 0.06±0.10 |
| Left PUT-DA | 0.26±0.09 | 0.15±0.04 | 0.05±0.08 |
| Left PUT-DP | 0.25±0.09 | 0.15±0.09 | 0.07±0.08 |
| Left PUT-VP | 0.31±0.08 | 0.21±0.04 | 0.09±0.08 |
| Right PUT-VA | 0.22±0.05 | 0.14±0.07 | 0.04±0.10 |
| Right PUT-DA | 0.25±0.07 | 0.15±0.06 | 0.03±0.14 |
| Right PUT-DP | 0.21±0.08 | 0.15±0.10 | 0.08±0.13 |
| Right PUT-VP | 0.28±0.11 | 0.21±0.07 | 0.14±0.09 |
Table 2 FC value in all subregions of the lenticular nucleus among different TCM syndromes
| Subregion | D-HIA group (n = 17) | P-SCS group (n = 23) | L-KYD group (n = 18) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Left PUT-VA | 0.27±0.11 | 0.14±0.07 | 0.06±0.10 |
| Left PUT-DA | 0.26±0.09 | 0.15±0.04 | 0.05±0.08 |
| Left PUT-DP | 0.25±0.09 | 0.15±0.09 | 0.07±0.08 |
| Left PUT-VP | 0.31±0.08 | 0.21±0.04 | 0.09±0.08 |
| Right PUT-VA | 0.22±0.05 | 0.14±0.07 | 0.04±0.10 |
| Right PUT-DA | 0.25±0.07 | 0.15±0.06 | 0.03±0.14 |
| Right PUT-DP | 0.21±0.08 | 0.15±0.10 | 0.08±0.13 |
| Right PUT-VP | 0.28±0.11 | 0.21±0.07 | 0.14±0.09 |
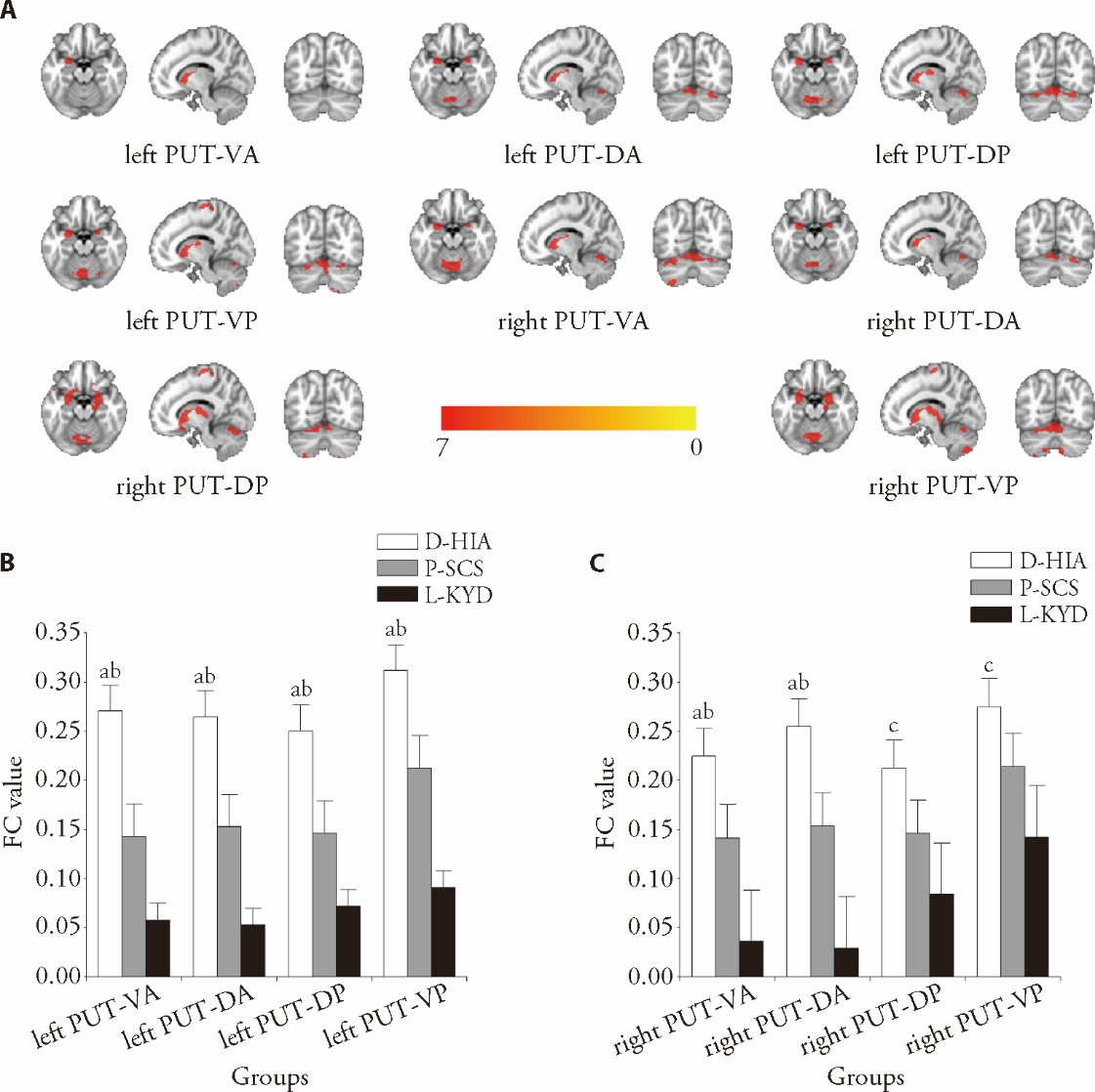
Figure 4 FC value changes in different TCM syndromes A: the seed-based FC map in all Wilson’s disease patients; B: FC value changes of left putamen in different TCM syndromes; C: FC value changes of right putamen in different TCM syndromes. D-HIA Group (n = 17), P-SCS group (n = 23), L-KYD group (n = 18). FC: functional connectivity; TCM: Traditional Chinese Medicine; D-HIA: Dampness-heat internal accumulation syndrome; P-SCS: Phlegm-stasis combination syndrome; L-KYD: Liver-kidney Yin deficiency syndrome; PUT-VA: ventral anterior putamen; PUT-DA: dorsal anterior putamen; PUT-DP: dorsal posterior putamen; PUT-VP: ventral posterior putamen. aP<0.05 vs P-SCS group; bP<0.001 vs L-KYD group, cP<0.05 vs L-KYD group. Data are presented as the mean ± standard deviation using one-way analysis of variance.
| 1. | Ala A, Walker AP, Ashkan K, Dooley JS, Schilsky ML. Wilson’s disease. Lancet 2007; 369: 397-408. |
| 2. |
Członkowska A, Litwin T, Chabik G. Wilson disease: neurologic features. Handb Clin Neurol 2017; 142: 101-19.
DOI PMID |
| 3. |
Zhang J, Xiao L, Yang W. Combined sodium dimercaptopro-panesulfonate and zinc versus D-penicillamine as first-line therapy for neurological Wilson’s disease. BMC Neurol 2020; 20: 255.
DOI PMID |
| 4. |
Zhang J, Li L, Chen H, Yang W. Clinical efficacy and safety of gandouling plus low-dose D-penicillamine for treatment of Wilson’s disease with neurological symptoms. J Tradit Chin Med 2018; 38: 89-94.
PMID |
| 5. |
Zhang J, Xie D, Li Y, et al. Evaluation of efficacy and safety of gandouling plus sodium dimercaptosulphonate in treatment of patients with neurological Wilson’s disease from China. J Tradit Chin Med 2018; 38: 781-6.
PMID |
| 6. | Zhang S, Yang W, Li X, et al. Clinical and genetic characterization of a large cohort of patients with Wilson’s disease in China. Transl Neurodegener 2022; 11: 13. |
| 7. | Daymond R, Curtis SL, Mishra V, Roberts NB. Assay in serum of exchangeable copper and total copper using inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS): development, optimisation and evaluation of a routine procedure. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 2020; 80: 630-9. |
| 8. |
Guillaud O, Brunet AS, Mallet I, et al. Relative exchangeable copper: a valuable tool for the diagnosis of Wilson disease. Liver Int 2018; 38: 350-7.
DOI PMID |
| 9. |
Catalani S, Paganelli M, Gilberti ME, et al. Free copper in serum: an analytical challenge and its possible applications. J Trace Elem Med Biol 2018; 45: 176-80.
DOI PMID |
| 10. |
El Balkhi S, Poupon J, Trocello JM, et al. Determination of ultrafiltrable and exchangeable copper in plasma: stability and reference values in healthy subjects. Anal Bioanal Chem 2009; 394: 1477-84.
DOI PMID |
| 11. | El Balkhi S, Trocello JM, Poupon J, et al. Relative exchangeable copper: a new highly sensitive and highly specific biomarker for Wilson’s disease diagnosis. Clin Chim Acta 2011; 412: 2254-60. |
| 12. | Schmitt F, Podevin G, Poupon J, et al. Evolution of exchangeable copper and relative exchangeable copper through the course of Wilson’s disease in the Long Evans Cinnamon rat. PLoS One 2013; 8: e82323. |
| 13. |
Lu A, Jiang M, Zhang C, Chan K. An integrative approach of linking Traditional Chinese Medicine pattern classification and biomedicine diagnosis. J Ethnopharmacol 2012; 141: 549-56.
DOI PMID |
| 14. |
Chen J, Ye C, Hu X, et al. Serum metabolomics model and its metabolic characteristics in patients with different syndromes of dyslipidemia based on nuclear magnetic resonance. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2019; 167: 100-13.
DOI PMID |
| 15. |
Wang J, Ma Q, Li Y, et al. Research progress on Traditional Chinese Medicine syndromes of diabetes mellitus. Biomed Pharmacother 2020; 121: 109565.
DOI PMID |
| 16. | Tang SQ, Wang YL, Xie ZY, et al. Serum metabolic profiling of Traditional Chinese Medicine syndromes in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. J Integr Med 2021; 19: 274-81. |
| 17. | Trocello JM, El Balkhi S, Woimant F, et al. Relative exchangeable copper: a promising tool for family screening in Wilson disease. Mov Disord 2014; 29: 558-62. |
| 18. |
Roberts EA, Schilsky ML, American Association for Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD). Diagnosis and treatment of Wilson disease: an update. Hepatology 2008; 47: 2089-111.
DOI PMID |
| 19. | European Association for Study of Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: Wilson’s disease. J Hepatol 2012; 56: 671-85. |
| 20. | Nagral A, Sarma MS, Matthai J, et al. Wilson’s Disease: clinical practice guidelines of the Indian national association for study of the liver, the Indian society of pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition, and the movement disorders society of India. J Clin Exp Hepatol 2019; 9: 74-98. |
| 21. | Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, et al. STARD 2015: an updated list of essential items for reporting diagnostic accuracy studies. BMJ. 2015; 351: h5527. |
| 22. |
Corpechot C, Carrat F, Poujol-Robert A, et al. Noninvasive elastography-based assessment of liver fibrosis progression and prognosis in primary biliary cirrhosis. Hepatology 2012; 56: 198-208.
DOI PMID |
| 23. |
de Lédinghen V, Wong VW, Vergniol J, et al. Diagnosis of liver fibrosis and cirrhosis using liver stiffness measurement: comparison between M and XL probe of FibroScan®. J Hepatol 2012; 56: 833-9.
DOI PMID |
| 24. | National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. TCM clinical pathways of 95 diseases in 22 specialties. Beijing: China Traditional Medicine Press, 2011: 21-4. |
| 25. | Yang W, Bao Y, Zhang B, et al. Traditional Chinese Medicine clinical pathway for Wilson disease. Zhong Yi Yao Lin Chuang Za Zhi 2012; 24: 1127-9. |
| 26. | Aggarwal A, Aggarwal N, Nagral A, Jankharia G, Bhatt M. A novel global assessment scale for Wilson’s disease (GAS for WD). Mov Disord 2009; 24: 509-18. |
| 27. |
Członkowska A, Tarnacka B, Möller JC, et al. Unified Wilson’s disease rating scale - a proposal for the neurological scoring of Wilson’s disease patients. Neurol Neurochir Pol 2007; 41: 1-12.
PMID |
| 28. | Yan CG, Wang XD, Zuo XN, Zang YF. DPABI: data processing & analysis for (resting-state) brain imaging. Neuroinformatics 2016; 14: 339-51. |
| 29. | Yang Y, Wei T, Yang W, et al. Dysfunction of the lenticular nucleus is associated with dystonia in Wilson’s disease. Brain Sci 2022; 13: 7. |
| 30. |
Ferenci P. Diagnosis of Wilson disease. Handb Clin Neurol 2017; 142: 171-80.
DOI PMID |
| 31. | Woimant F, Djebrani-Oussedik N, Poujois A. New tools for Wilson’s disease diagnosis: exchangeable copper fraction. Ann Transl Med 2019; 7: S70. |
| 32. | Kang NL, Zhang JM, Lin MX, et al. Serum ceruloplasmin can predict liver fibrosis in hepatitis B virus-infected patients. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26: 3952-62. |
| 33. |
Woimant F, Trocello JM. Disorders of heavy metals. Handb Clin Neurol 2014; 120: 851-64.
DOI PMID |
| 34. | Sánchez-Albisua I, Garde T, Hierro L, et al. A high index of suspicion: the key to an early diagnosis of Wilson’s disease in childhood. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1999; 28: 186-90. |
| 35. | Lu X, Li S, Zhang W, et al. Assessment of the diagnostic value of serum ceruloplasmin for Wilson’s disease in children. BMC Gastroenterol 2022; 22: 124. |
| [1] | WANG Zhibo, LI Ying, WANG Daoping, MA Bo, MIAO Lan, REN Junguo, LIU Jinghua, LIU Jianxun. Proteomics analysis of coronary atherosclerotic heart disease with different Traditional Chinese Medicine syndrome types before and after percutaneous coronary intervention [J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2024, 44(3): 554-563. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||

