Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine ›› 2023, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 770-779.DOI: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.20230526.003
Previous Articles Next Articles
Dry eye disease due to meibomian gland dysfunction treated with Pinggan Yuyin Qingre formula (平肝育阴清热方): a stratified randomized controlled trial
GAO Yinli1, LIAN Haihong1( ), DENG Shijing2(
), DENG Shijing2( ), DUAN Ying1, ZHANG Peng1, WANG Zhiqun3, ZHANG Yang3
), DUAN Ying1, ZHANG Peng1, WANG Zhiqun3, ZHANG Yang3
- 1 Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100005, China
2 Beijing Tongren Eye Center, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University; Beijing Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences Key Laboratory, Beijing 100005, China
3 Beijing Institute of Ophthalmology, Beijing Tongren Eye Center, Beijing Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100005, China
-
Received:2022-10-15Accepted:2023-05-04Online:2023-08-15Published:2023-05-26 -
Contact:DENG Shijing, Beijing Tongren Eye Center, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University; Beijing Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences Key Laboratory, Beijing 100005, China. dengsj26@163.com. Telephone: +86-10-58268082
LIAN Haihong, Department of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100005, China. lianhh@163.com -
Supported by:Capital Health Development Research Project: Clinical Efficacy of the Pinggan Yuyin Qingre Formula in Treating Evaporative Dry Eye Disease Causing by Meibomian Gland Dysfunction(2016-2-2055);Zhi Nan National Famous and Senior Chinese Medicine Experts Inheritance Studio Construction Project(75 (2022));Zhi Nan National Famous and Senior Chinese Medicine Experts Inheritance Studio Construction Project(Personnel and Education Department of the National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine promulgated);Sixth Batch of Beijing Municipal Academic Experience Inheritance Project for Traditional Chinese Medicine Experts(160 (2021));Sixth Batch of Beijing Municipal Academic Experience Inheritance Project for Traditional Chinese Medicine Experts(Beijing Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine promulgated)
Cite this article
GAO Yinli, LIAN Haihong, DENG Shijing, DUAN Ying, ZHANG Peng, WANG Zhiqun, ZHANG Yang. Dry eye disease due to meibomian gland dysfunction treated with Pinggan Yuyin Qingre formula (平肝育阴清热方): a stratified randomized controlled trial[J]. Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2023, 43(4): 770-779.
share this article
| Item | 0 point | 2 points | 4 points | 6 points |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry eyes | None | Occasionally, not obvious | Frequent dryness and discomfort, relieved on its own | Persistent, severe, unbearable dryness |
| Burning sensation in the eyes | None | Occasionally | Persistent, tolerable | Very obvious, intolerable, affecting daily life |
| Itchy eyes | None | Occasionally | Usually | All the time |
| Painful eyes | None | Mild pain in the eyes, occasionally | Persistent pain, tolerable, eye available | Obvious pain, eyes unavailable |
Table 1 Scoring criteria of the main symptoms
| Item | 0 point | 2 points | 4 points | 6 points |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry eyes | None | Occasionally, not obvious | Frequent dryness and discomfort, relieved on its own | Persistent, severe, unbearable dryness |
| Burning sensation in the eyes | None | Occasionally | Persistent, tolerable | Very obvious, intolerable, affecting daily life |
| Itchy eyes | None | Occasionally | Usually | All the time |
| Painful eyes | None | Mild pain in the eyes, occasionally | Persistent pain, tolerable, eye available | Obvious pain, eyes unavailable |
| Item | 0 point | 1 point | 2 points | 3 points |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dizziness | None | Sometimes, occasionally tinnitus | Persistent, frequent tinnitus | Dizziness, persistent tinnitus |
| Vexation and irritability | None | Vexation, occasional irritability | Upset, impatient, irritable | Uncontrollable vexation and irritability |
| Insomnia and excessive dreaming | None | Occasionally insomnia and forgetfulness | Wake up during sleeping sometimes, excessive dreaming, often forget things | Sleepless all night, forget things quickly |
| Dry mouth | None | Mild dry mouth and throat | Dry mouth and throat | Dry mouth and throat with the desire to drink |
| Sore waist | None | Mild soreness, stop by beating | Persistent, weak knees, cannot carry heavy things | Unbearable sore waist and weak knees, cannot walk |
| Yellow urine | None | Have | ||
| Dry stool | None | Have |
Table 2 Scoring criteria of the secondary symptoms
| Item | 0 point | 1 point | 2 points | 3 points |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dizziness | None | Sometimes, occasionally tinnitus | Persistent, frequent tinnitus | Dizziness, persistent tinnitus |
| Vexation and irritability | None | Vexation, occasional irritability | Upset, impatient, irritable | Uncontrollable vexation and irritability |
| Insomnia and excessive dreaming | None | Occasionally insomnia and forgetfulness | Wake up during sleeping sometimes, excessive dreaming, often forget things | Sleepless all night, forget things quickly |
| Dry mouth | None | Mild dry mouth and throat | Dry mouth and throat | Dry mouth and throat with the desire to drink |
| Sore waist | None | Mild soreness, stop by beating | Persistent, weak knees, cannot carry heavy things | Unbearable sore waist and weak knees, cannot walk |
| Yellow urine | None | Have | ||
| Dry stool | None | Have |
| Item | Control group (n = 57) | Treatment group (n = 59) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 42.00 (32.00-49.50) | 41.00 (31.00-49.00) |
| Gender [n (%)] | ||
| Male | 22 (39) | 18 (31) |
| Female | 35 (61) | 41 (69) |
| Duration of DED (years) | 8.00 (5.00-12.00) | 10.00 (6.00-12.00) |
| MGD level [n (%)] | ||
| MGD 1 | 18 (32) | 19 (32) |
| MGD 2 | 19 (33) | 20 (34) |
| MGD 3 | 20 (35) | 20 (34) |
| Score of the properties of MG secretion (scores) | 2.00 (2.00-2.00) | 2.00 (2.00-2.00) |
| Score of palpebral margins (scores) | 2.00 (1.00-2.00) | 2.00 (2.00-2.00) |
| NITBUTav (seconds) | 8.69 (5.62-10.50) | 8.23 (6.18-11.31) |
| LLT (nm) | 65.00 (50.00-92.00) | 60.00 (42.00-80.00) |
| TCM syndrome score (scores) | 13.00 (11.00-15.00) | 13.00 (11.00-17.00) |
Table 3 Baseline characteristics
| Item | Control group (n = 57) | Treatment group (n = 59) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 42.00 (32.00-49.50) | 41.00 (31.00-49.00) |
| Gender [n (%)] | ||
| Male | 22 (39) | 18 (31) |
| Female | 35 (61) | 41 (69) |
| Duration of DED (years) | 8.00 (5.00-12.00) | 10.00 (6.00-12.00) |
| MGD level [n (%)] | ||
| MGD 1 | 18 (32) | 19 (32) |
| MGD 2 | 19 (33) | 20 (34) |
| MGD 3 | 20 (35) | 20 (34) |
| Score of the properties of MG secretion (scores) | 2.00 (2.00-2.00) | 2.00 (2.00-2.00) |
| Score of palpebral margins (scores) | 2.00 (1.00-2.00) | 2.00 (2.00-2.00) |
| NITBUTav (seconds) | 8.69 (5.62-10.50) | 8.23 (6.18-11.31) |
| LLT (nm) | 65.00 (50.00-92.00) | 60.00 (42.00-80.00) |
| TCM syndrome score (scores) | 13.00 (11.00-15.00) | 13.00 (11.00-17.00) |
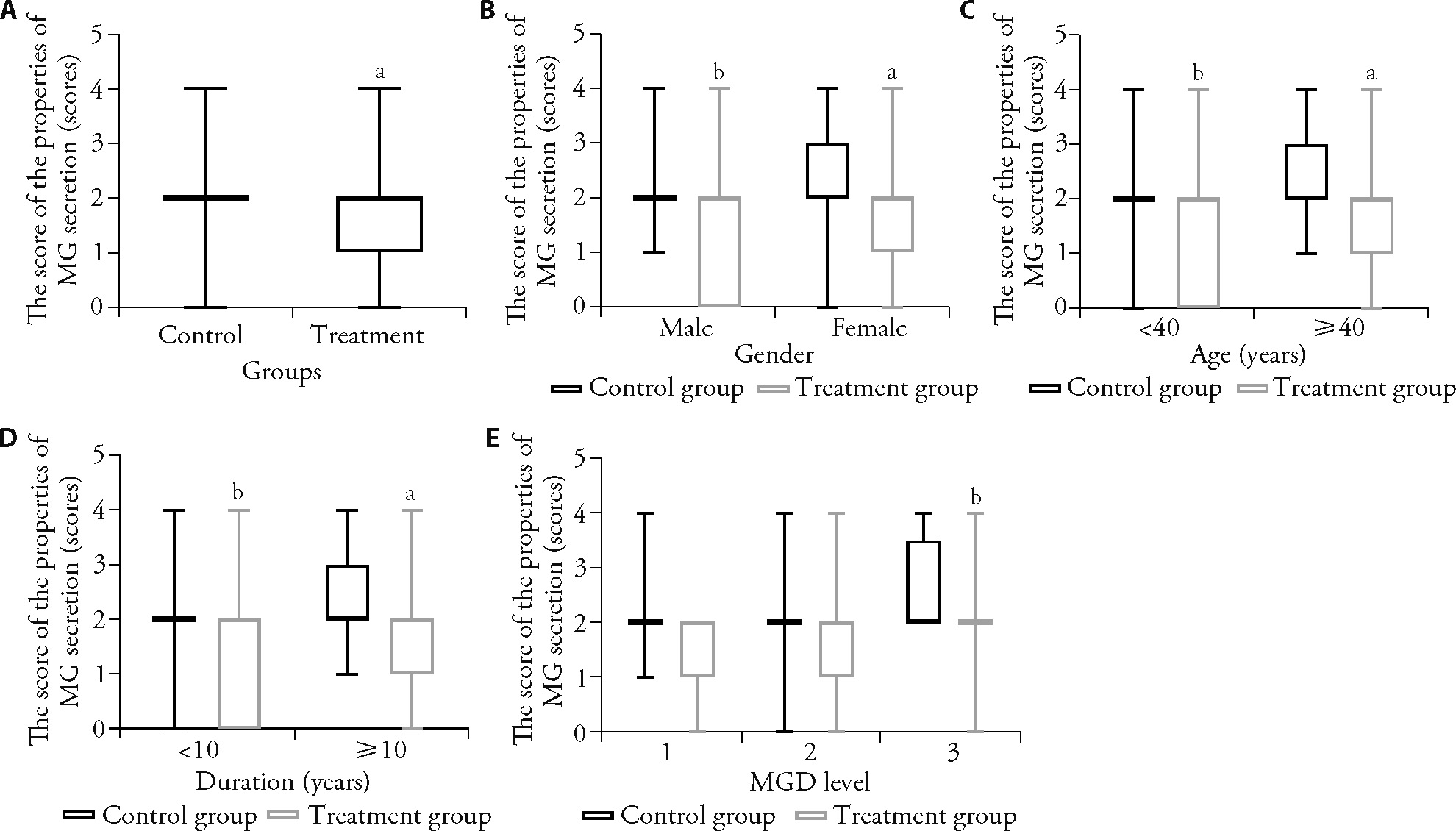
Figure 2 Comparison of the score of the properties of MG secretion A: total comparison; B-E: subgroup comparison. B: the subgroup variable was gender; C: the subgroup variable was age; D: the subgroup variable was duration; E: the subgroup variable was MGD level. Control group: treated only with sodium hyaluronate eye drops (n = 57); treatment group: treated with PGYYQR granules and sodium hyaluronate eye drops (n = 59). MG: meibomian gland; MGD: meibomian gland dysfunction; PGYYQR: Pinggan Yuyin Qingre formula. Compared with the control group, aP < 0.01, bP < 0.05 (Wilcoxon test).
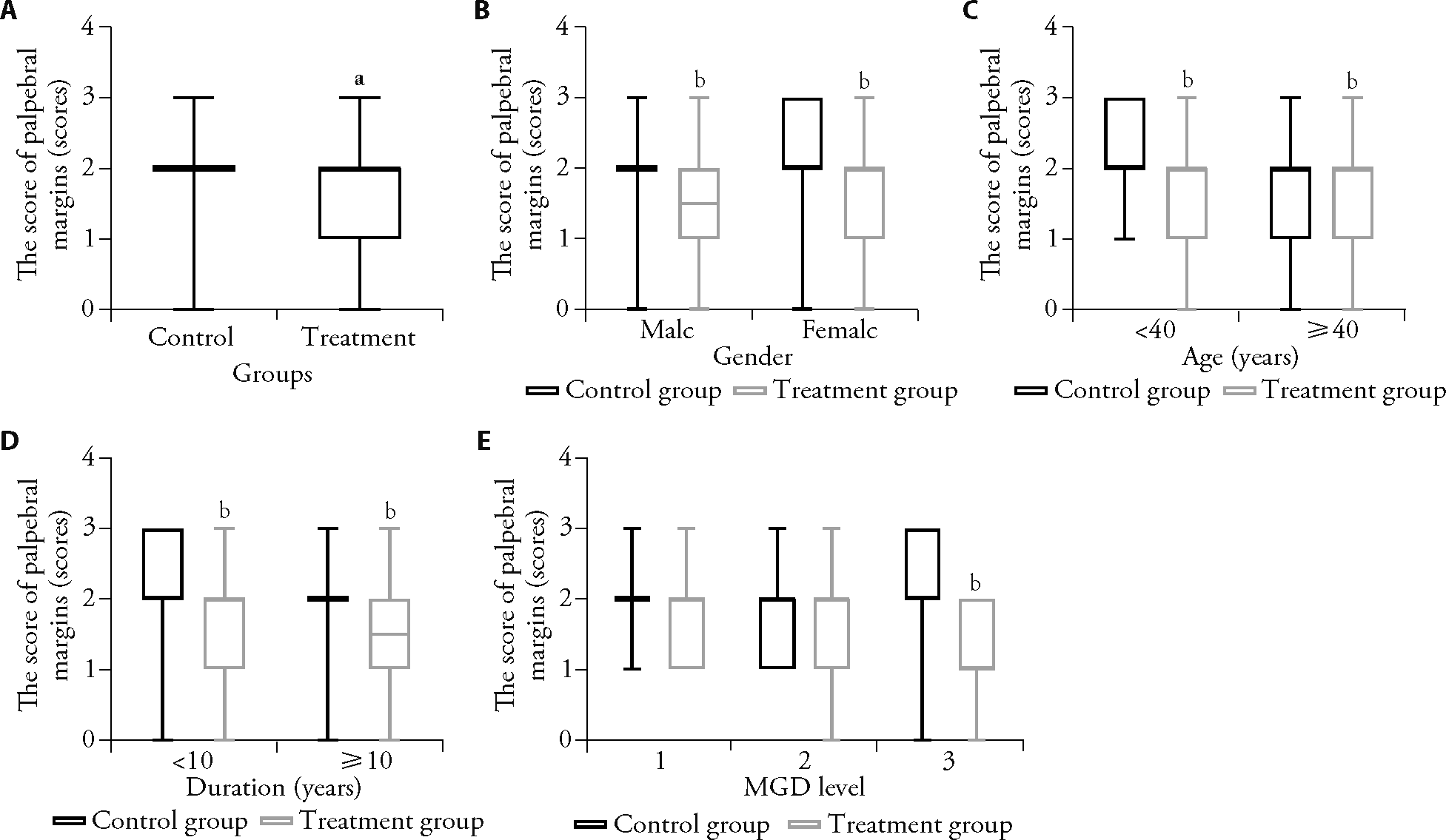
Figure 3 Comparison of the score of palpebral margins A: total comparison; B-E: subgroup comparison. B: the subgroup variable was gender; C: the subgroup variable was age; D: the subgroup variable was duration; E: the subgroup variable was MGD level. Control group: treated only with sodium hyaluronate eye drops (n = 57); treatment group: treated with PGYYQR granules and sodium hyaluronate eye drops (n = 59). MGD: meibomian gland dysfunction; PGYYQR: Pinggan Yuyin Qingre formula. Compared with the control group, aP < 0.01, bP < 0.05 (Wilcoxon test).
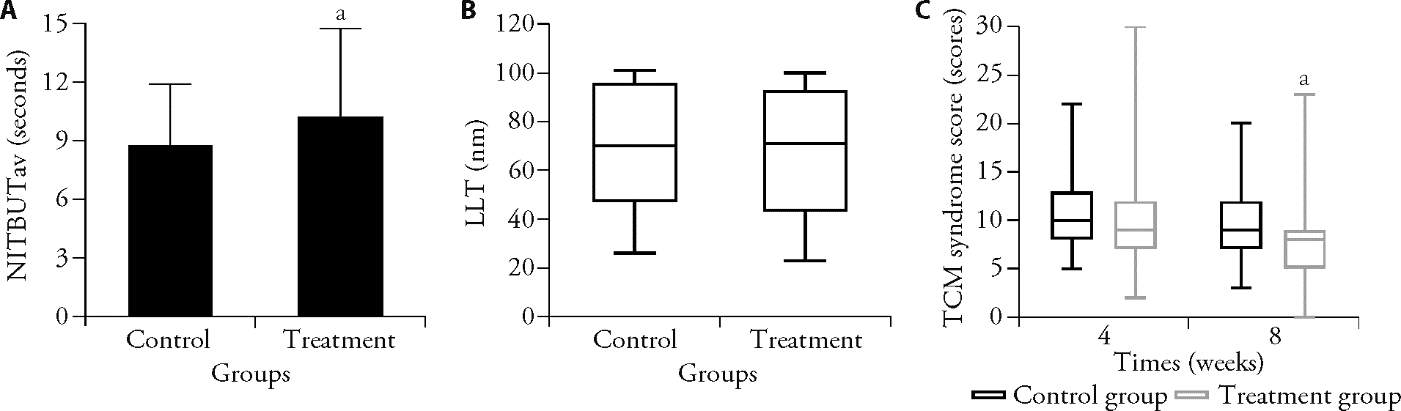
Figure 4 Comparison of the secondary outcome A: comparison of NITBUTav, compared with the control group, aP < 0.05 (t-test); B: comparison of LLT; C: comparison of TCM syndrome score at 4 and 8 weeks, compared with the control group, aP < 0.01 (Wilcoxon test). Control group: treated only with sodium hyaluronate eye drops (n = 57); treatment group: treated with PGYYQR granules and sodium hyaluronate eye drops (n = 59). NITBUTav: the average noninvasive tear breakup time; LLT: lipid layer thickness; TCM: traditional Chinese medicine; PGYYQR: Pinggan Yuyin Qingre formula.
| Group | n | Recovery (n) | Excellent (n) | Effective (n) | Invalid (n) | Total effective rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 57 | 0 | 3 | 26 | 28 | 50.9 |
| Treatment | 59 | 1 | 10 | 39 | 9 | 84.7 a |
Table 4 Comparison of the clinical efficacy of the two groups
| Group | n | Recovery (n) | Excellent (n) | Effective (n) | Invalid (n) | Total effective rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 57 | 0 | 3 | 26 | 28 | 50.9 |
| Treatment | 59 | 1 | 10 | 39 | 9 | 84.7 a |
| 1. | Chinese Branch of the Asian Dry Eye Society, Ocular Surface and Tear Film Diseases Group of Ophthalmology Committee of Cross-Straits Medicine Exchange Association, Ocular Surface and Dry Eye Group of Chinese Ophthalmologist Association. Chinese expert consensus on dry eye: definition and classification (2020). Zhong Hua Yan Ke Za Zhi 2020; 56: 418-22. |
| 2. |
Labetoulle M, Bourcier T, Doan S. Classifying signs and symptoms of dry eye disease according to underlying mechanism via the Delphi method: the DIDACTIC study. Br J Ophthalmol 2019; 103: 1475-80.
DOI PMID |
| 3. | Chinese Branch of the Asian Dry Eye Society, Ocular Surface and Tear Film Diseases Group of Ophthalmology Committee of Cross-Straits Medicine Exchange Association. Chinese expert consensus on the diagnosis and management of meibomian gland dysfunction (2017). Zhong Hua Yan Ke Za Zhi 2017; 53: 657-61. |
| 4. |
Viso E, Rodriguez-Ares MT, Abelenda D, Oubiña B, Gude F. Prevalence of asymptomatic and symptomatic meibomian gland dysfunction in the general population of Spain. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2012; 53: 2601-6.
DOI URL |
| 5. | Stapleton F, Alves M, Bunya VY, et al. TFOS DEWS Ⅱ epidemiology report. Ocul Surf 2017; 15: 334-65. |
| 6. | Yu T, Hong J. Current and emerging treatment options for meibomian gland dysfunction. Zhong Hua Shi Yan Yan Ke Za Zhi 2018; 36: 150-5. |
| 7. | Zhang MM, Zhuang ZY, Hu HB, Pang XY, Deng GJ. Etiology, pathogenesis and study progress on Chinese therapies for meibomian gland dysfunction. Zhong Guo Zhong Yi Yan Ke Za Zhi 2017; 27: 134-6. |
| 8. | Ma XL, Zhi N. Experience of veteran TCM doctor KONG Si-bo in treating optical disease. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Za Zhi 2009; 24: 485-7. |
| 9. | Gao YL, Zhang P, Liang HH, Kong LZ, Zhi N. Efficacy of Pinggan Yuyin Qingre recipe for treatment of hyperevaporative dry eye disease caused by meibomian gland dysfunction. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi 2021; 27: 92-9. |
| 10. | Sun XG. Blepharitis and meibomian gland dysfunction. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2015: 205-10. |
| 11. | National Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Criteria of diagnosis and therapeutic effect of diseases and syndromes in Traditional Chinese Medicine: ZY/T 001.1-94. Nanjing: Nanjing University Press, 1994: 65, 75. |
| 12. | Peng QH. Ophthalmology of Traditional Chinese Medicine. 5th ed. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2021: 129-31. |
| 13. | Lian HH. Dry eye syndrome treated by liver-calming and Yin fluid-tonifying and internal heat-clearing method. Zhong Hua Zhong Yi Yao Xue Kan 2016; 34: 1259-62. |
| 14. | Zheng XY. Guiding principles for clinical research of new Chinese Medicines (Trial). Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2002: 303-16. |
| 15. | Zang YX, Li SY, Zhu L, et al. Morphological correlation between sacral margin and meibomian gland in patients with meibomian gland dysfunction. Yan Ke 2020; 29: 355-60. |
| 16. | Shao Y. Interpretation of TFOS DEWSⅡ. Yan Ke Xin Jin Zhan 2018; 38: 1-12. |
| 17. | Xie LY, Yan XM. Role of inflammation in pathogenesis of meibomian gland dysfunction. Guo Ji Yan Ke Zong Lan 2021; 45: 535-40. |
| 18. |
Paranjpe V, Tan J, Nguyen J, et al. Clinical signs of meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) are associated with changes in meibum sphingolipid composition. Ocul Surf 2019; 17: 318-26.
DOI PMID |
| 19. |
Zhang SD, He JN, Niu TT, et al. Bacteriological profile of ocular surface flora in meibomian gland dysfunction. Ocul Surf 2017; 15: 242-7.
DOI PMID |
| 20. |
Jiang X, Deng A, Yang J, et al. Pathogens in the Meibomian gland and conjunctival sac: microbiome of normal subjects and patients with Meibomian gland dysfunction. Infect Drug Resist 2018; 11: 1729-40.
DOI PMID |
| 21. | Xu KK, Huang YK, Liu X, Zhang MC, Xie HT. Organotypic culture of mouse meibomian gland: a novel model to study meibomian gland dysfunction in vitro. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2020; 61: 30. |
| 22. | Reyes NJ, Yu C, Mathew R, et al. Neutrophils cause obstruction of eyelid sebaceous glands in inflammatory eye disease in mice. Sci Transl Med 2018; 10: 451. |
| 23. |
Baudouin C, Messmer EM, Aragona P, et al. Revisiting the vicious circle of dry eye disease: a focus on the pathophysiology of meibomian gland dysfunction. Br J Ophthalmol 2016; 100: 300-6.
DOI PMID |
| 24. |
Kwon J, Han SB. Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation can improve both symptoms and signs of dry eye disease. Clin Interv Aging 2017; 12: 485-6.
DOI URL |
| 25. |
Bron AJ, Tiffany JM, Gouveia SM, Yokoi N, Voon LW. Functional aspects of the tear film lipid layer. Exp Eye Res 2004; 78: 347-60.
DOI PMID |
| 26. | Liang QF, Du XH, Su YD, Li B, Labbe A. Lipid layer thickness of tear film and its association with clinical characteristics in different types of dry eye patients. Zhong Hua Shi Yan Yan Ke Za Zhi 2018; 36: 124-9. |
| 27. |
Zhao Y, Tan CL, Tong L. Intra-observer and inter-observer repeatability of ocular surface interferometer in measuring lipid layer thickness. BMC Ophthalmol 2015; 15: 53.
DOI PMID |
| 28. |
Fenner BJ, Tong L. More to stable tears than thickness of the tear film lipid layer. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2015; 56: 1601.
DOI URL |
| 29. | Pi WM, Han NN, Yuan ZH, et al. Analysis of antipyretic compatibility law and material basis of Gypsum Fibrosum based on “ dry-method+wet-method” and “ coordination chemistry”. Zhong Cao Yao 2022; 53: 1471-82. |
| 30. | Jiang W, Li JF, Gao JT, Zhang H, Sun JM. Chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of abalone shell. Jilin Zhong Yi Yao 2015; 35: 272-4. |
| 31. | Zhang LF, Hu JH, Zhang YQ. Research overview of the pharmacological action of Cornu Saigae Tataricae. Zhong Guo Yi Yao Dao Bao 2013; 10: 23-6, 33. |
| 32. |
Yan B, Wang JB, Tian GQ. Efficacy of quercetin, oleanolic acid, icariin on apoptosis and mitogen-activated protein kinases signaling pathways in hippocampal neurons of Sprague-Dawley rats cultured with high glucose medium. J Tradit Chin Med 2021; 41: 732-8.
DOI PMID |
| 33. | Li GG, Lu Y, He P, et al. Target prediction and activity verification for the antidepressant action of Huangqin (Radix Scutellariae Baicalensis). J Tradit Chin Med 2021; 41: 845-52. |
| 34. | Zhu CL, Feng CL, Feng F, et al. Baicalin inhibits inflammation of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via toll like receptor-4/myeloid differentiation primary response 88/nuclear factor-kappa B signaling pathway. J Tradit Chin Med 2022; 42: 200-12. |
| 35. | Hong JX, Zhai ZM. Oxidative stress-lipometabolism-MAPKs pathway in meibomian gland dysfunction. 42500762X--18QA1401100/01, 2021: 1-19. |
| No related articles found! |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||


